| 基于Remez迭代算法求解差分系数的双相介质自适应有限差分正演模拟 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 王文化, 文晓涛, 张波, 张懿疆, 王威. 2020. 基于Remez迭代算法求解差分系数的双相介质自适应有限差分正演模拟. 地球物理学报, 63(6): 2400-2414, doi: 10.6038/cjg2020N0068 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 王文化 文晓涛 张波 张懿疆 王威 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1. 成都理工大学油气藏地质及开发工程国家重点实验室, 成都 610059; 2. 成都理工大学地球物理学院, 成都 610059; 3. 美国阿拉巴马大学地质科学系, 塔斯卡卢萨 35401; 4. 中国石油化工股份有限公司勘探分公司, 成都 610041 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 国家自然科学基金(41774142),国家自然科学基金联合基金项目(U1562111),国家科技重大专项(2016ZX05002-004)联合资助. |
| |
| 摘 要: | 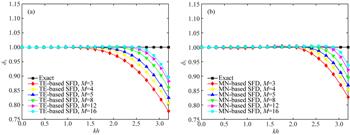
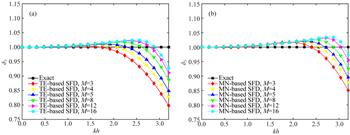
利用传统有限差分方法对基于Biot理论的双相介质波动方程进行数值求解时,由于慢纵波的存在,数值频散效应较为明显,影响模拟精度.相对于声学近似方程及普通弹性波方程,Biot双相介质波动方程在同等数值求解算法和精度要求条件下,其地震波场正演模拟需要更多的计算时间.本文针对Biot一阶速度-应力方程组发展了一种变阶数优化有限差分数值模拟方法,旨在同时提高其正演模拟的精度和效率.首先结合交错网格差分格式推导Biot方程的数值频散关系式.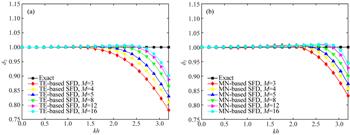
然后基于Remez迭代算法求取一阶空间偏导数的优化差分系数,并用于Biot方程的交错网格有限差分数值模拟.在此基础上把三类波的平均频散误差参数限制在给定的频散误差阈值和频率范围内,此时优化有限差分算子的长度就能自适应非均匀双相介质模型中的不同速度区间.数值频散曲线分析表明:基于Remez迭代算法的优化有限差分方法相较传统泰勒级数展开方法在大波数范围对频散误差的压制效果更明显;可变阶数的优化有限差分方法能取得与固定阶数优化有限差分方法相近的模拟精度.在均匀介质和河道模型的数值模拟实验中将本文变阶数优化有限差分算法与传统泰勒展开算法、最小二乘优化算法进行比较,进一步证明其在复杂地下介质中的有效性和适用性.
|
| 关 键 词: | 正演模拟 Remez迭代算法 最小二乘 双相介质 自适应有限差分 |
| 收稿时间: | 2019-05-05 |
| 修稿时间: | 2019-09-06 |
| 本文献已被 CNKI 等数据库收录! |
| 点击此处可从《地球物理学报》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《地球物理学报》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|



