| 现代黄河三角洲沉积物磁性地层年代框架及环境磁学研究 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 王琬璋, 周良勇, 段宗奇, 姜兆霞, 刘建兴, 刘青松. 2019. 现代黄河三角洲沉积物磁性地层年代框架及环境磁学研究. 地球物理学报, 62(5): 1772-1788, doi: 10.6038/cjg2019M0158 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 王琬璋 周良勇 段宗奇 姜兆霞 刘建兴 刘青松 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1. 中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所, 岩石圈演化国家重点实验室, 北京 100029; 2. 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049; 3. 中国地质调查局青岛海洋地质研究所, 青岛 266071; 4. 中国地质调查局滨海湿地生物地质重点实验室, 青岛 266071; 5. 中国海洋大学海洋地球科学学院, 海底科学与探测技术教育部重点实验室, 青岛 266100; 6. 国家海洋局第一海洋研究所, 青岛 266061; 7. 南方科技大学海洋科学与工程系, 深圳 518055; 8. 青岛海洋科学与技术国家实验室海洋地质过程与环境功能实验室, 青岛 266237 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 国家基金委-山东省联合基金项目-海洋地质过程与环境(U1606401),国家重点研发计划(2016YFA0601903),亚洲大陆边缘项目"全球变化与海气相互作用"专项(GASI-GEOGE-03)和国家自然科学基金(41430962,41506075)联合资助. |
| |
| 摘 要: | 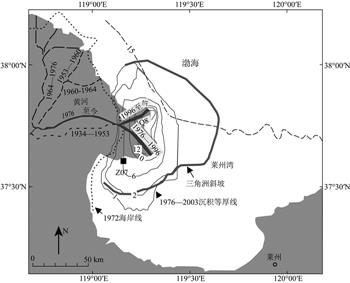
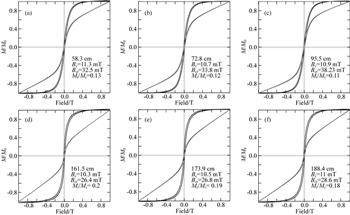
本文对黄河三角洲Z07孔沉积物进行了系统的磁性地层学和环境磁学研究.通过结合沉积速率和古地磁长期变化数据,我们为该孔建立了较为精确可信的年代框架(1999-03-2006-06 A.D.).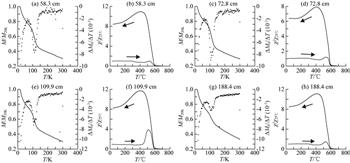
环境磁学结果表明黄河三角洲沉积物与中国黄土的磁学特征相似,主要载磁矿物为单畴(SD)磁铁矿,超顺磁颗粒(SP)含量也较高.整体上,该孔沉积物磁学参数的变化主要受粒度和含量控制.岩芯磁性参数在2003年前后发生了系统变化.我们认为,黄河自2002年起进行调水调沙工程,黄河下游河道冲刷加剧,形成新的物质来源,河流输入的沉积物粒度变粗,输沙量增加,这一新的物质来源是造成Z07钻孔磁性参数发生显著变化的主因.
|
| 关 键 词: | 黄河三角洲 磁性地层学 环境磁学 沉积环境演化 |
| 收稿时间: | 2018-03-14 |
| 修稿时间: | 2018-10-26 |
| 本文献已被 CNKI 维普 等数据库收录! |
| 点击此处可从《地球物理学报》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《地球物理学报》下载全文 |
|



