 PDF(1717 KB)
PDF(1717 KB)


 PDF(1717 KB)
PDF(1717 KB)
 PDF(1717 KB)
PDF(1717 KB)
渭河流域水土流失治理效率的时空格局演化与影响因素
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Spatio-temporal Pattern Evolution and Influencing Factors of Governance Efficiency of Soil and Water Loss in the Weihe River Catchment
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}运用Bootstrap-DEA模型计算2000~2015年渭河流域陕西段39个县区水土流失治理效率;结合探索性空间分析方法(ESDA)和地理加权回归模型(GWR)分析各县水土流失治理效率的时空演化特征及其影响因素。研究结果表明:① 2000~2015年,研究区水土流失治理效率从0.263增至0.336,整体治理效率仍处较低水平;前期生态治理效率的增加缘于纯技术效率的提高,后期规模效率对治理效率的增加起到了主导作用。② 县域的治理效率在空间上呈现集聚状态;热点分析结果进一步显示,2005年治理效率表现出2个热点集聚区,即以宝鸡市千阳县为热点区、乾县和武功县为核心辐射至永寿县和礼泉县的热点集聚区,冷点区域则以临潼为中心,辐射到西安市辖区、高陵、富平和三原县;2010~2015年治理效率的热点区域与冷点区域较2005年有所收缩且保持相对稳定。③ 渭河流域水土流失治理效率的时空变化是降水、坡度、灌草面积覆盖度、人口经济和农业生产共同作用的结果,且各影响因素在不同时期对各县的治理效率的贡献呈动态变化,这意味着政策制定者需要从全局角度权衡不同因素的影响效果。
Objectively assessing the effectiveness of ecological restoration measures and analyzing effective ways to promote the efficiency of ecological management are important scientific and policy issues in the Weihe River Basin. Using an interdisciplinary approach, the aim of this study is to measure the control efficiency of the Sloping Land Conversion Program(SLCP)and terrace fields on soil and water loss by adopting the Bootstrap-DEA model and using a comprehensive dataset (including biophysical and socioeconomic data) from 39 counties in the period 2000-2015. Then, exploratory spatial data analysis (ESDA) was used to capture the spatial correlation in overall control efficiency. Finally, geographically weighted regression (GWR) was employed to identify the spatial heterogeneity and evolutionary characteristics in the relationship between control efficiency and natural conditions and socioeconomic development in each sample county.Results show that the control efficiency of soil erosion increased from 0.263 to 0.336 during the study period. The increase of the treatment efficiency for soil and water loss in the early stage was due to the improvement of pure technical efficiency; while later the scale efficiency played a leading role in promoting the treatment efficiency. In addition, the efficiency showed a stable spatial agglomeration. The hotspots of efficiency were concentrated primarily in Baoji City, while the cold-spot center was Lintong, the radius of which extended to the municipality districts of Xi'an, Gaoling, and Fuping. The difference in control efficiency is the result of a combination of multiple factors; the factors affecting control efficiency vary across counties, indicating that regional governments should consider full-scale initiatives.
退耕还林(草) / Bootstrap-DEA / 地理空间加权模型(GWR Model) / 探索性空间分析(ESDA) / 渭河流域 / 治理效率 {{custom_keyword}} /
sloping land conversion program / Bootstrap-DEA / Geographically Weighted Regression(GWR) / exploratory spatial data analysis(ESDA) / the Weihe River catchment / control efficiency {{custom_keyword}} /
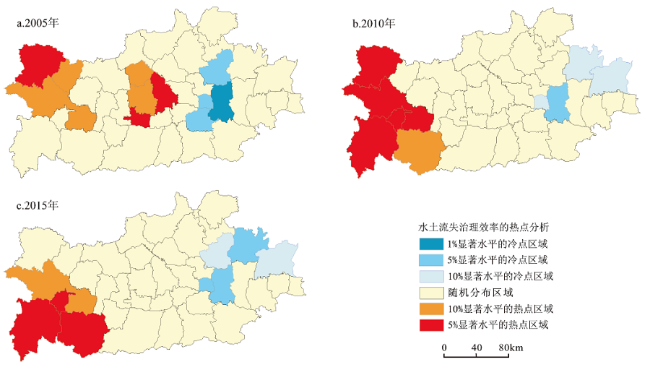
