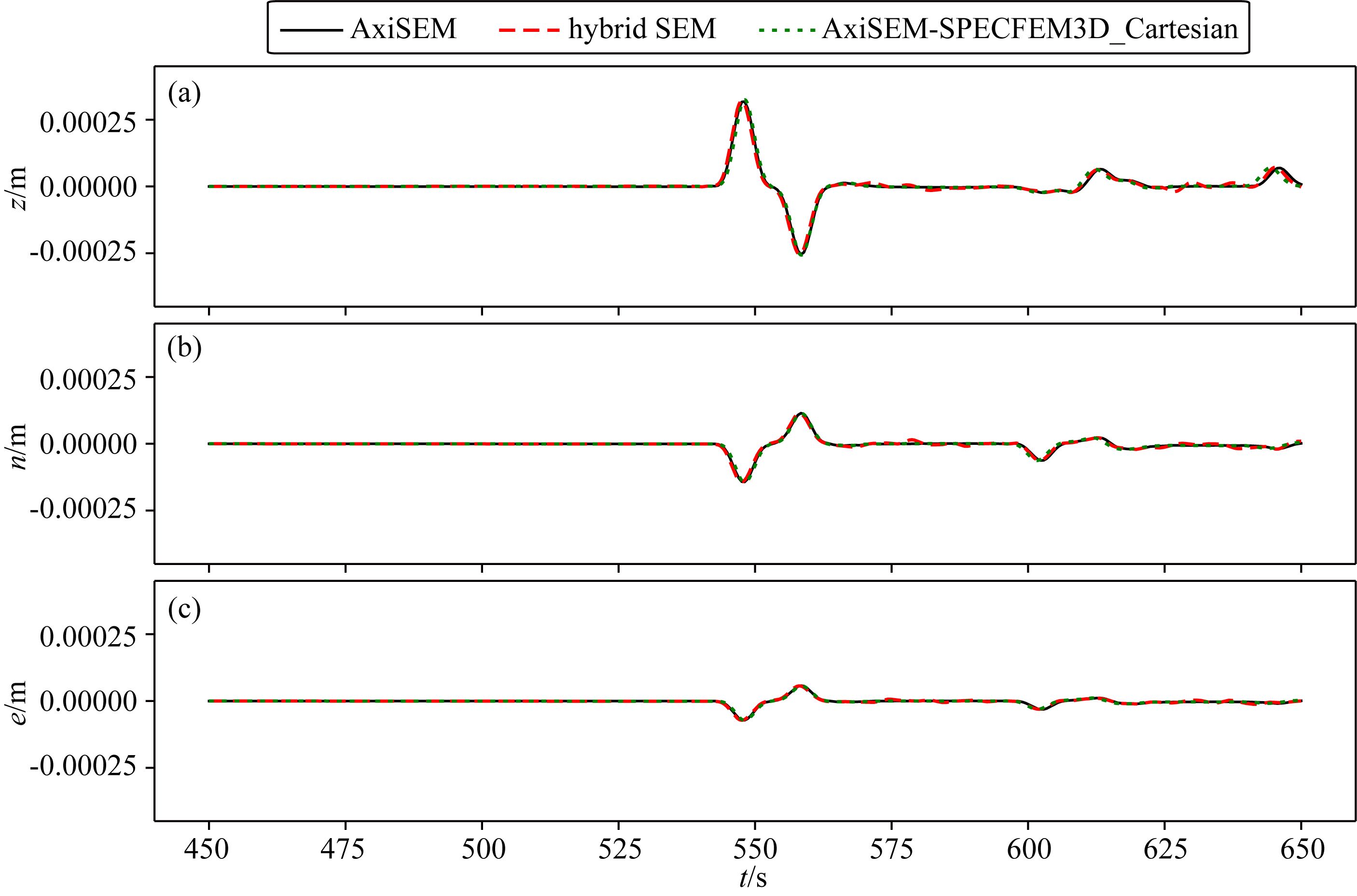
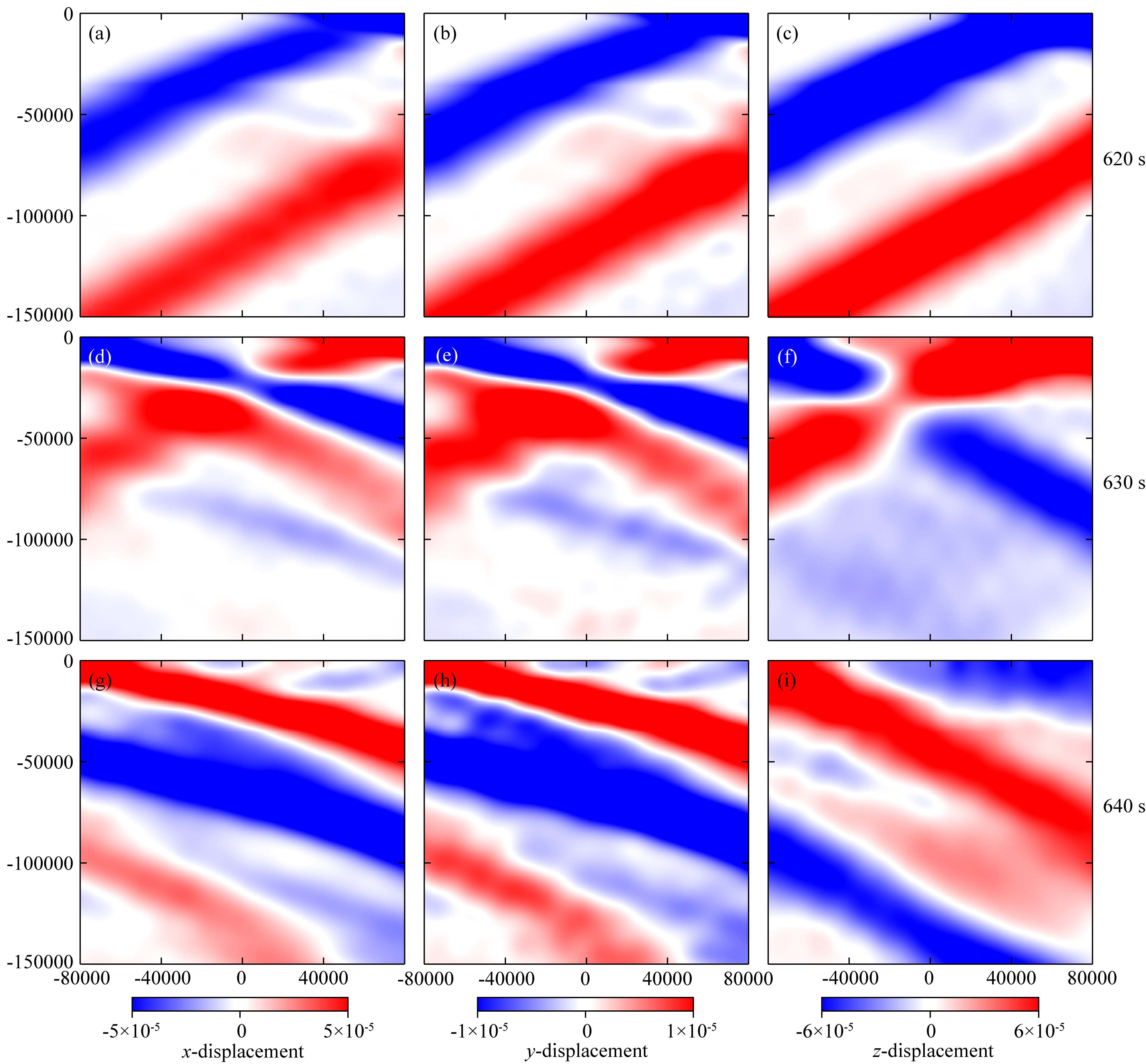
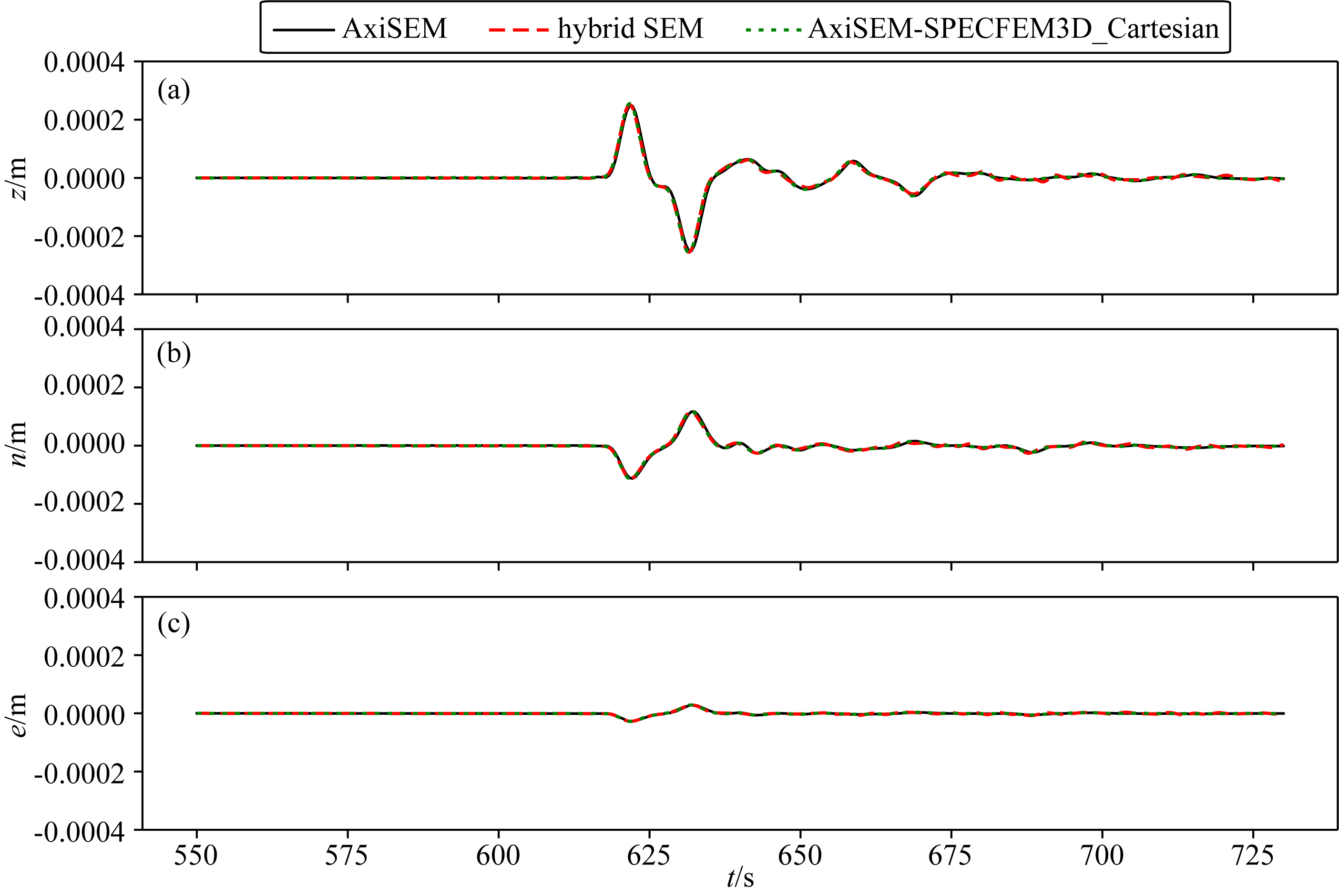
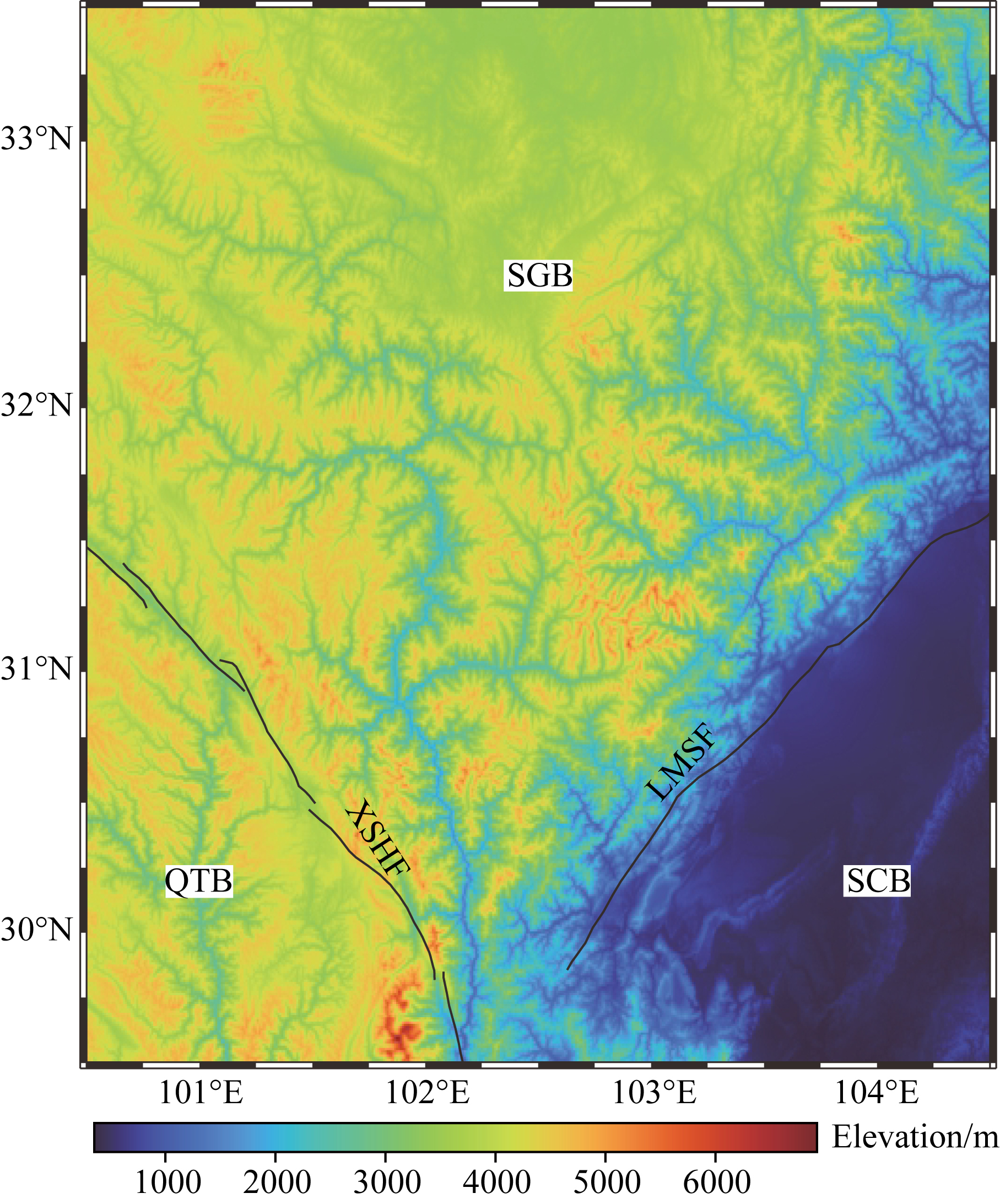
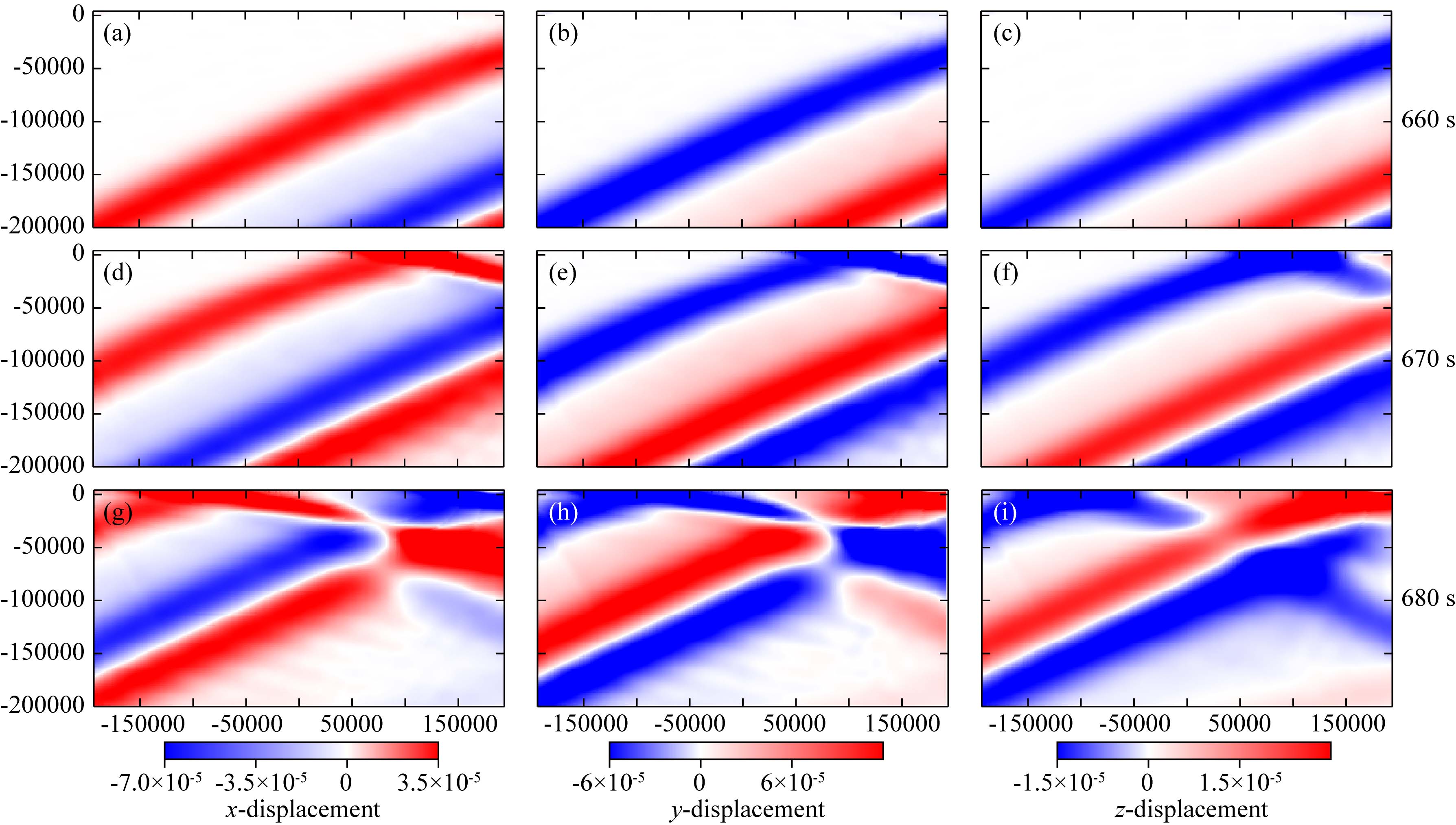
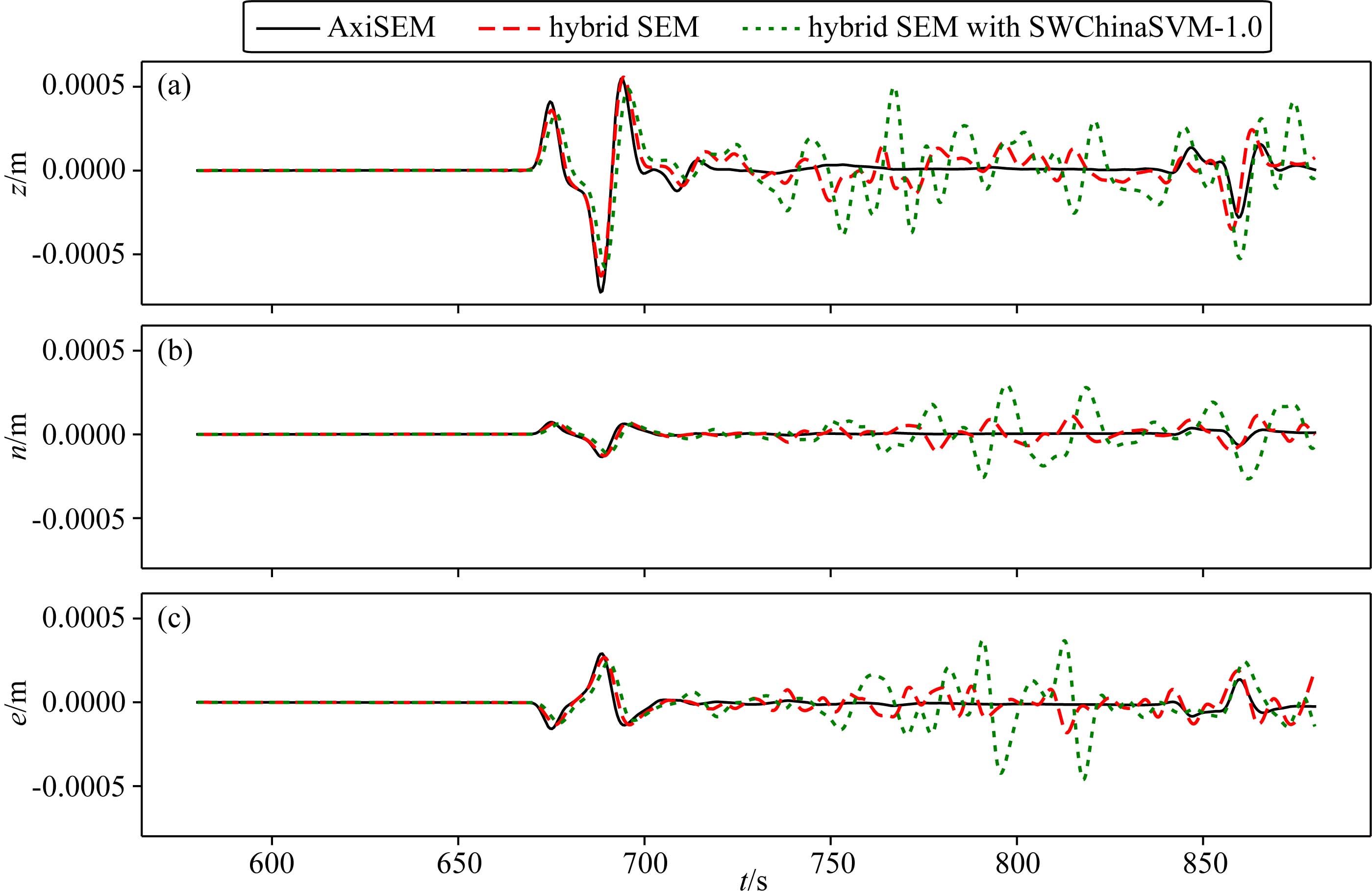
Hybrid method based on element-by-element and axisymmetric spectral element method for teleseismic wavefield simulation
-
摘要:
远震波形成像是研究地球内部结构和动力学过程的重要手段. 然而,由于巨大的计算需求,当前在全球尺度(包含震源-台站)数值模拟高频(频率到2 Hz)地震波传播并不现实. 谱元法是一种高有效性的数值模拟算法,具有高精度和网格剖分灵活的优点,并且已经成功应用于弹性波方程求解中. 但缺点是求解远震问题时计算量和存储量较大. 为了克服上述难题,本文发展了一种基于逐元并行谱元法与轴对称谱元法相结合的混合方法:即在全球尺度层状模型下使用具有快速计算效率的轴对称谱元法模拟远震背景波场,而在研究区域内使用逐元并行谱元法精确计算非均匀介质中远震波场传播. 该方法减少了非均匀介质中远震波场模拟的计算量与存储量,并保持了逐元并行谱元法高精度、低存储量、易并行的优点.数值实验验证了该混合方法的可行性和精确性,并有望进一步应用于实际地震数据远震波形成像研究中.
Abstract:Teleseismic full-waveform tomography is an important tool for studying the internal structure and dynamical processes of the earth. However, the current numerical simulation of high frequency (frequency up to 2 Hz) seismic waves at the global scale is not practical due to its huge amount of calculation. The spectral element method (SEM) is a highly efficient numerical algorithm with high accuracy and flexible grid dissection and has been successfully applied to the solution of elastic wave equation. However, it has large computational and storage requirements for teleseismic wavefield modeling. To overcome these difficulties, we develop a hybrid method based on the element-by-element parallel spectral-element method (EBE-SEM) and the axisymmetric spectral element method (AxiSEM) to simulate the teleseismic background wavefield. For layered media, AxiSEM is used to compute the long-distance propagation of teleseismic waves, and EBE-SEM is applied to accurately simulate the wavefield in heterogeneous medium. This method keeps the advantages of high precision, low storage capacity, and high parallelism, while its computational time and memory of teleseismic wavefield simulation can be reduced significantly. Numerical experiments verify the feasibility and accuracy of our hybrid algorithm, and it can be further applied to teleseismic waveform tomography using real seismic data.
-

-
-
Alterman Z, Karal F C Jr. 1968. Propagation of elastic waves in layered media by finite difference methods. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 58(1): 367-398.
Beller S, Monteiller V, Combe L, et al. 2018a. On the sensitivity of teleseismic full-waveform inversion to earth parametrization, initial model and acquisition design. Geophysical Journal International, 212(2): 1344-1368, doi: 10.1093/gji/ggx480.
Beller S, Monteiller V, Operto S, et al. 2018b. Lithospheric architecture of the South-Western Alps revealed by multiparameter teleseismic full-waveform inversion. Geophysical Journal International, 212(2): 1369-1388, doi: 10.1093/gji/ggx216.
Boore D M. 1970. Love waves in nonuniform wave guides: Finite difference calculations. Journal of Geophysical Research, 75(8): 1512-1527, doi: 10.1029/JB075i008p01512.
Chaljub E, Capdeville Y, Vilotte J P. 2003. Solving elastodynamics in a fluid-solid heterogeneous sphere: a parallel spectral element approximation on non-conforming grids. Journal of Computational Physics, 187(2): 457-491, doi: 10.1016/S0021-9991(03)00119-0.
Chaljub E, Valette B. 2004. Spectral element modelling of three-dimensional wave propagation in a self-gravitating Earth with an arbitrarily stratified outer core. Geophysical Journal International, 158(1): 131-141, doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2004.02267.x.
De Basabe J D, Sen M K. 2010. Stability of the high-order finite elements for acoustic or elastic wave propagation with high-order time stepping. Geophysical Journal International, 181(1): 577-590, doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2010.04536.x.
Dong X P, Yang D H, Niu F L. 2019. Passive adjoint tomography of the crustal and upper mantle beneath eastern Tibet with a W2-norm misfit function. Geophysical Research Letters, 46(22): 12986-12995, doi: 10.1029/2019gl085515.
Dong X P, Yang D H. 2017. Numerical modeling of the 3-D seismic wavefield with the spectral element method in spherical coordinates. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 60(12): 4671-4680, doi: 10.6038/cjg20171211.
Faccioli E, Maggio F, Paolucci R, et al. 1997. 2D and 3D elastic wave propagation by a pseudo-spectral domain decomposition method. Journal of Seismology, 1(3): 237-251, doi: 10.1023/A:1009758820546.
Fichtner A. 2011. Full Seismic Waveform Modelling and Inversion. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer.
Komatitsch D, Barnes C, Tromp J. 2000. Simulation of anisotropic wave propagation based upon a spectral element method. Geophysics, 65(4): 1251-1260, doi: 10.1190/1.1444816.
Komatitsch D, Tromp J. 2002a. Spectral-element simulations of global seismic wave propagation - I. Validation. Geophysical Journal International, 149(2): 390-412, doi: 10.1046/j.1365-246X.2002.01653.x.
Komatitsch D, Tromp J. 2002b. Spectral-element simulations of global seismic wave propagation - II. Three-dimensional models, oceans, rotation and self-gravitation. Geophysical Journal International, 150(1): 303-318, doi: 10.1046/j.1365-246X.2002.01716.x.
Komatitsch D, Vilotte J P, Vai R, et al. 1999. The spectral element method for elastic wave equations - Application to 2-D and 3-D seismic problems. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 45(9): 1139-1164, doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0207(1999 0730)45:9<1139::AID-NME617>3.0.CO;2-T.
Komatitsch D, Vilotte J P. 1998. The spectral element method: An efficient tool to simulate the seismic response of 2D and 3D geological structures. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 88(2): 368-392, doi: 10.1785/BSSA0880020368.
Kosloff D, Kessler D, Filho A Q, et al. 1990. Solution of the equations of dynamic elasticity by a Chebychev spectral method. Geophysics, 55(6): 734-748, doi: 10.1190/1.1442885.
Leng K D, Nissen-Meyer T, van Driel M, et al. 2019. AxiSEM3D: broad-band seismic wavefields in 3-D global earth models with undulating discontinuities. Geophysical Journal International, 217(3): 2125-2146, doi: 10.1093/gji/ggz092.
Li L, Liu T, Hu T Y. 2014. Spectral element method with triangular mesh and its application in seismic modeling. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 57(4): 1224-1234, doi: 10.6038/cjg20140419.
Liu S L, Li X F, Liu Y S, et al. 2014. Dispersion analysis of triangle-based finite element method for acoustic and elastic wave simulations. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 57(8): 2620-2630, doi: 10.6038/cjg20140821.
Liu S L, Li X F, Wang W S, et al. 2014. A mixed-grid finite element method with PML absorbing boundary conditions for seismic wave modelling. Journal of Geophysics and Engineering, 11(5): 055009, doi: 10.1088/1742-2132/11/5/055009.
Liu S L, Yang D H, Dong X P, et al. 2017. Element-by-element parallel spectral-element methods for 3-D teleseismic wave modeling. Solid Earth, 8(5): 969-986, doi: 10.5194/se-8-969-2017.
Liu S L, Yang D H, Meng X L, et al. 2022. A Legendre spectral element method with optimal mass matrix for seismic wave modeling. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 65(12): 4802-4815, doi: 10.6038/cjg2022Q0145.
Liu S L, Yang D H, Xu X W, et al. 2021. Three-dimensional element-by-element parallel spectral-element method for seismic wave modeling. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 64(3): 993-1005, doi: 10.6038/cjg2021O0405.
Liu Y S, Teng J W, Liu S L, et al. 2013. Explicit finite element method with triangle meshes stored by sparse format and its perfectly matched layers absorbing boundary condition. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 56(9): 3085-3099, doi: 10.6038/cjg20130921.
Liu Y, Yao H J, Zhang H J, et al. 2021. The community velocity model V. 1.0 of Southwest China, constructed from joint body- and surface-wave travel-time tomography. Seismological Research Letters, 92(5): 2972-2987,doi: 10.1785/0220200318.
Lysmer J, Drake L A. 1972. A finite element method for seismology. Methods in Computational Physics:Advances in Research and Applications, 11: 181-216.
Ma J, Yang D H, Tong P, et al. 2018. TSOS and TSOS-FK hybrid methods for modelling the propagation of seismic waves. Geophysical Journal International, 214(3): 1665-1682, doi: 10.1093/gji/ggy215.
Meng W J, Yang D H, Dong X P, et al. 2021. A 3D optimized frequency-wavenumber (FK), time-space optimized symplectic (TSOS) hybrid method for teleseismic wave modeling. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 111(6): 3403-3419, doi: 10.1785/0120210040.
Mizutani H, Geller R J, Takeuchi N. 2000. Comparison of accuracy and efficiency of time-domain schemes for calculating synthetic seismograms. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 119(1-2): 75-97, doi: 10.1016/S0031-9201(99)00154-5.
Moczo P, Robertsson J O A, Eisner L. 2007. The finite-difference time-domain method for modeling of seismic wave propagation. Advances in Geophysics, 48: 421-516, doi: 10.1016/S0065-2687(06)48008-0.
Monteiller V, Beller S, Plazolles B, et al. 2021. On the validity of the planar wave approximation to compute synthetic seismograms of teleseismic body waves in a 3-D regional model. Geophysical Journal International, 224(3): 2060-2076, doi: 10.1093/gji/ggaa570.
Monteiller V, Chevrot S, Komatitsch D, et al. 2013. A hybrid method to compute short-period synthetic seismograms of teleseismic body waves in a 3-D regional model. Geophysical Journal International, 192(1): 230-247, doi: 10.1093/gji/ggs006.
Nissen-Meyer T, Fournier A, Dahlen F A. 2007. A two-dimensional spectral-element method for computing spherical-earth seismograms - I. Moment-tensor source. Geophysical Journal International, 168(3): 1067-1092, doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.03121.x.
Nissen-Meyer T, van Driel M, Stähler S C, et al. 2014. AxiSEM: broadband 3-D seismic wavefields in axisymmetric media. Solid Earth, 5(1): 425-445, doi: 10.5194/se-5-425-2014.
Patera A T. 1984. A spectral element method for fluid dynamics: laminar flow in a channel expansion. Journal of Computational Physics, 54(3): 468-488, doi: 10.1016/0021-9991(84)90128-1.
Qiao X J, Wang Q, Du R L. 2004. Characteristics of current crustal deformation of active blocks in the Sichuan-Yunnan region. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 47(5): 805-811.
Seriani G. 1997. A parallel spectral element method for acoustic wave modeling. Journal of Computational Acoustics, 5(1): 53-69, doi: 10.1142/S0218396x97000058.
Su B, Li H L, Liu S L, et al. 2019. Modified symplectic scheme with finite element method for seismic wavefield modeling. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 62(4): 1440-1452, doi: 10.6038/cjg2019M0538.
Tarantola A. 1984. Inversion of seismic reflection data in the acoustic approximation. Geophysics, 49(8): 1259-1266, doi: 10.1190/1.1441754.
Tong P, Chen C W, Komatitsch D, et al. 2014a. High-resolution seismic array imaging based on an SEM-FK hybrid method. Geophysical Journal International, 197(1): 369-395, doi: 10.1093/gji/ggt508.
Tong P, Komatitsch D, Tseng T L, et al. 2014b. A 3-D spectral-element and frequency-wave number hybrid method for high-resolution seismic array imaging. Geophysical Research Letters, 41(20): 7025-7034, doi: 10.1002/2014gl061644.
Tozer B, Sandwell D T, Smith W H F, et al. 2019. Global bathymetry and topography at 15 arc sec: SRTM15+. Earth and Space Science, 6(10): 1847-1864, doi: 10.1029/2019ea000658.
Tromp J, Komatitsch D, Liu Q Y. 2008. Spectral-element and adjoint methods in seismology. Communications in Computational Physics, 3(1): 1-32.
Tromp J, Tape C, Liu Q Y. 2004. Seismic tomography, adjoint methods, time reversal and banana-doughnut kernels. Geophysical Journal International, 160(1): 195-216, doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2004.02453.x.
van Driel M, Krischer L, Stähler S C, et al. 2015. Instaseis: instant global seismograms based on a broadband waveform database. Solid Earth, 6(2): 701-717, doi: 10.5194/se-6-701-2015.
Wang W S, Li X F, Lu M W, et al. 2012. Structure-preserving modeling for seismic wavefields based upon a multisymplectic spectral element method. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 55(10): 3427-3439, doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.10.026.
Wang Y, Chevrot S, Monteiller V, et al. 2016. The deep roots of the western Pyrenees revealed by full waveform inversion of teleseismic P waves. Geology, 44(6): 475-478, doi: 10.1130/G37812.1.
Wu W B, Ni S D, Zhan Z W, et al. 2018. An SEM-DSM three-dimensional hybrid method for modelling teleseismic waves with complicated source-side structures. Geophysical Journal International, 215(1): 133-154, doi: 10.1093/gji/ggy273.
Yang D H, Teng J W, Zhang Z J, et al. 2003. A nearly analytic discrete method for acoustic and elastic wave equations in anisotropic media. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 93(2): 882-890, doi: 10.1785/0120020125.
Zhu L P, Rivera L A. 2002. A note on the dynamic and static displacements from a point source in multilayered media. Geophysical Journal International, 148(3): 619-627, doi: 10.1046/j.1365-246X.2002.01610.x.
董兴朋, 杨顶辉. 2017. 球坐标系下谱元法三维地震波场模拟. 地球物理学报, 60(12): 4671-4680, doi: 10.6038/cjg20171211.
李琳, 刘韬, 胡天跃. 2014. 三角谱元法及其在地震正演模拟中的应用. 地球物理学报, 57(4): 1224-1234, doi: 10.6038/cjg20140419.
刘少林, 李小凡, 刘有山等. 2014. 三角网格有限元法声波与弹性波模拟频散分析. 地球物理学报, 57(8): 2620-2630, doi: 10.6038/cjg20140821.
刘少林, 杨顶辉, 孟雪莉等. 2022. 模拟地震波传播的优化质量矩阵Legendre谱元法. 地球物理学报, 65(12): 4802-4815, doi: 10.6038/cjg2022Q0145.
刘少林, 杨顶辉, 徐锡伟等. 2021. 模拟地震波传播的三维逐元并行谱元法. 地球物理学报, 64(3): 993-1005, doi: 10.6038/cjg2021O0405.
刘有山, 滕吉文, 刘少林等. 2013. 稀疏存储的显式有限元三角网格地震波数值模拟及其PML吸收边界条件. 地球物理学报, 56(9): 3085-3099, doi: 10.6038/cjg20130921.
乔学军, 王琪, 杜瑞林. 2004. 川滇地区活动地块现今地壳形变特征. 地球物理学报, 47(5): 805-811, doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2004.05.011.
苏波, 李怀良, 刘少林等. 2019. 修正辛格式有限元法的地震波场模拟. 地球物理学报, 62(4): 1440-1452, doi: 10.6038/cjg2019M0538.
汪文帅, 李小凡, 鲁明文等. 2012. 基于多辛结构谱元法的保结构地震波场模拟. 地球物理学报, 55(10): 3427-3439, doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.10.026.
-



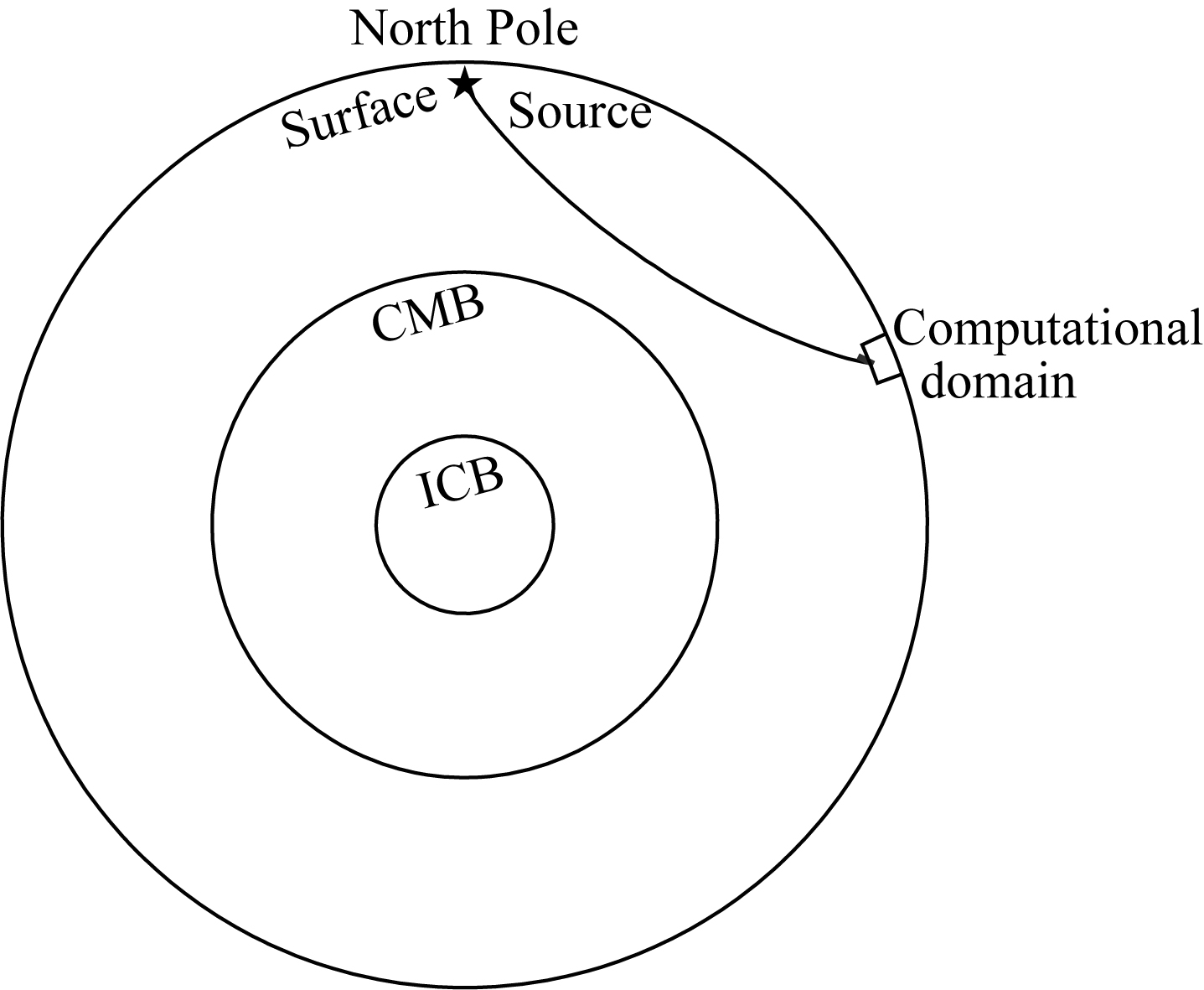
 下载:
下载: