| 摘 要: | 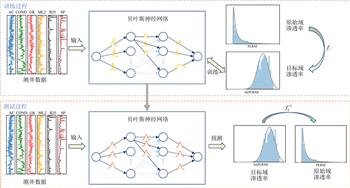
渗透率是储层评价和油气藏开发的关键参数.传统测井方法与常规机器学习方法估算的渗透率都是固定值.但由于测井数据本身存在噪声, 渗透率的预测结果可能受到噪声的影响出现测量性的随机误差(即任意不确定性); 同时, 当测试数据与训练数据存在差异时, 机器学习模型在预测渗透率时可能出现模型参数的不确定性(即认知不确定性).为实现渗透率的准确预测并量化两种不确定性对结果的影响, 本文提出基于数据分布域变换和贝叶斯神经网络同时实现渗透率预测及其不确定性的估计.提出方法主要包括两个部分: 一部分是不同域数据分布的相互转换, 另一部分是基于贝叶斯理论的神经网络渗透率建模预测和不确定性估计.由于贝叶斯神经网络存在数据分布的假设, 当标签的概率分布与网络的分布保持一致时, 贝叶斯神经网络可以更好的学习到数据之间的关系.因此通过寻找一个函数将一个原始域的渗透率标签转换为目标域的与渗透率有关的变量(我们称为目标域渗透率), 使得该变量符合贝叶斯神经网络的分布假设.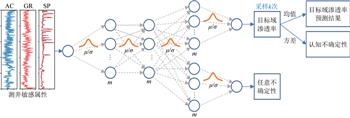
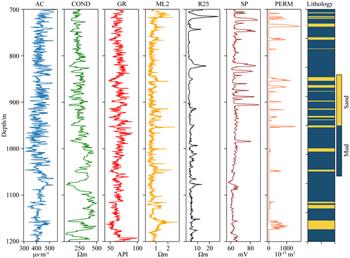
我们使用贝叶斯神经网络预测目标域渗透率以及任意不确定性和认知不确定性.随后, 通过分布域的逆变换, 我们将目标域渗透率还原回原始域渗透率.应用本文方法到某油田的18口井的测井数据中, 使用16口井的数据进行训练, 2口井进行测试.测试井的预测渗透率与真实渗透率基本一致.同时, 任意不确定性的预测结果提供了渗透率预测值受到的测井数据噪声影响的位置.认知不确定的预测结果说明数据量少的位置具有更高的认知不确定性.我们提出的这一流程不仅显示了在储层表征方面的巨大潜力, 同时可以降低测井解释时的风险.
|



