ABUNDANCE AND COMMUNITY STRUCTURE OF THE PHYTOPLANKTON IN SURFACE SEDIMENTS RECORDED BY BIOMARKERS FROM LIAODONG BAY
-
摘要:
对渤海辽东湾海域表层沉积物中浮游植物生物标志物的分布进行了研究。通过对辽东湾51个站位的调查研究发现,硅藻、甲藻和颗石藻这3种浮游植物的生物标志物含量分布规律不明显,为了消除粒度和沉积速率的影响,将这3种生物标志物总量与总有机碳(TOC)含量做比值,得到的相对含量从湾内到湾口随着离岸距离增加而增加,生物标志物指示的初级生产力与现场调查的结果一致,表明生物标志物法基本可以用来重建初级生产力。辽东湾海域初级生产力在湾口高于湾内,表明其主要控制因素是水体浊度而不是陆源营养盐的输入。辽东湾西侧菊花岛附近初级生产力的高值主要与人类养殖、陆源排污等导致的水体富营养化相关。生物标志物的相对比例结果显示,辽东湾两侧近岸区硅藻和甲藻相对贡献高,尤其是硅藻占据绝对优势,这主要与硅藻在高营养盐的情况下具有竞争优势有关,而在辽东湾中部发现高的颗石藻相对贡献与黄海暖流入侵路径相对应。
Abstract:This paper reported the distribution of phytoplankton biomarkers in surface sediments of Liaodong Bay, Bohai Sea. The distribution of biomarkers of three phytoplankton species, diatoms, dinoflagellates and haptophytes was not obvious in 51 surface sediments from Liaodong Bay. Biomarker contents were normalized to the total organic carbon (TOC) to eliminate the influence of grain size and sedimentation rate, it was found that the relative content increased from the bay to the estuary in Liaodong Bay. The primary productivity indicated by biomarkers is consistent with the results from modern water column phytoplankton surveys, indicating that the biomarkers can be used to reconstruct the primary productivity. The primary productivity in the Liaodong Bay is higher than that in the Bay mouth, which indicates that the main controlling factor is the turbidity of the water column rather than the input of terrestrial nutrients. The high primary productivity near Juhua Island on the west side of Liaodong Bay is mainly related to eutrophication caused by human culture and land-based sewage discharge. The relative proportion of biomarkers showed that diatom and dinoflagellate contributed more to the coastal area of Liaodong Bay, especially diatom occupied an absolute advantage, which was mainly related to the competitive advantage of diatom under the condition of high nutrient salts, while high haptophytes was found in the middle of Liaodong Bay, which corresponded to the invasion path of the Yellow Sea Warm Current (YSWC).
-
Key words:
- Liaodong Bay /
- primary productivity /
- biomarkers /
- phytoplankton community structure
-
0. 引言
海洋初级生产力指海洋中初级生产者通过同化作用生产有机物的能力,作为海洋生态系统中最主要的初级生产者,海洋浮游植物生产力和群落结构的变化影响着海洋生物地球化学关键过程[1]。研究长时间尺度海洋中浮游植物生产力和种群结构变化,对于理解碳循环的变化及气候变化机理,寻找环境变迁规律有着重要的意义。在短时间尺度上浮游植物种群变化可以影响生物地球化学循环,也可以影响海洋中高营养层次的种群结构, 从而改变整个生态系统,例如赤潮主要就是由于营养盐含量和组分增加而导致了浮游植物种群结构的变化和初级生产力的增加[2, 3]。
辽东湾位于渤海东北部,周边主要有辽河、滦河、六股河、小凌河、大凌河、大辽河、复州河等中小型河流注入,是多种经济鱼类、虾类和贝类的产卵场、索饵场和育肥场。近年来,过度捕捞和环境污染等多种因素对该区初级生产力和生物群落产生较大影响[4]。如宋广军等依据2012—2014年对辽东湾浮游植物群落的调查,分析了19-3油田溢油事故发生后辽东湾浮游植物种类、细胞丰度、生物多样性和优势种的变化以及影响因素。调查发现,辽东湾浮游植物种类数在2012年有明显的降低,而在2013年和2014年浮游植物种类数明显上升。辽东湾浮游植物细胞丰度在夏季异常升高,这可能与海水中油类含量的升高有一定关系[5]。
前人对辽东湾生态系统的变化进行了初步研究,主要是通过采取水样进行浮游植物群落和初级生产力的研究,认为硅藻在种类和数量上占绝对优势[6, 7],而初级生产力具有明显的区域特征,与渔业资源关系密切[8]。以上研究为了解辽东湾生态结构的变化提供了基础数据,但这些数据的时间尺度短,且调查区域有限,不足以揭示辽东湾的生态结构的变化规律。对海洋浮游植物丰度和群落的研究,除传统的形态统计外,植物色素和生物标志物等化学方法也越来越受到重视和关注[9, 10],生物标志物分子能在地质环境中较稳定存在,其含量与比值的变化被广泛用于总生产力或者某一种浮游植物生产力与群落结构变化的重建。已有研究者利用这一方法在我国东海[11-13]、南海[9, 14]、南黄海[15, 16]、渤海和北黄海[17, 18]重建了浮游植物生产力变化。对北黄海和渤海表层浮游植物生物标志物的研究发现,硅藻、甲藻和颗石藻生物标志物可以指示海洋浮游植物生产量,是海源有机质的良好指标[17, 18],显示出脂类分子在研究海洋生态结构及环境演变方面的应用潜力,而脂类分子在辽东湾海域的研究还相对比较薄弱, 亟待加强。
特定脂类标志物的含量变化可以反映产生此种标志物的母源生物的信息,二者呈正相关关系,因此常被用来指示母源生物量的变化。本研究选用菜籽甾醇(Brassicasterol)、甲藻甾醇(Dinosterol)、直链C37烯酮(C37-alkenones)这3种生物标志物分别指示海洋硅藻、甲藻、颗石藻3类浮游藻类[10, 19]。通过分析各种生物标志物的含量变化趋势和特征,并与现代海洋调查结果对比,探讨了辽东湾海域的浮游植物分布特点及其原因,为脂类分子重建辽东湾过去浮游植物生态结构提供验证数据和基础资料。
1. 样品采集和测试
1.1 样品采集
2015年8月,通过中国地质调查局海洋地质调查项目的航次,在“浙嘉渔科001”号调查船上用箱式采样器采得沉积物样品,0~5 cm为表层沉积物样品,-20 ℃条件下冷冻保存。对其中51个样品进行了分析(图 1),辽东湾中部沉积速率较小,沉积速率在0.22~0.77 cm/a之间,近岸海区的站位沉积速率较高,在0.41~1.1 cm/a左右[20]。因此,表层沉积物样品时间尺度大概在5~25 a之间。
1.2 粒度和有机碳分析
粒度和有机碳分析在青岛海洋地质研究所完成,粒度测定步骤如下:样品冷冻干燥后取1 g左右的样品加入10 mL含5%H2O2静置24 h,以去除有机质组分,再加入稀盐酸去除生物CaCO3。然后用仪器自带的超声波振荡器超声分散30 min,试验采用英国Malvern公司生产的Mastersizer 2000型激光粒度分布测量仪进行粒度分析。测量范围为0.02~2 000 μm,分辨率0.01,分析误差±2%。
用重铬酸钾氧化-还原容量法测定总有机碳(TOC)。称取0.5 g干燥后的样品于试管中,加0.1 g硫酸银、10 mL重铬酸钾-硫酸标准溶液,在加入3 mL上述溶液时,应将样品摇散,勿使结块。将试管内的溶液及残渣倒入250 mL烧杯中,将冲洗小漏斗及试管的水洗液并入烧杯中。加入5 mL磷酸溶液用硫酸亚铁标准溶液滴定至黄色大部分褪去,加入2~3滴苯基代邻氨基苯甲酸指示剂溶液,继续滴至溶液由紫色突变到绿色即为终点。按重铬酸钾的消耗量,计算样品中有机碳的含量。
1.3 脂类生物标志物的提取和分析
脂类生物标志物分析在中国科学院海洋地质与环境重点实验室完成,测定分为样品预处理和上机分析2个过程。
样品预处理:样品冷冻干燥后进行研磨,准确称取5 g样品进行冷冻干燥研磨,加入萃取剂二氯甲烷和甲醇(3:1)以及内标(19醇和24氘烷),震荡、超声15 min,萃取4次,萃取液经氮吹富集后加入KOH甲醇溶液进行水解,水解液用正己烷萃取4次后氮吹富集,然后用硅胶柱分离去除烃类组分得到醇类、烯酮组分,加BST-FA和CH2Cl2衍生化(70 ℃,1 h)后用于上机分析。
仪器分析:所有样品进GC(Agilent 6890 N)定量分析,由生标的峰面积与内标峰面积对比计算得到。GC条件色谱柱为毛细管柱HP-1(型号Agilent 19091Z-433,30 m×0.25 mm×0.25 μm),进样口温度:300 ℃,FID检测器温度:300 ℃,采用不分流进样,所用载气为氢气,流速为1.3 mL/min。实验的相对标准偏差<±10%。在GC分析中, 菜籽甾醇(Brassicasterol)、甲藻甾醇(Dinosterol)、直链C37烯酮(C37-alkenones)这3种生物标志物依据标准样品进行保留时间定位, 同时选取个别样品进行了气相色谱-质谱(Gas Chromatograph-Mass Spectrometry, GC-MS)定性分析, 确定所研究脂类分子是否存在共溢出等现象。
2. 结果
2.1 粒度和TOC
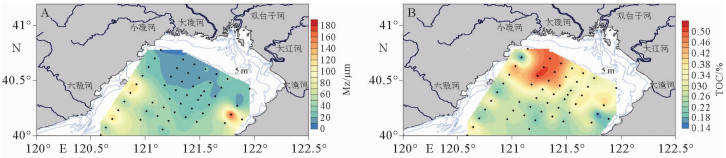
研究区域表层沉积物的平均粒径为7.46~185.68 μm,平均为39.90 μm。细颗粒沉积物主要分布在辽东湾东北部的浅滩区,而砂质沉积物则主要分布在东西两侧的近岸区域,最粗的沉积物主要分布在东南近岸区(图 2A)。表层沉积物中TOC含量为0.12%~0.52%,平均为0.32%;东北浅滩区的TOC含量明显高于其他区域,最高值出现在研究区西北部,最低值是研究区东南部的砂质沉积区域(图 2B)。TOC含量与沉积物粒度平均值呈明显的负相关关系(图 2C,R2=0.41),表明沉积物中的有机质主要吸附在细颗粒沉积物。
2.2 海源生物标志物
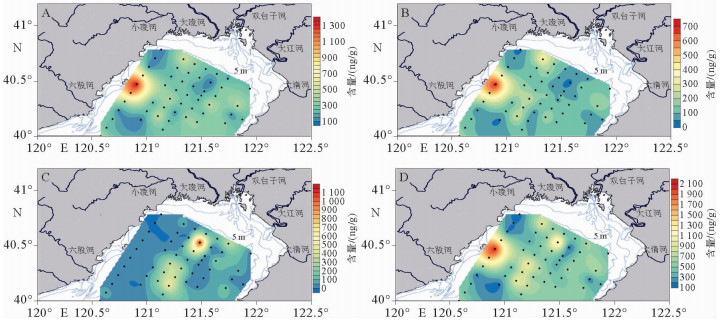
菜子甾醇、甲藻甾醇、长链烯酮以及3种海源生物标志物之和(MOM)的含量分布如图 3所示,菜子甾醇的含量变化范围为81~1 376 ng/g,甲藻甾醇的含量变化范围为29~707 ng/g,长链烯酮的含量变化范围为0~1 194 ng/g,总含量变化范围为114~2 122 ng/g。菜子甾醇和甲藻甾醇含量分布一致,高值主要出现在近岸区域,最高值出现在菊花岛海域附近。长链烯酮含量分布的高值主要在辽东湾中部区域,相对低值分布在辽东湾近岸的两侧, 最低值主要出现在辽东湾西侧区域。
3. 讨论
3.1 初级生产力变化
海源生物标志物的绝对含量可以从一定程度上反映海源有机物的相对贡献,但会受到沉积速率和降解速率等因素的影响,而生物标志物在TOC中的相对含量可以在一定程度上消除沉积速率和降解速率的影响,将菜子甾醇、甲藻甾醇、长链烯酮、三者总量与TOC做比值,含量变化范围分别为185~5 679、63~2 829、0~3 144、249~8 538 ng/g TOC(图 4)。
图 4显示菜子甾醇/TOC、甲藻甾醇/TOC、长链烯酮/TOC的分布与菜子甾醇、甲藻甾醇、长链烯酮的含量分布有明显的差异。菜子甾醇/TOC和甲藻甾醇/TOC的含量分布变化趋势一致,二者含量从辽东湾东北近岸区向西南区随着水深的增加而增加,在六股河口外的近岸区又有所降低。长链烯酮/TOC含量在辽东湾两侧都表现为低值,而在中间远离岸区出现高值。虽然藻类生物标志物分子的含量和生物量之间的对应关系在不同生物间存在差异,但对总体变化规律和模式的讨论没有显著影响[9]。脂类标志物的研究结果显示, 辽东湾浮游植物群落中硅藻的生物标志物含量占绝对优势,这与前人对辽东湾网采浮游植物群落结构组成的研究结果一致[6, 20, 21]。
本研究将3类浮游藻类标志物的总和指示表层浮游植物生物总量, 虽然该统计并不完全, 但也基本反映了海水表层浮游植物生物量的变化规律。据此计算,浮游植物生物量呈现随离岸距离和水深的增加而逐渐增加的趋势(图 4D)。前人对辽东湾海域叶绿素的研究表明,夏季的叶绿素质量浓度明显高于冬季,夏季辽东湾湾口的平均叶绿素质量浓度明显高于湾内的平均质量浓度,表明辽东湾水域湾口的初级生产力是高于湾内和湾顶[23],这与本文的生物标志物记录基本一致。
营养盐和光照是决定浮游植物生长的关键因素,辽东湾沿岸由于地表径流和降雨汇流等陆源输入的影响,对湾顶及内部的水体起到了一定的稀释作用,而辽东湾是位于渤海最北部的典型半封闭海湾,水体的平面交换能力非常有限,导致近岸初级生产力反而低于湾口[23]。近岸海域由于受河口冲淡水的影响,水体盐度较低,营养盐含量较高,但水体浊度较大,水深增加导致水体盐度增高、营养盐含量降低。这些环境因子共同形成了辽东湾海域的初级生产力的空间变化特征,例如河口近岸区其较低的初级生产力可能与水体浑浊影响了浮游植物的生长有关。北黄海和渤海海域、东海海域的结果也表明初级生产力在河口区低、陆架区高,这主要是因为河口区的水体浑浊度较高, 光合作用较弱, 而陆架区由于径流营养盐的输入以及海水浊度下降产生较高生产力, 外海则由于低营养盐的海水生产力下降[2, 18, 24]。辽东湾海域初级生产力最高值出现在西部的兴城菊花岛附近海域,它是辽宁省兴城市最重要贝类养殖区,底播增养殖主要集中于该海域,海域N、P含量也不断增加,富营养化程度加剧,导致生态环境质量日趋恶化,赤潮时有发生,生物标志物指示的初级生产力在该海域也达到峰值(图 4D)。
3.2 群落结构变化
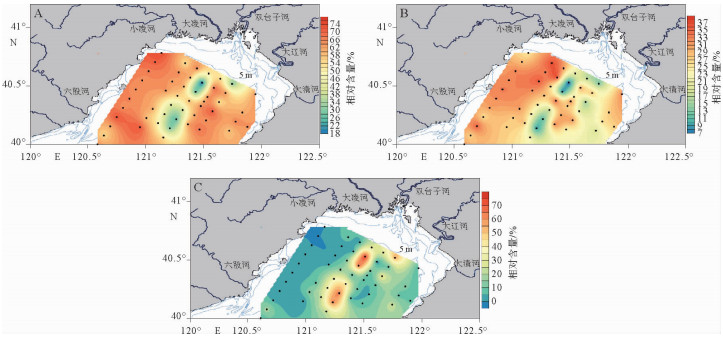
从图 5A可以看出,辽东湾两侧海域浮游植物群落中硅藻的生物标志物含量占绝对优势, 大部分站位超过了总脂类分子的60%,而整个辽东湾海域只有8个站位低于50%,表明硅藻是辽东湾海域的主要浮游植物。辽东湾河口沿岸区的硅藻丰度高于近岸丰度,主要是由于河口沿岸海域受到入海河流和陆源输入的影响,水体中的营养盐较为丰富,有利于硅藻的繁殖[7, 22]。前人研究表明,由于河流的输入,沿岸海域的硅酸盐浓度比离岸海域的高,高浓度硅有利于硅藻的生长,所以在山东半岛沿岸附近及黄河口附近硅藻的相对贡献明显高于渤海中部海域,在渤海海域硅藻的相对贡献明显高于北黄海,在长江口离岸越远硅藻比例下降[2, 17, 18]。辽东湾的研究结果与前人研究结果一致,硅藻在近岸河口区占据绝对优势,主要受到营养盐控制。
从图 5B可以看出,甲藻的相对贡献分布与硅藻的相对贡献在整个海域的分布上有一致的趋势,都是在辽东湾两侧的近岸贡献比例高于中间远离岸的区域。但是在细节变化上,两者又不一致,如甲藻在辽东湾东侧近岸海域的贡献比例明显要低于西侧近岸海域,而硅藻在两侧区域都为高值。这与同一海域内甲藻与硅藻对营养盐的竞争有关,在硅藻相对贡献较高的辽东湾东侧近岸区域甲藻相对贡献较低,主要是因为硅藻更适应低盐和高营养盐的环境而比甲藻更具竞争优势[25]。
在整个浮游植物群落中颗石藻的生物量相对较小(图 5C),贡献比例最高在辽东湾中部海域,其中有4个站位超过了50%,其次是在辽东湾东侧海域,贡献比例最低的为辽东湾西侧海域。中国浅海颗石藻以大洋桥石藻(Gephyrocapsa oceanica)和赫氏艾密里藻(Emiliania huxleyi)为优势种,从近岸到远离海岸的海域,颗石藻类丰度逐渐增高,如冲绳海槽的丰度比内陆架高数千倍[26]。前人对黄渤海表沉积物中钙质超微化石的研究表明,颗石藻的分布与黄海暖流有密切的关系,黄海暖流流经区域,颗石藻丰度高[27, 28],对北黄海—渤海表层沉积物生物标志物的研究也表明高的颗石藻的相对比例与黄海暖流入侵的路径相对应[17]。黄海暖流由黄海东南部进入黄海,沿着黄海槽北上,绕过山东半岛进入北黄海,然后转向西从渤海海峡的北侧进入渤海,之后分为向西的渤海中心支和向北的辽东湾支[29]。黄海暖流对辽东湾的入侵将带来温暖高盐的大洋海水及高丰度的颗石藻,因此在辽东湾中部海域高的颗石藻相对比例与黄海暖流入侵路径相对应。此外,颗石藻对海水中的营养盐具有很高的吸附能力,经常出现在高光照的、稳定而成层的以及低营养盐的环境中,如在胶州湾,依据Gephyrocapsa oceanica丰度的变化,自岸向海可以划分向岸常见带、浅水丰富带和深水富集带[30]。辽东湾中部海域相对两侧海域光照更好、受陆源河流影响较小,较低的营养盐更适于颗石藻的生长。
4. 结论
(1) 辽东湾表层沉积物中3种浮游植物生物标志物总量相对TOC的相对含量分布具有湾内低、湾口高的趋势,与现代海洋叶绿素a含量变化一致,表明辽东湾初级生产力主要受控于水体浊度的影响,而陆源输送营养盐并不是最主要的控制因素。兴城菊花岛附近海域的高初级生产力,主要由人类养殖和陆源排污导致的富营养化程度加剧导致。
(2) 辽东湾表层沉积物中生物标志物比例用作生物种群的替代指标, 其变化趋势与已有资料相符。辽东湾海域硅藻为主要优势种,其次为甲藻,黄海暖流对辽东湾的入侵带来温暖高盐的外海海水,控制着颗石藻的分布,高的颗石藻相对贡献与黄海暖流入侵路径相对应,主要分布在辽东湾中部海域。
-
[1] 郑重.海洋浮游生物学[M].北京:海洋出版社, 1984.
[2] 张海龙, 邢磊, 赵美训, 等.东海和黄海表层沉积物生物标志物的分布特征及古生态重建潜力[J].中国海洋大学学报:自然科学版, 2008, 38(6): 992-996. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qdhydxxb200806021
[3] 赵美训, 赵晓晨, 陈建芳, 等.南海表层沉积物生物标志物的分布特征及古生产力重建意义[J].热带海洋学报, 2009, 28(3): 45-53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2009.03.008
[4] 方志刚, 穆云侠.渤海辽东湾富营养化的趋势研究[J].环境保护科学, 2001, 27(3): 15-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6216.2001.03.006
[5] 宋广军, 李爱, 吴金浩, 等. 19-3油田溢油对辽东湾浮游植物群落的影响[J].渔业科学进展, 2016, 37(4): 60-66. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hyscyj201604009
[6] 双秀芝, 宫相忠, 何青, 等. 2009年春季辽东湾浮游植物群落[J].海洋湖沼通报, 2011, 35(3): 32-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2011.03.005
[7] 高伟, 宫相忠, 双秀芝, 等. 2009年夏、冬季辽东湾网采浮游植物群落结构分析[J].海洋科学, 2012, 36(5): 57-64. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hyhztb201204024
[8] 马志强, 周遵春, 薛克, 等.辽东湾北部海区初级生产力与渔业资源的关系[J].水产科学, 2004, 23(4): 12-15. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sckx200404004
[9] 李丽, 刘杰, 贺娟, 等. 2008年夏季南海北部浮游藻类生物量和群落组成特征及其影响因素:生物标记物研究[J].科学通报, 2014, 59(11): 1016-1025. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KXTB201411009.htm
[10] 李丽, 汪品先.大洋"生物泵"——海洋浮游植物生物标志物[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2004, 24(4): 73-79. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz200404011
[11] Zhao J, Bianchi T S, Li X, et al. Historical eutrophication in the Changjiang and Mississippi delta-front estuaries: Stable sedimentary chloropigments as biomarkers[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2012, 47(10): 133-144.
[12] Xing L, Zhao M X, Zhang H L, et al. Biomarker reconstruction of phytoplankton productivity and community structure changes in the middle Okinawa Trough during the last 15 ka[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2008, 53(16): 2552-2559.
[13] Xing L, Zhang H L, Yuan Z N, et al. Terrestrial and marine biomarker estimates of organic matter sources and distributions in surface sediments from the East China Sea shelf[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2011, 31(10): 1106-1115. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2011.04.003
[14] He J, Zhao M X, Wang P X, et al. Changes in phytoplankton productivity and community structure in the northern South China Sea during the past 260 ka[J]. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology, 2013, 392: 312-323. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2013.09.010
[15] Xing L, Tao S Q, Zhang H L, et al. Distributions and origins of lipid biomarkers in surface sediments from the southern Yellow Sea[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2011, 26(8): 1584-1593. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2011.06.024
[16] Xing L, Zhao M X, Gao W, et al. Multiple proxy estimates of source and spatial variation in organic matter in surface sediments from the southern Yellow Sea[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2014, 76: 72-81. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2014.07.005
[17] 王星辰, 邢磊, 张海龙, 等.北黄海—渤海表层沉积物中浮游植物生物标志物的分布特征及指示意义[J].中国海洋大学学报:自然科学版, 2014, 44(5):69-73. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qdhydxxb201405010
[18] Xing L, Hou D, Wang X C, et al. Assessment of the sources of sedimentary organic matter in the Bohai Sea and the northern Yellow Sea using biomarker proxies[J]. Estuarine Coastal & Shelf Science, 2016, 176: 67-75. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e45d13acb23240a47e2c80686d07e1c1
[19] Volkman J K, Barrett S M, Blackburn S I, et al. Microalgal biomarkers: a review of recent research developments[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1998, 29(5-7): 1163-1179. doi: 10.1016/S0146-6380(98)00062-X
[20] 杨松林, 刘国贤, 杜瑞芝, 等.用210Pb年代学方法对辽东湾现代沉积速率研究[J].沉积学报, 1993, 11(1):128-135. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-CJXB199301014.htm
[21] 高伟, 宫相忠, 双秀芝, 等. 2009年夏、冬季辽东湾网采浮游植物群落结构分析[J].海洋湖沼通报, 2012, 36(4): 57-64. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hyhztb201204024
[22] 卞少伟, 韩龙, 张震, 等. 2013年8月和11月辽东湾近岸海域浮游植物群落结构[J].湿地科学, 2016, 14(4): 493-498. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=shidkx201604007
[23] 王昆, 吴景, 杜静, 等.夏季和冬季辽东湾海域水体中叶绿素a含量分布特征[J].水产科学, 2016, 35(6): 675-680. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sckx201606012
[24] Wu Y L, Zhang Y S, Zhou C X. Phytoplankton distribution and community structure in the East China Sea(ECS) Continental Shelf[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology & Limnology, 2000, 18(1): 74-79. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HYFW200001010.htm
[25] Chen Y L L, Chen H Y, Chung C W. Seasonal variability of coccolithophore abundance and assemblage in the northern South China Sea[J]. Deep Sea Research PartⅡ: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2007, 54(14): 1617-1633. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=96137aa14e71eca0c6dab1627df2d029
[26] 汪品先, 成鑫荣.东海底质中钙质超微化石的分布[J].海洋学报:中文版, 1988, 10(1): 76-85. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SEAC198801009.htm
[27] 李文勤.黄、渤海表层沉积物中钙质超微化石分布规律与黄海暖流流路[J].黄渤海海洋, 1991, 9(1): 7-11. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HBHH199101001.htm
[28] 芮晓庆, 刘传联, 梁丹, 等.南黄海表层沉积物中钙质超微化石的分布[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(5): 89-93. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201105013
[29] 温国义, 李广雪, 赵东波, 等.根据AVHRRSST探讨中国北部海域冬季环流演变[J].海洋环境科学, 2008, 27(s2): 19-23. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hyhjkx2008z2004
[30] 钟石兰, 汪亚平, 高抒, 等.胶州湾表层沉积颗石藻Gephyrocapsa oceanica的分布模式及其与环境的关系(英文)[J].古生物学报, 2001, 40(4): 505-513. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-6616.2001.04.011
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 王愉宁,陈军辉,何秀平,王九明,辛明,王保栋,王小如. 液相色谱-掺杂辅助大气压光电离质谱测定海洋沉积物中的植物甾醇. 分析化学. 2021(02): 282-291 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 朱韻洁,朱晓艳,林英姿,许秋瑾,雷坤. 辽东湾营养盐基准值的研究与确定. 环境工程技术学报. 2021(06): 1131-1136 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李顺,吴聪,陈炽新,荆夏,李学杰,蔡观强,钟和贤,张江勇,李波,张金鹏. 南海中北部表层沉积硅藻的高分辨空间分布及其与现代环境因子的关系. 地学前缘. 2020(06): 241-254 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)
-





 下载:
下载: