|
|||||
|
|
| 俯冲带库仑楔形体力学 | |
| 引用本文: | 胡岩. 2022. 俯冲带库仑楔形体力学. 地球物理学报, 65(2): 417-426, doi: 10.6038/cjg2022P0894 |
| 作者姓名: | 胡岩 |
| 作者单位: | 中国科学技术大学地球和空间科学学院,合肥230026;中国科学技术大学蒙城地球物理国家野外科学观测研究站,安徽蒙城233527;中国科学院比较行星学卓越创新中心,合肥230026 |
| 基金项目: | 科技部重点研发项目(2018YFC504103);国家自然科学基金委员会面上项目(41774109)共同资助。 |
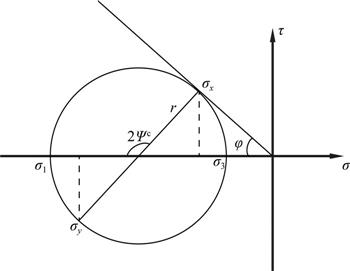
| 摘 要: | 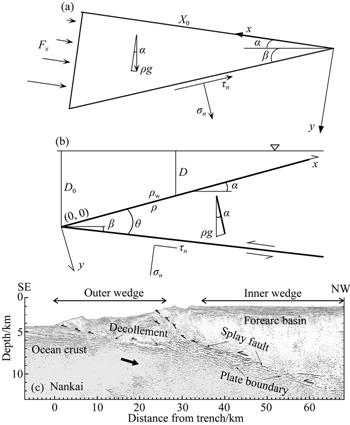 楔形体理论研究楔形体在底部摩擦力、重力和边界外力共同作用下内部的应力状态,有助于我们定量分析断层强度和岩石性质与楔形体稳定状态之间的关系.本文首先简要介绍基于不同楔形体材料而得出的应力解析解.然后介绍基于理想弹塑性材料的俯冲带库仑楔应力解析解.最后介绍基于该解析解而提出的动态库仑楔形体理论.俯冲带地震反射剖面数据表明,弧前靠近海沟部分地表坡度比较陡,其内部经历复杂永久塑性变形(称为外部楔形体,outer wedge). 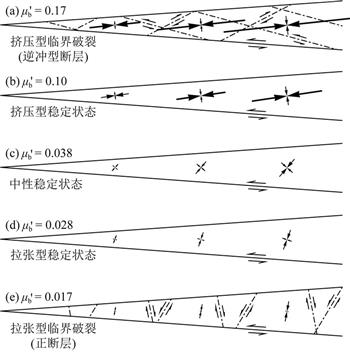 |
| 关 键 词: | 楔形体 应力解析解 断层面摩擦性质 弧前形变 |
| 收稿时间: | 2021-11-30 |
| 修稿时间: | 2022-01-11 |
| 本文献已被 维普 万方数据 等数据库收录! | |
| 点击此处可从《地球物理学报》浏览原始摘要信息 | |
| 点击此处可从《地球物理学报》下载免费的PDF全文 | |