图5 2005~2015年水土流失治理效率热点分布Fig.5 Hotspot distribution of control efficiency in 2005(a), 2010(b) and 2015(c) |
表2 2005~2015年GWR模型各自变量对治理效率的影响系数Table 2 Regression coefficient of GWR in 2005-2015 |
| 变量 | 2005年 | 2010年 | 2015年 |
|---|---|---|---|
| lnintercept | -1.91~-1.52*** | -1.55~-1.05*** | -1.39~-1.24*** |
| lncover | 0.17~0.39** | 0.05~0.12 | 0.17~0.23* |
| (0.22) | (0.06) | (0.20) | |
| lnslope | -0.32~0.01 | -0.42~-0.20* | -0.32~-0.15* |
| (-0.09) | (-0.26) | (-0.25) | |
| lnprep | -0.17~0.01* | -0.01~0.36 | 0.40~0.55*** |
| (-0.12) | (0.12) | (0.49) | |
| lnpgdp | 1.83~13.12* | -2.45~2.31 | -1.18~1.51 |
| (7.14) | (-1.72) | (-0.82) | |
| (lnpgdp)2 | -13.48~-2.18** | 1.14~2.44 | 0.47~1.48 |
| (-7.51) | (1.77) | (0.65) | |
| lnpgrain | 0.16~0.33* | 0.01~0.20 | 0.05~0.68** |
| (0.25) | (0.10) | (0.43) | |
| lndensity | -0.46~-0.24** | -0.77~-0.25*** | -0.90~0.01** |
| (-0.35) | (-0.53) | (-0.60) | |
| 带宽 | 100 | 90 | 90 |
| AIC | 104.60 | 118.31 | 104.78 |
| R2 | 0.58 | 0.50 | 0.63 |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.36 | 0.28 | 0.42 |
| GWR Residuals | 15.18 | 16.43 | 11.87 |
| Global Residuals | 17.94 | 25.50 | 16.42 |
| [1] |
党小虎, 吴彦斌, 刘国彬, 等. 生态建设15年黄土高原生态足迹时空变化[J]. 地理研究, 2018,37(4):761-771.
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [2] |
陕西省统计局, 国家统计局陕西调查总队. 陕西统计年鉴[M]. 西安: 中国统计出版社,2001- 2016.
[ Shaanxi Provincial Bureau of Statistics, NBS Survey Office in Shaanxi. Shaanxi Statistical Yearbook. Xi’an: China Statistics Press, 2001- 2016.]
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [3] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [4] |
孔凡斌, 廖文梅. 集体林分权条件下的林地细碎化程度及与农户林地投入产出的关系——基于江西省8县602户农户调查数据的分析[J]. 林业科学, 2012,48(4):119-126.
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [5] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [6] |
牛最荣, 赵文智, 刘进琪, 等. 甘肃渭河流域土地利用及覆被变化对径流的影响研究[J]. 水利水电技术, 2012,43(4):5-10.
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [7] |
刘晓燕, 刘昌明, 杨胜天, 等. 基于遥感的黄土高原林草植被变化对河川径流的影响分析[J]. 地理学报, 2014,69(11):1595-1603.
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [8] |
刘晓燕, 杨胜天, 王富贵, 等. 黄土高原现状梯田和林草植被的减沙作用分析[J]. 水利学报, 2014,45(11):1293-1300.
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [9] |
王明玉, 王百田. 不同水土保持措施对黄土高原小流域年径流和产沙的影响——以平凉纸坊沟为例[J]. 林业科学, 2016,52(8):10-20.
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [10] |
王雅, 蒙吉军. 基于INVEST模型的黑河中游土地利用变化水文效应时空分析[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2015,51(6):1157-1165.
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [11] |
黎云云, 畅建霞, 王义民, 等. 渭河流域径流对土地利用变化的时空响应[J]. 农业工程学报, 2016,32(15):232-238.
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [12] |
武国胜, 林惠花, 曾宏达. 用RS和GIS技术评价福建省长汀县土壤保持功能对生态系统变化的响应[J]. 生态学报, 2017,37(1):321-330.
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [13] |
王连芬, 孙平平. 区域环境治理效率测的评价指标体系研究[J]. 统计与决策, 2012(10):60-62.
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [14] |
侯燕. 中国生态治理效率及其变动[J]. 北京理工大学学报(社会科学版), 2015,17(6):21-29.
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [15] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [16] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [17] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [18] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [19] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [20] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [21] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [22] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [23] |
陕西省水利厅. 陕西水利统计年鉴[M]. 西安: 陕西科学技术出版社,2001- 2016.
[ Shaanxi Provincial Department of Water Resources. Water conservancy statistical yearbook of Shaanxi. Xi’an: Shaanxi Science and Technology Press,2001- 2016.]
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [24] |
中华人民共和国水利部. 黄河流域水文资料年鉴(泾渭洛河水系)[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2001- 2016.
[ The Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China. Hydrological statistics yearbook of Yellow River Bain. Beijing: China Water Conservancy and Hydropower Press, 2001- 2016.]
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [25] |
刘纪远, 匡文慧, 张增祥, 等. 20世纪80年代末以来中国土地利用变化的基本特征与空间格局[J]. 地理学报, 2014,69(1):3-14.
土地利用/土地覆被变化(LUCC)是人类活动与自然环境相互作用最直接的表现形式,本文采用相同空间分辨率的卫星遥感信息源和相同的技术方法,对中国1980 年代末到2010 年土地利用变化数据进行定期更新。在此基础上,提出并发展土地利用动态区划的方法,研究土地利用变化的空间格局与时空特征。我们发现:1990-2010 年的20 年间,中国土地利用变化表现出明显的时空差异。“南减北增,总量基本持衡,新增耕地的重心逐步由东北向西北移动”是耕地变化的基本特征;“扩展提速,东部为重心,向中西部蔓延”是城乡建设用地变化的基本特征;“林地前减后增,荒漠前增后减,草地持续减少”是非人工土地利用类型变化的主要特征。20 世纪末与21 世纪初两个10 年相比,中国土地利用变化空间格局出现了一些新特征,原有的13 个土地利用变化区划单元演变为15 个单元,且部分区划单元边界发生变化。主要变化格局特征为黄淮海地区、东南部沿海地区、长江中游地区和四川盆地城镇工矿用地呈现明显的加速扩张态势;北方地区耕地开垦重心由东北地区和内蒙古东部转向西北绿洲农业区;东北地区旱作耕地持续转变为水田;内蒙古农牧交错带南部、黄土高原和西南山地退耕还林还草效果初显。近20 年间,尽管气候变化对北方地区的耕地变化有一定的影响,但政策调控和经济驱动仍然是导致我国土地利用变化及其时空差异的主要原因。2000 年后的第一个10 年,土地利用格局变化的人为驱动因素已由单向国土开发为主,转变为开发与保护并重。在空间格局变化的分析方法方面,应用“动态区划法”开展世纪之交两个10 年中国LUCC空间格局变化的分析,有效揭示了20 年来中国LUCC“格局的变化过程”,即动态区划边界的推移、区划单元内部特征的变化与单元的消长等;以及“变化过程的格局”,即土地利用变化过程与特征的分阶段区域差异,清晰刻画了LUCC动态区划中区划单元的消长,单元边界的变动,以及前后10 年的变化强度特征,揭示了土地利用“格局”与“过程”之间的交替转化规律,以及不同类型和区域的变化原因,证明了该分析方法的有效性。
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [26] |
National Climatic Center of the China Meteorological Administration. China’s surface climate data of daily value dataset. 2000-2015(v3.0,http://cdc.nmic.cn/.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [27] |
ASTER-GDEMV2 30m DEM model. National Aeronautics and Space Administration(search.earthdata.nasa.gov)
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [28] |
China has undertaken several major programs of terrestrial ecosystem restoration (ERPs) in recent years, including the Natural Forest Protection Program (NFPP) and the Sloping Land Conversion Program (SLCP). There have been reports on the implementation of these programs, their preliminary impacts, and the problems encountered in carrying them out; a great deal has been learned from these studies. Nonetheless, China's ERPs are not limited to the NFPP and the SLCP. Because a complete documentation and a timely update of these major efforts are still missing from the literature, it is difficult to gauge the scope of these programs and the scale of their impacts. In addition, a more thorough and critical analysis of both the general ERP policy and the specific technical measures used in implementing the ERPs remains urgently needed. The purpose of this article is to tackle these tasks. Overall, with the huge government investments in the ERPs, tremendous progress has been made in implementing them. To complete them successfully and to fundamentally improve the targeted ecosystems, however, it is essential for China to have a more balanced and comprehensive approach to ecological restoration. This approach must include: adopting better planning and management practices; strengthening the governance of program implementation; emphasizing the active engagement of local people; establishing an independent, competent monitoring network; and conducting adequate assessments of program effectiveness and impact.
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [29] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [30] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [31] |
AbstractNatural gas has become increasingly important as a source of energy in recent years. It is widely viewed as an attractive means of realizing environmental objectives post Kyoto, and individual country gas industries have been extensively restructured to encourage investment from the private sector. Barriers to international trade in gas have fallen particularly in areas such as Europe and Asia as pipeline facilities have expanded and trading systems have become established. An important question for policy makers concerns the use of scarce resources by this expanding industry. Regulatory authorities increasingly use efficiency comparators to incentivise minimum cost use of resources by price cap methods, yardstick competition and other techniques. This paper explores some of the policy developments, which affect efficiency of resource use in the gas industry, and uses data envelopment analysis to measure relative performance at the individual country level. Recent developments in bootstrapping techniques are used to correct efficiency estimates for bias and to assess the uncertainty surrounding such estimates. The implications of these results for regulatory authorities are then explored. {{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [32] |
王静爱. 中国政区和流域的多样性与可持续发展[J]. 北京师范大学学报社会科学版, 2002(4):115-121.
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [33] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [34] |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [35] |
刘晓燕, 刘斌, 杨胜天. 黄土高塬沟壑区产沙驱动力及减沙潜力分析[J]. 人民黄河, 2014,36(5):1-3.
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [36] |
刘晓燕. 黄河近年水沙锐减成因[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016.
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [37] |
李薇, 谈明洪. 西南山区人口空间重组及其对植被的影响—以河流沿线为例[J]. 生态学报, 2018,38(24):8879-8887.
随着城市化的快速推进,山区人口迁出及空间重组成为影响中国山区人地关系的重要因素,这可能对山区植被恢复和生态改善产生巨大影响。基于人口空间数据、河流分布数据和MODIS数据,本文分析了河流沿线人口空间重组情况,以生长季EVI值为表征植被绿度的指标,采用基于像元的趋势分析方法和基于样本的相关分析模型,对2000-2010年间中国西南山区不同级别河流沿线的人口空间变化和植被变化作了系统性分析,并定量研究了人口空间重组与植被变化之间的关系。结果表明:(1)三级及以上河流出现人口往河流沿线聚集的趋势,人口在河流的影响区聚集程度大于对比区。其中,一级和二级河流沿线影响区人口密度增加量比对比区分别高75.9%和42.1%。(2)三级及以上各河流沿线影响区和对比区EVI均呈现出增加的趋势,且影响区增加趋势低于对比区。(3)植被EVI变化趋势与人口密度变化呈负相关关系,河流沿线人口密度增加不利于植被的恢复;河流级别越高,植被EVI变化趋势与人口密度变化的相关性越强。
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [38] |
苑韶峰, 杨丽霞, 杨桂山, 等. 耕地非农化的社会经济驱动因素异质性研究—基于STIRPAT和GWR模型的实证分析[J]. 经济地理, 2013,33(5):137-143.
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [39] |
武玮, 徐宗学, 李发鹏. 渭河关中段水文情势改变程度分析[J]. 自然资源学报, 2012,27(7):1124-1137.
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| [40] |
卓蓉蓉, 余斌, 曾菊新, 等. 湖北省经济空间格局演变与经济空间战略效应[J]. 经济地理, 2018,38(3):37-45.
[
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
 PDF(1717 KB)
PDF(1717 KB)
 图1 研究区位置
图1 研究区位置 表1 影响治理效率的指标选取说明
表1 影响治理效率的指标选取说明 图2 2000~2015年研究区主要观测站水沙量与降水的年际波动变化趋势
图2 2000~2015年研究区主要观测站水沙量与降水的年际波动变化趋势 图3 2005~2015年研究区水土流失治理效率空间分布
图3 2005~2015年研究区水土流失治理效率空间分布 图4 2005~2015年研究区水土流失治理效率分解
图4 2005~2015年研究区水土流失治理效率分解 图5 2005~2015年水土流失治理效率热点分布
图5 2005~2015年水土流失治理效率热点分布 表2 2005~2015年GWR模型各自变量对治理效率的影响系数
表2 2005~2015年GWR模型各自变量对治理效率的影响系数/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |