Study on grain size indicator of surface soil and terminal lake sediments in closed basins over Qilian Mountains
-
摘要:
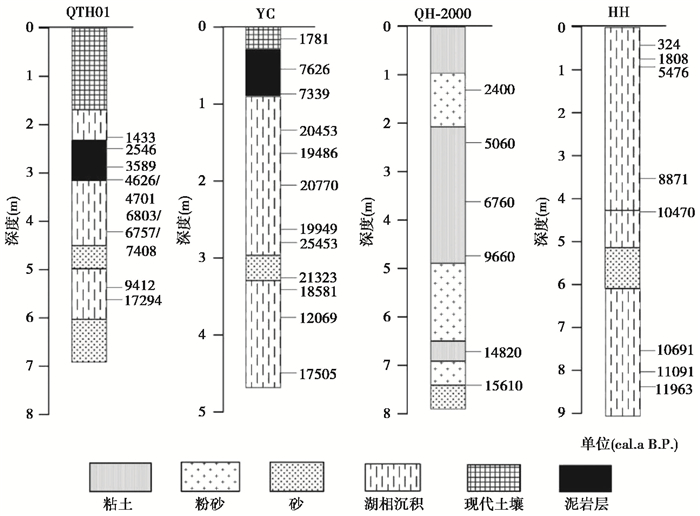
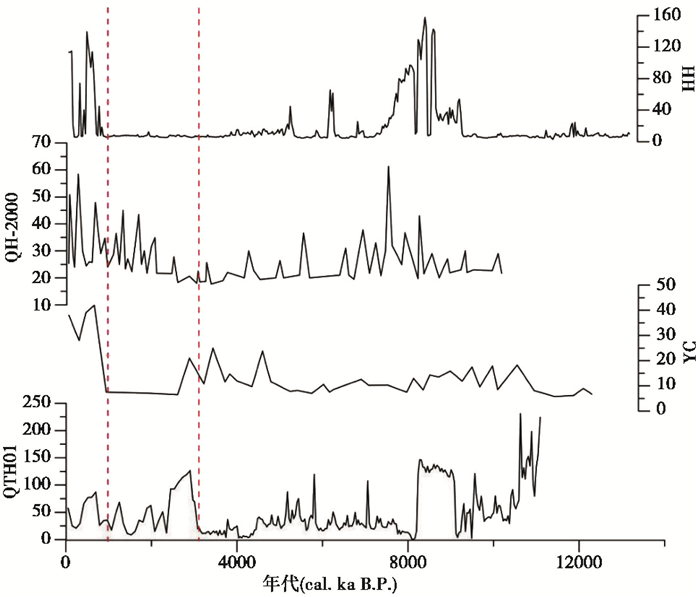
通过对祁连山地区典型内流河——石羊河、丰乐河、石油河和布哈河流域表土及终端湖全新世剖面沉积物中粒度指标的分析和对比,结果表明:1)流域表土粒径随海拔变化具有明显的空间分异特征,大致以河流出山口海拔为界分为上下游两部分,除石油河外,上游以粉砂组分为主,粒度频率曲线表现为河流沉积的双峰特征,粒径波动较小并随海拔有降低趋势,反映河流初始水动力较强并逐渐减弱;下游以砂组分为主,粒度频率曲线具有风成沉积特征,指示干旱化趋势,粒径变化幅度和频率大,表明受人类活动影响强烈;2)终端湖剖面沉积物粒度显示了全新世以来复杂的干湿变化,在约3 cal.ka B.P.之后均出现粒径增大波动增大的现象,指示不同程度的干旱化,在1~3 cal.ka B.P.之间出现人类活动的影响并逐渐加剧;3)基于流域表土粒度指标现代过程分析表明祁连山内流河流域终端湖剖面粒度指标可以在一定程度上指示流域干湿变化并识别人类活动强度,区域环境在长期干旱化的背景下受到人类活动的强烈干扰。
Abstract:Four typical closed basins of Qilian Mountains, Shiyang River basin, Fengle River basin, Shiyou River basin and Buha River basin are selected as the study areas. Surface soil and 30 cm underground soil samples along both sides of the river are collected to analyze the grain size characteristics of these regions. Median grain size and average grain size of the soil samples, combined with the terminal lakes records of these basins (including median grain size, average grain size, and grain size composition) are used to analyze the characteristics of the environmental changes in these four river basins during the Holocene. The results show:
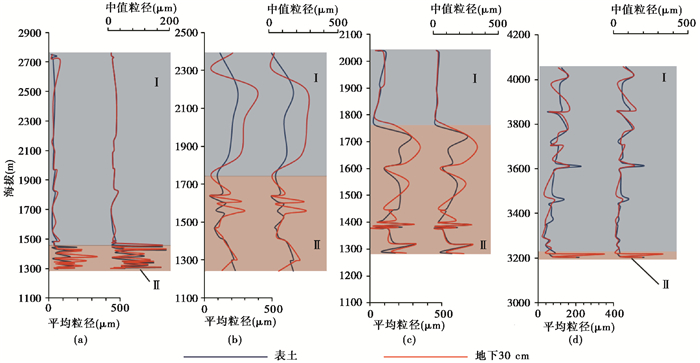
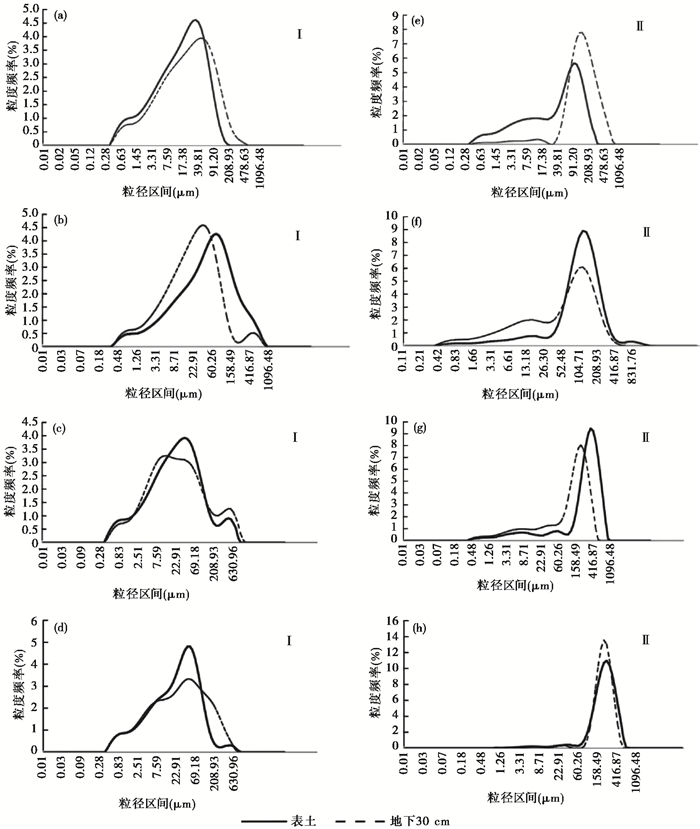
(1) Soil grain size in these basins has obvious spatial differentiation along with changing altitudes, which roughly divides the basin into two parts of the upstream and downstream depending on the position of the river flowing out of the mountain. Except for the Shiyou river basin, silt component takes advantage in the upstream, and the grain size frequency curve shows the double peak characteristics of river deposition with low fluctuation. However, sand component prevails in the downstream parts, the grain size frequency curve has the characteristics of aeolian deposition with more and higher fluctuation, indicating strong influence by human activities;
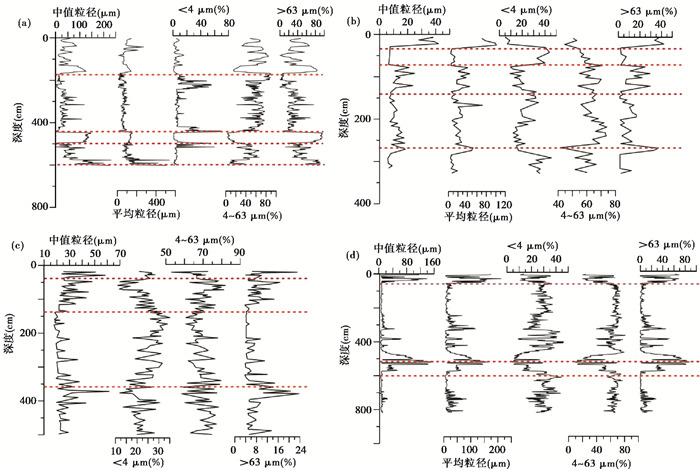
(2) The grain size records from terminal lakes show complex dry-wet changes during the Holocene. However, a consistent change that the mean grain size and fluctuation both increased since about 3000 years ago in these records is confirmed. The increase of grain size indicates that the terminal lake area has experienced different aridity process, and the fluctuation anomaly indicates that the deposition process may be affected by modern human activities which gradually increases between 1 cal.ka B.P. and 3 cal.ka B.P.;
(3) The modern process analysis shows that the grain size of terminal lake sections in the closed basins over Qilian mountains can indicate the change of dry and wet climate in the past and identify the intensity of human activities, and the regional environment is strongly disturbed by human activities under the background of long-term drought. In the future, the process of aridity will continue, and the extent and intensity of human activities will be further enhanced.
-
Key words:
- Qilian Mountains /
- interior river /
- sediment /
- grain size /
- environmental change
-

-
-
[1] 肖晨曦, 李志忠.粒度分析及其在沉积学中应用研究[J].新疆师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 25(3):118-123. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xjsfdxxb200603035
Xiao Chenxi, Li Zhizhong. The research summary of grain size analysis and its application in the sedimentation[J]. Journal of Xinjiang Normal University(Natural Sciences Edition), 2006, 25(3):118-123. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xjsfdxxb200603035
[2] 张志高, 张宏亮, 刘青利, 等.河西走廊不同类型地表沉积物粒度研究[J].人民黄河, 2015, 37(7):95-100. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=rmhh201507024
Zhang Zhigao, Zhang Hongliang, Liu Qingli, et al. Particle size analysis of surface sediments and its significance in Hexi Corridor of China[J]. Yellow River, 2015, 37(7):95-100. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=rmhh201507024
[3] 陈敬安, 万国江, 张峰, 等.不同时间尺度下的湖泊沉积物环境记录——以沉积物粒度为例[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2003, 33(6):563-568. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd200306010
Chen Jing'an, Wan Guojiang, Zhang Feng, et al. Lake sediments under different scales-Taking the granularity of sediment as an example[J]. Science China:Earth Sciences, 2003, 33(6):563-568. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd200306010
[4] 于秋莲, 张展适, 杜后发.粒度分析在古环境中的应用[J].能源研究与管理, 2010, (2):49-52. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-7676.2010.02.014.
Yu Qiulian, Zhang Zhanshi, Du Houfa. The application of granularity analysis in paleoenvironment[J]. Energy Research and Management, 2010, (2):49-52. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-7676.2010.02.014.
[5] 李腾飞, 李金凤, 鲁瑞洁, 等.青海湖东岸沙地风成沉积物粒度敏感组分及其古气候意义[J].中国沙漠, 2017, 37(5):60-66. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgsm201705008
Li Tengfei, Li Jinfeng, Lu Ruijie, et al. Extraction of grain-size components with environmentlly sensitivity of aeolian sediments in eastern shore of Qinghai Lake and their palaeoclimatic implications[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2017, 37(5):60-66. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgsm201705008
[6] 刘静玲, 包坤, 李毅, 等.滦河流域水库对河流表层沉积物粒度空间分布影响的研究[J].农业环境科学学报, 2015, 34(5):955-963. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=nyhjbh201505019
Liu Jingling, Bao Kun, Li Yi, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics in grain size of river surface sediments under the influence of reservoirs in the Luanhe River Basin[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2015, 34(5):955-963. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=nyhjbh201505019
[7] 王勇, 韩广, 杨林, 等.河岸沙丘粒度分布特征[J].干旱区研究, 2016, 33(1):210-214. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ghqyj201601028
Wang Yong, Han Guang, Yang Lin, et al. Grain size distribution of sand dunes at river banks[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2016, 33(1):210-214. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ghqyj201601028
[8] 蒲佳, 马龙, 吉力力·阿不都外力, 等.新疆博斯腾湖表层沉积物粒度空间分布特征[J].干旱区研究, 2018, 35(2):477-485. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ghqyj201802028
Pu Jia, Ma Long, Jilili Abudouwaili, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics of surface sediments in Bosten Lake, Xinjiang[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2018, 35(2):477-485. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ghqyj201802028
[9] 叶远达, 徐海, 蓝江湖, 等.云南程海沉积物粒度对水深的指示意义[J].第四纪研究, 2018, 38(4):1007-1016. http://www.dsjyj.com.cn/CN/abstract/abstract11515.shtml
Ye Yuanda, Xu Hai, Lan Jianghu, et al. Sedimentary grain size at Lake Chenghai, Yunnan Province:Indicator for water depth[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2018, 38(4):1007-1016. http://www.dsjyj.com.cn/CN/abstract/abstract11515.shtml
[10] 付超, 于兴河, 李顺利, 等.气候变化与粗砾冲积扇的改造过程的响应与其影响因素分析——以岱海湖园子沟-半滩子冲积扇为例[J].第四纪研究, 2019, 39(6):1393-1403. http://www.dsjyj.com.cn/CN/abstract/abstract11696.shtml
Fu Chao, Yu Xinghe, Li Shunli, et al. Reworking process of climatic change in the coarse-grained alluvial fan and its impact factors analysis:A case study of Yuanzigou and Bantanzi, Daihai Lake, North China[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2019, 39(6):1393-1403. http://www.dsjyj.com.cn/CN/abstract/abstract11696.shtml
[11] 李育, 王岳, 张成琦, 等.干旱区内陆河流域中游地区全新世沉积相变与环境变化——以石羊河流域为例[J].地理研究, 2014, 33(10):1866-1880. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dlyj201410008
Li Yu, Wang Yue, Zhang Chengqi, et al. Changes of sedimentary facies and Holocene environments in the middle reaches of inland rivers, arid China:A case study of the Shiyang River[J]. Geographical Research, 2014, 33(10):1866-1880. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dlyj201410008
[12] 隆浩, 王乃昂, 李育, 等.猪野泽记录的季风边缘区全新世中期气候环境演化历史[J].第四纪研究, 2007, 27(3):371-381. http://www.dsjyj.com.cn/CN/abstract/abstract8740.shtml
Long Hao, Wang Nai'ang, Li Yu, et al. Mid-Holocene climate variations from lake records of the East Asian monsoon margin a multi-proxy and geomorphological study[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2007, 27(3):371-381. http://www.dsjyj.com.cn/CN/abstract/abstract8740.shtml
[13] 袁杰, 曹广超, 鄂崇毅, 等.环青海湖表层土壤沉积物粒度分布特征及其指示意义[J].水土保持研究, 2015, 22(3):150-154. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=stbcyj201503028
Yuan Jie, Cao Guangchao, E Chongyi, et al. Grain size distributions of the surface soil deposit around Qinghai Lake and its implications[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2015, 22(3):150-154. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=stbcyj201503028
[14] 胡刚, 王乃昂, 罗建育, 等.花海湖泊古风成砂的粒度特征及其环境意义[J].沉积学报, 2001, 19(4):642-647. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb200104027
Hu Gang, Wang Nai'ang, Luo Jianyu, et al. The grain size characteristics of aeolian sand its environmental significance[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2001, 19(4):642-647. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb200104027
[15] Li Yu, Wang Nai'ang, Li Zhuolun, et al. Climatic and environmental change in Yanchi Lake, Northwest China since the Late Glacial:A comprehensive analysis of lake sediments[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2013, 23(5):932-946. doi: 10.1007/s11442-013-1053-3
[16] Gong S L, Zhang X Y, Zhao T L, et al. A simulated climatology of Asian dust aerosol and its trans-Pacific transport. Part Ⅱ:Interannual variability and climate connections[J]. Journal of Climate, 2006, 19(1):104-122. doi: 10.1175/JCLI3606.1
[17] Li Y, Wang N, Cheng H, et al. Holocene environmental change in the marginal area of the Asian monsoon:A record from Zhuye Lake, NW China[J]. Boreas, 2009, 38(2):349-361. doi: 10.1111/j.1502-3885.2008.00063.x
[18] Chen F, Zhu Y, Li J, et al. Abrupt Holocene changes of the Asian monsoon at millennial-and centennial-scales:Evidence from lake sediment document in Minqin Basin, NW China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2001, 46(23):1942-1947. doi: 10.1007/BF02901902
[19] Zhang H C, Peng J L, Ma Y Z, et al. Late Quaternary palaeolake levels in Tengger Desert, NW China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2004, 211(1-2):45-58. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2004.04.006
[20] Yang X, Rost K T, Lehmkuhl F, et al. The evolution of dry lands in Northern China and in the Republic of Mongolia since the Last Glacial Maximum[J]. Quaternary International, 2004, 118/119:69-85. doi10.1016/S1040-6182(03)00131-9. doi: 10.1016/S1040-6182(03)00131-9
[21] Zhao S Q. A new scheme for comprehensive physical regionalization in China[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1983, 50(1):1-10.
[22] Shao Y, Dong C H. A review on East Asian dust storm climate, modelling and monitoring[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2006, 52(1-4):1-22. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2006.02.011
[23] Li Y, Wang N, Morrill C, et al. Millennial-scale erosion rates in three inland drainage basins and their controlling factors since the Last Deglaciation, arid China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2012, 365-366:263-275. doi:10.1016/j.gloplacha.2006.02.011.
[24] 罗晓玲, 王润元, 齐月.石羊河流域干旱特征及预测方法探讨[J].江西农业学报, 2017, 29(12):107-114. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jxnyxb201712022
Luo Xiaoling, Wang Runyuan, Qi Yue. Study on drought characteristics and prediction method in Shiyang River basin[J]. Acta Agriculture Jiangxi, 2017, 29(12):107-114. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jxnyxb201712022
[25] 郑国璋, 岳乐平, 何军锋, 等.疏勒河下游安西古沼泽全新世沉积物粒度特征及其古气候环境意义[J].沉积学报, 2006, 24(5):733-739. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb200605015
Zheng Guozhang, Yue Leping, He Junfeng, et al. Grain-size characteristics of the sediments at palaeoswamp in Anxi County in downstream of Shulehe River during holocene and its paleoclimatic significance[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2006, 24(5):733-739. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb200605015
[26] 丁宏伟, 魏余广, 李爱军, 等.疏勒河出山径流量变化特征及趋势分析[J].干旱区研究, 2001, 18(3):48-53. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ghqyj200103010
Ding Hongwei, Wei Yugiang, Li Aijun, et al. The change characteristics and the trend prediction of streamflow at the debouchure of Shulehe River[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2001, 18(3):48-53. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ghqyj200103010
[27] 丁宏伟, 赵成, 黄晓辉.疏勒河流域的生态环境与沙漠化[J].干旱区研究, 2001, 18(2):6-11. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ghqyj200102002
Ding Hongwei, Zhao Cheng, Huang Xiaohui. Ecological environment and desertification in Shulehe River Basin[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2001, 18(2):6-11. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ghqyj200102002
[28] 郑炳林, 史志林, 郝勇.黑河流域历史时期环境演变研究回顾与展望[J].敦煌学辑刊, 2017, (1):137-150. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-6252.2017.01.015.
Zheng Binglin, Shi Zhilin, Hao Yong. Retrospect and prospect of research on environmental evolution in the historical period of the Heihe River basin[J]. Journal of Dunhuang Studies, 2017, (1):137-150. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-6252.2017.01.015.
[29] 程国栋, 肖洪浪.中国内陆河水资源高效利用与流域生态恢复——黑河流域水-生态-经济管理试验示范[C].北京: 全国水土保持生态修复研讨会, 2004: 171-174.
Cheng Guodong, Xiao Honglang. Efficient Utilization of Inland River Water Resources and Ecological Restoration of Watersheds in China: Experimental Demonstration of Water-ecological-economic Management in the Heihe River Basin[C]. Beijing: National Soil and Water Conservation Ecological Rehabilitation Seminar, 2004: 171-174.
[30] 许健.黑河下游木能诺尔湖泊沉积记录的环境演变信息研究[D].上海: 华东师范大学硕士学位论文, 2006: 1-49.
Xu Jian. Environment Changed Information Reseach Which Have Been Recorded By Muneng Nur Sediment, Lower Stream of Heihe River[D]. Shanghai: The Master's Thesis of East China Normal University, 2006: 1-49.
[31] 龙银平, 张耀南, 赵国辉, 等. SWAT模型水文过程模拟的数据不确定性分析——以青海湖布哈河流域为例[J].冰川冻土, 2012, 34(3):660-667. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=bcdt201203021
Long Yinping, Zhang Yaonan, Zhao Guohui, et al. The uncertainty in meteorological and hydrological processes modeled by using SWAT model-A case study in the Buhachu River Basin[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2012, 34(3):660-667. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=bcdt201203021
[32] 彭红明, 许伟林, 何青, 等.布哈河流域中上游地区水文地球化学与同位素特征[J].干旱区研究, 2015, 32(5):1032-1038. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ghqyj201505028
Peng Hongming, Xu Weilin, He Qing, et al. Hydrogeochemistry and isotope features in the middle and upper reaches of Buha River Basin[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2015, 32(5):1032-1038. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ghqyj201505028
[33] 胡菊芳, 沙占江, 马玉军, 等.青海湖布哈河口沉积物粒度特征及其环境意义[J].干旱区研究, 2017, 34(2):445-451. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ghqyj201702029
Hu Jufang, Sha Zhanjiang, Ma Yujun, et al. Characteristics of grain size and their environmental significance of sediments at the Buha estuary of the Qinghai Lake[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2017, 34(2):445-451. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ghqyj201702029
[34] 李育, 王乃昂, 李卓仑, 等.石羊河流域全新世孢粉记录及其对气候系统响应争论的启示[J].科学通报, 2011, 56(2):161-173. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201102010
Li Yu, Wang Nai'ang, Li Zhuolun, et al. The Holocene sporopollen record in the Shiyang River basin and its implications for the climate system response[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2011, 56(2):161-173. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201102010
[35] Li Yu, Zhang Chengqi, Li Pengcheng, et al. Basin-wide sediment grain-size numerical analysis and paleo-climate interpretation in the Shiyang River drainage basin[J]. Geographical Analysis, 2017, 49(3):309-327. doi: 10.1111/gean.12123
[36] 刘兴起, 王苏民, 沈吉.青海湖QH-2000钻孔沉积物粒度组成的古气候古环境意义[J].湖泊科学, 2003, 15(2):112-117. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hpkx200302003
Liu Xingqi, Wang Sumin, Shen Ji. The grain-size of the core QH-2000 in Qinghai Lake and its implication for paleoclimate and paleoenvironment[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2003, 15(2):112-117. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hpkx200302003
[37] 刘兴起, 沈吉, 王苏民, 等.晚冰期以来青海湖地区气候变迁受西南季风控制的介形类壳体氧同位素证据[J].科学通报, 2006, 51(22):116-120. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb200622018
Liu Xingqi, Shen Ji, Wang Sumin, et al. Oxygen isotopic evidence of ostracods in Qinghai Lake area controlled by southwest monsoon since Late Glaciation[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2006, 51(22):116-120. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb200622018
[38] Li Zhuolun, Wang Nai'ang, Cheng Hongyi, et al. Early-Middle Holocene hydroclimate changes in the Asian monsoon margin of Northwest China inferred from Huahai terminal lake records[J]. Journal of Paleolimnology, 2016, 55(3):289-302. doi: 10.1007/s10933-016-9880-8
[39] 李卓仑, 王乃昂, 李育, 等.河西走廊花海古湖泊早、中全新世湖水盐度变化及其环境意义[J].冰川冻土, 2013, 35(6):131-139. doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0240.2013.0164
Li Zhuolun, Wang Nai'ang, Li Yu, et al. The salinity change and its environmental significance in Huahai Lake, Hexi Corridor, Northwest China during the Early-Middle Holocene[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2013, 35(6):131-139. doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0240.2013.0164
[40] 李卓仑, 张乃梦, 王乃昂, 等.晚冰期以来河西走廊花海古湖泊演化过程及其对气候变化的响应[J].中国沙漠, 2014, 34(2):342-348. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgsm201402006
Li Zhuolun, Zhang Naimeng, Wang Nai'ang, et al. Lake evolution and its response to climate change during the Late Glacial:A record from the Huahai Lake in the Hexi Corridor of Northwest China[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2014, 34(2):342-348. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgsm201402006
[41] 王乃昂, 李卓仑, 李育, 等.河西走廊花海剖面晚冰期以来年代学及沉积特征研究[J].沉积学报, 2011, 29(3):552-560. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb201103016
Wang Nai'ang, Li Zhuolun, Li Yu, et al. The chronology and characteristics of sediments since Late Glacial in Huahai Lake, Hexi Corridor, NW China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2011, 29(3):552-560. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb201103016
[42] Li Zhuolun, Wei Zhiqiao, Dong Shipei, et al. The paleoenvironmental significance of spatial distributions of grain size in groundwater-recharged lakes:A case study in the hinterland of the Badain Jaran Desert, Northwest China[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2018, 43:363-372. doi:10.1002/esp.4248.
[43] 汪海斌, 陈发虎, 张家武.黄土高原西部地区黄土粒度的环境指示意义[J].中国沙漠, 2002, 22(1):21-26. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgsm200201005
Wang Haibin, Chen Fahu, Zhang Jiawu. Environmental significance of grain size of loess-paleosol sequence in western part of Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2002, 22(1):21-26. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgsm200201005
[44] 牛红义, 吴群河, 陈新庚, 等.珠江(广州河段)表层沉积物粒度分布特征[J].生态环境学报, 2007, 16(5):1353-1357. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2007.05.005
Niu Hongyi, Wu Qunhe, Chen Xingeng, et al. Particle size distribution characteristics of surface sediments in the Pearl River(Guangzhou section)[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2007, 16(5):1353-1357. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2007.05.005
[45] 李开封, 穆桂金, 徐立帅, 等.塔里木河干流古河道表层沉积物粒度特征及其意义[J].水土保持通报, 2012, 32(1):161-164. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=stbctb201201034
Li Kaifeng, Mu Guijin, Xu Lishuai, et al. Grain size characteristics and significance for surface sediment of paleochannels along main stream of Tarim River[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2012, 32(1):161-164. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=stbctb201201034
[46] 施祺, 王建民, 陈发虎.石羊河古终端湖泊沉积物粒度特征与沉积环境初探[J].兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 1999, 35(1):195-198. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=3482045
Shi Qi, Wang Jianmin, Chen Fahu. Preliminary study on grain size characteristics of sediments and depositional environment of palaeo-terminal lake of Shiyang River[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University(Natural Sciences), 1999, 35(1):195-198. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=3482045
[47] 孙千里, 周杰, 肖举乐.岱海沉积物粒度特征及其古环境意义[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2001, 1(1):93-95. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz200101015
Sun Qianli, Zhou Jie, Xiao Jule. Grain-size characteristics of Lake Daihai sediments and its paleao-environment significance[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2001, 21(1):93-95. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz200101015
[48] 蒲晓强, 陶小晚.南黄海部分典型海域沉积物粒度特征[J].海洋科学, 2009, 33(8):63-66. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hykx200908013
Pu Xiaoqiang, Tao Xiaowan. Grain size characteristics of sediments in some typical sea areas of the South Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Sciences, 2009, 33(8):63-66. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hykx200908013
[49] 古立峰, 刘永, 占玄, 等.湖泊沉积物粒度分析方法在古气候环境研究中的应用[J].化工矿产地质, 2012, 34(3):169-174. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hgkcdz201203009
Gu Lifeng, Liu Yong, Zhan Xuan, et al. The appliction of grain size of lake sediments in reconstructing the paleolimate and paleoenvironment[J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals, 2012, 34(3):169-174. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hgkcdz201203009
[50] 雷国良, 张虎才, 张文翔, 等.柴达木盆地察尔汗古湖贝壳堤剖面粒度特征及其沉积环境[J].沉积学报, 2007, 25(2):274-282. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb200702016
Lei Guoliang, Zhang Hucai, Zhang Wenxiang, et al. Characteristics of grain-size and sedimentation of shellbar section in salt Lake Qarhan, Qaidam Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2007, 25(2):274-282. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb200702016
[51] 郭晓阳, 王维, 王国良, 等.季风边缘区湖泊表层沉积物粒度组分分布特征与影响因素[J].地理研究, 2016, 35(4):677-691. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dlyj201604007
Guo Xiaoyang, Wang Wei, Wang Guoliang, et al. Within-lake distributions of grain-size components and environmental implications based on the survey of lake surface sediment of Chinese monsoon marginal area[J]. Geographical Research, 2016, 35(4):677-691. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dlyj201604007
[52] 陈殿宝, 陈进军, 胡小飞, 等.祁连山北麓梨园河沉积物粒径的变化特征与分析[J].第四纪研究, 2018, 38(6):1336-1347. http://www.dsjyj.com.cn/CN/abstract/abstract11546.shtml
Chen Dianbao, Chen Jinjun, Hu Xiaofei, et al. Characteristics and analysis on the sediment grain size along the Liyuan River on the north piedmont of the Qilian Shan[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2018, 38(6):1336-1347. http://www.dsjyj.com.cn/CN/abstract/abstract11546.shtml
[53] 袁悦, 李成龙, 左书豪, 等.太湖YLL1孔沉积特征揭示的全新世太湖演化史[J].第四纪研究, 2019, 39(5):1133-1147. http://www.dsjyj.com.cn/CN/abstract/abstract11671.shtml
Yuan Yue, Li Chenglong, Zuo Shuhao, et al. Holocene sedimentary characteristics of the core YLL1 of Taihu Lake revealing evolution history of Taihu Lake basin[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2019, 39(5):1133-1147. http://www.dsjyj.com.cn/CN/abstract/abstract11671.shtml
[54] 刘小槺, 鲁瑞洁, 高尚玉, 等末次冰期毛乌素沙地湖泊消涨过程:沉积证据[J].第四纪研究, 2019, 39(4):825-836. http://www.dsjyj.com.cn/CN/abstract/abstract11644.shtml
Liu Xiaokang, Lu Ruijie, Gao Shangyu, et al. The processes of lacustrine evolution during last glacial period inferred from sedimentary records in Mu Us dune field, North China[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2019, 39(4):825-836. http://www.dsjyj.com.cn/CN/abstract/abstract11644.shtml
[55] 张雪蕾, 王万瑞, 王刘明, 等.石羊河流域干旱变化趋势及气候影响因素[J].兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 53(5):598-603, 608. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=lzdxxb201705006
Zhang Xuelei, Wang Wanrui, Wang Liuming, et al. Drought variations and their influential climate factors in the Shiyang River Basin[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University(Natural Sciences), 2017, 53(5):598-603, 608. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=lzdxxb201705006
[56] 刘明春.石羊河流域气候干湿状况分析及评价[J].生态学杂志, 2006, 25(8):880-884. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=stxzz200608002
Liu Mingchun. Analysis and assessment of climatic dry and wet conditions in Shiyang River basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2006, 25(8):880-884. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=stxzz200608002
[57] 傅开道, 杨文辉, 苏斌, 等.流域环境变化的河流沉积物粒度响应——澜沧江案例[J].地理科学进展, 2015, 34(9):1148-1155. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dlkxjz201509007
Fu Kaidao, Yang Wenhui, Su Bin, et al. Response of river sediments to basin environmental changes:A case study of the Lancang River[J]. Progress in Geography, 2015, 34(9):1148-1155. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dlkxjz201509007
[58] 刘静玲, 李毅, 史璇, 等.海河流域典型河流沉积物粒度特征及分布规律[J].水资源保护, 2017, 33(6):9-19. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=szybh201706002
Liu Jingling, Li Yi, Shi Xuan, et al. Grain size characteristics and distribution regularities of typical river sediments in Haihe River Basin[J]. Water Resources Protection, 2017, 33(6):9-19. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=szybh201706002
[59] 吕顺昌, 鄂崇毅, 孙永娟, 等.小柴旦湖表层沉积物粒度分布特征[J].地球环境学报, 2017, 8(5):53-64. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqhjxb201705006
Lü Shunchang, E Chongyi, Sun Yongjuan, et al. Grain size distribution characteristics of surface sediments in Xiao Qaidam Lake[J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 2017, 8(5):53-64. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqhjxb201705006
[60] 肖生春, 肖洪浪.黑河流域水环境演变及其驱动机制研究进展[J].地球科学进展, 2008, 23(7):748-755. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkxjz200807014
Xiao Shengchun, Xiao Honglang. Advances in the study of the water regime process and driving mechanism in the Heihe River basin[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2008, 23(7):748-755. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkxjz200807014
[61] 李小妹, 严平, 吴伟, 等.克里雅河中下游流域地表沉积物的粒度与化学元素空间分布[J].地理科学, 2016, 36(8):1269-1276. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dlkx201608019
Li Xiaomei, Yan Ping, Wu Wei, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics of the grain size and geochemical spatial distribution characteristics of the grain size and geochemical elements of surface sediments in the Keriya River[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2016, 36(8):1269-1276. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dlkx201608019
[62] Bullard J E, Mctainsh G H. Aeolian-fluvial interactions in dryland environments:Examples, concepts, and Australia case study[J]. Progress in Physical Geography, 2003, 27(4):471-501. doi: 10.1191/0309133303pp386ra
[63] 靳立亚, 陈发虎, 朱艳.西北干旱区湖泊沉积记录反映的全新世气候波动周期性变化[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2004, 24(2):101-108. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz200402017
Jin Liya, Chen Fahu, Zhu Yan. Holocene climatic periodicities recorded from lake sediments in the arid-semiarid areas of Northwestern China[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2004, 24(2):101-108. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz200402017
[64] 张龙吴, 张虎才, 常凤琴, 等.云南异龙湖沉积物粒度空间变化特征及其环境指示意义[J].第四纪研究, 2019, 39(5):1159-1170. http://www.dsjyj.com.cn/CN/abstract/abstract11673.shtml
Zhang Longwu, Zhang Hucai, Chang Fenqin, et al. Spatial variation characteristics of sediment size and its environmental indication significance in Lake Yilong, Yunnan Province[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2019, 39(5):1159-1170. http://www.dsjyj.com.cn/CN/abstract/abstract11673.shtml
[65] 赵强, 王乃昂, 程弘毅, 等.青土湖沉积物粒度特征及其古环境意义[J].干旱区地理, 2003, 26(1):1-5. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ghqdl200301001
Zhao Qiang, Wang Nai'ang, Cheng Hongyi, et al. Grain-size characteristics of Qingtu Lake sediments and its paleaoenvironment explanation[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2003, 26(1):1-5. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ghqdl200301001
[66] 王乃昂, 程弘毅, 李育.石羊河与黑河下游湖泊变迁——气候变化和人类活动的影响[C]//中国地理学会百年庆典学术论文摘要集, 2009: 79.
Wang Nai'ang, Cheng Hongyi, Li Yu. Shiyang River and Lake Changes in the Lower Reaches of Heihe River: Impact of Climate Change and Human Activities[C]//Summary of Academic Papers on the Centennial Celebration of the Chinese Geographic Society, 2009: 79.
[67] 胡刚, 王乃昂, 高顺尉, 等.花海湖泊全新世古风成砂的发现及其古环境解释[J].中国沙漠, 2002, 22(2):159-165. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgsm200202011
Hu gang, Wang Nai'ang, Gao Shunwei, et al. Discovery of Holocene aeolian sand in Huhai Lake and its environmental significance[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2002, 22(2):159-165. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgsm200202011
-




 下载:
下载: