| 我国季风边缘区湖泊沉积记录的全新世亚洲夏季风衰退事件 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 吴铎, 周爱锋, 张家武, 陈建徽, 程波, 陈婕, 魏海涛. 我国季风边缘区湖泊沉积记录的全新世亚洲夏季风衰退事件[J]. 第四纪研究, 2019, 39(3): 665-677. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2019.03.13 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 吴铎 周爱锋 张家武 陈建徽 程波 陈婕 魏海涛 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1. 兰州大学资源环境学院, 西部环境教育部重点实验室, 甘肃 兰州 730000; 2. 华中师范大学城市与环境科学学院, 湖北 武汉 430079 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 国家自然科学基金;中央高校基本科研业务费专项;国家重点基础研究发展计划(973计划) |
| |
| 摘 要: | 
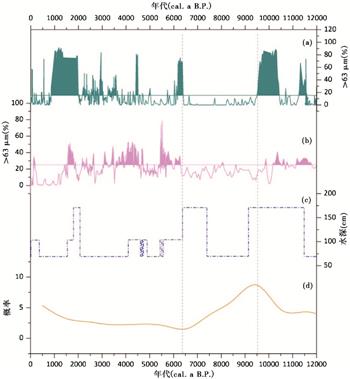
亚洲夏季风是全球季风系统的重要组成部分,亚洲夏季风的变化对其控制区域自然生态系统的多样性和生态平衡,以及社会经济发展有重要的影响。本文选择位于现代亚洲夏季风边缘区对季风变化响应敏感的湖泊达连海为研究对象,基于陆生植物残体和全有机质的AMS 14C定年建立了钻孔顶部24.6 m沉积物的年代框架,利用粒度指标重建了全新世研究区水文变化过程以及亚洲夏季风衰退事件序列。结果显示,沉积物中存在数层砂层,代表了湖泊低水位时期,进而指示了亚洲夏季风衰退事件。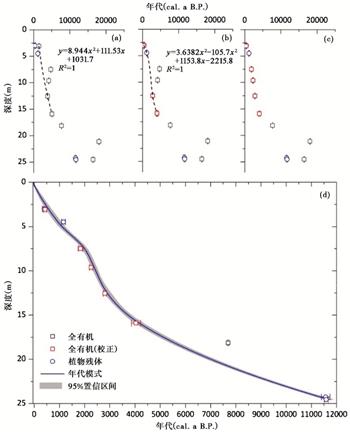
这些事件处在11.6~11.3 cal.ka B.P.、10.4~9.5 cal.ka B.P.、6.4~6.0 cal.ka B.P.、4.6~4.4 cal.ka B.P.、3.7~3.4 cal.ka B.P.、3.1~2.9 cal.ka B.P.以及2.0~0.9 cal.ka B.P.,可以发现中晚全新世以来亚洲夏季风衰退事件发生的频率显著增加。进一步与北半球高纬地区与低纬地区的气候突变事件记录对比显示,全新世百年-千年时间尺度上亚洲夏季风强度的变化与低纬ENSO活动存在密切的联系。
|
| 关 键 词: | 季风边缘区 达连海 湖泊沉积 全新世 亚洲夏季风 衰退事件 |
| 收稿时间: | 2019-01-03 |
| 修稿时间: | 2019-02-18 |
| 本文献已被 维普 万方数据 等数据库收录! |
| 点击此处可从《第四纪研究》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《第四纪研究》下载全文 |
|



