The crustal and uppermost mantle structure of the Qinling-Tongbai-Dabie orogenic belt from integrated geophysical observations
-
摘要:
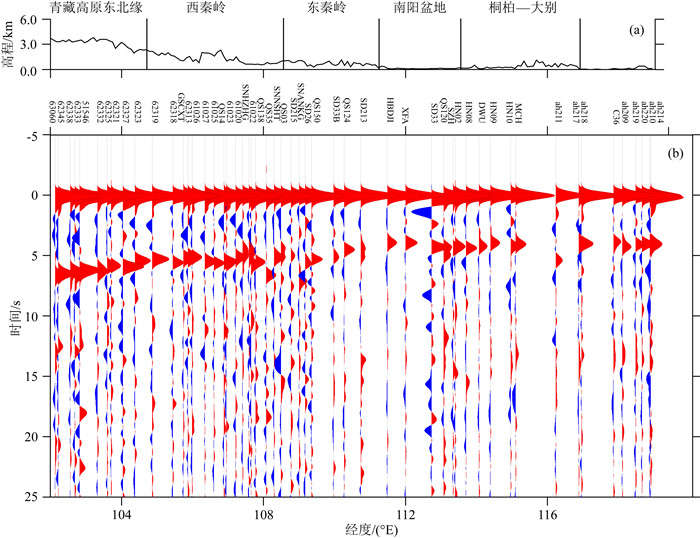
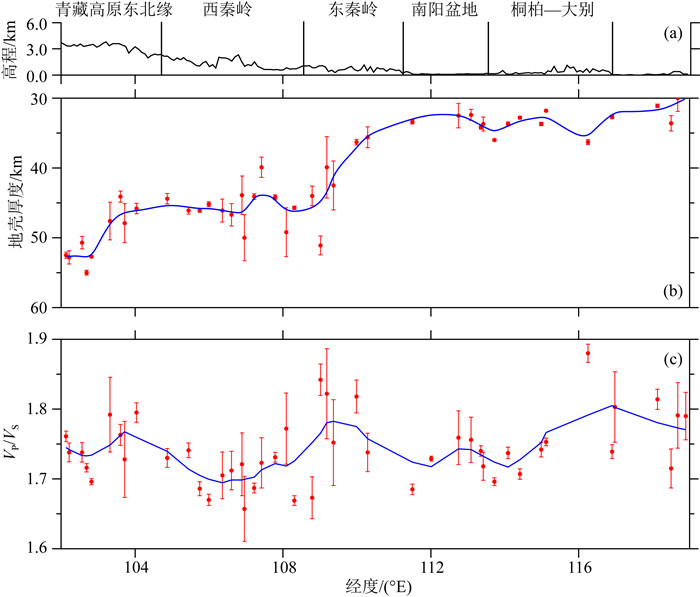
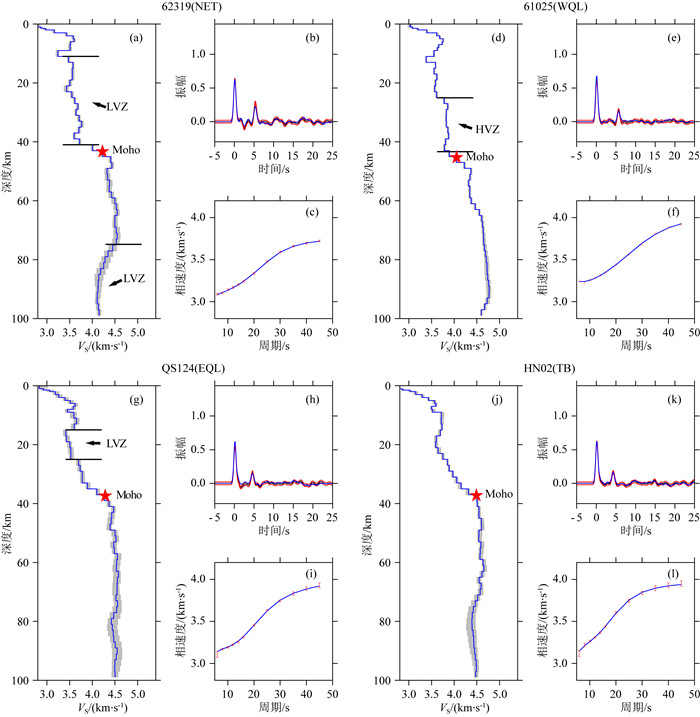
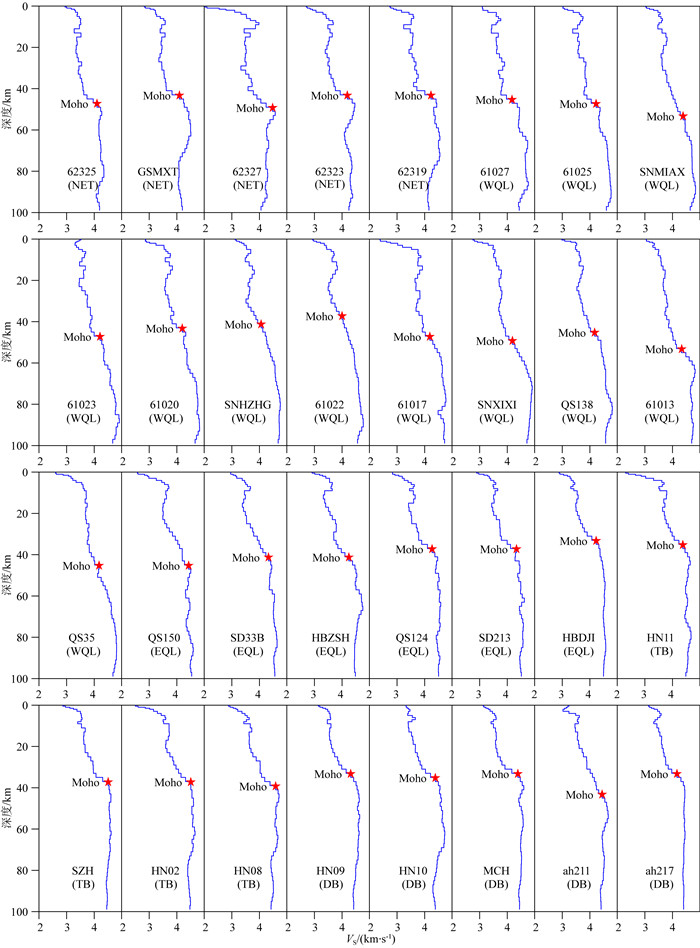
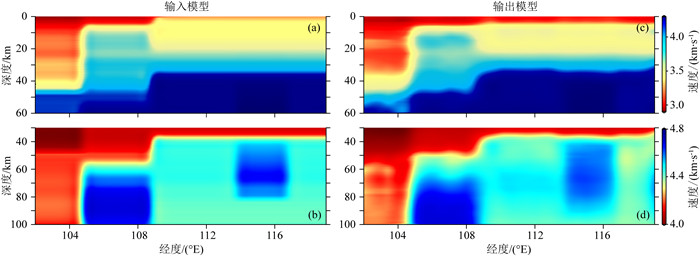
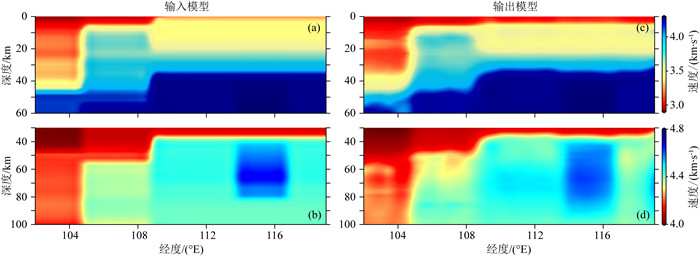
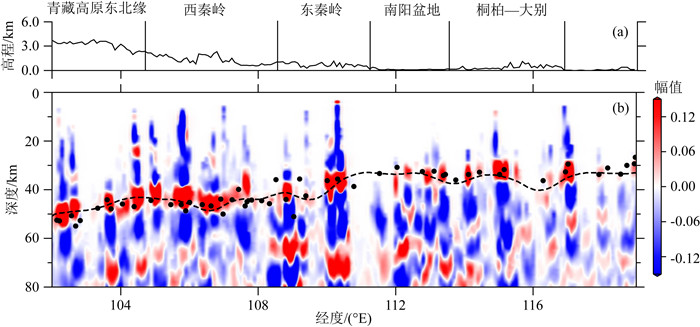
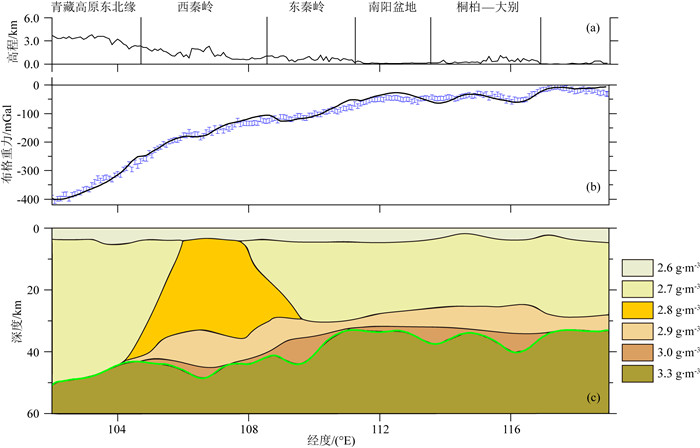
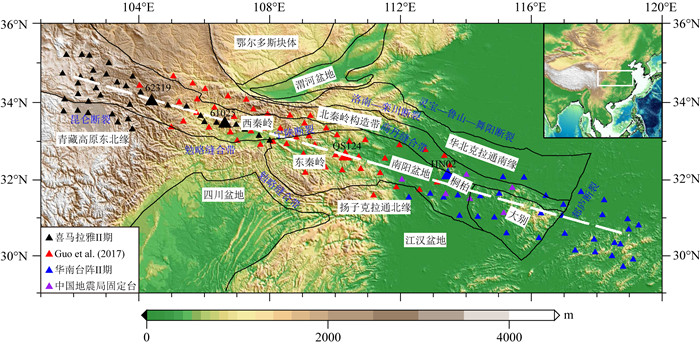
秦岭—桐柏—大别复合造山带(以下称为秦岭大别造山带)属于中国中央造山带的一部分,由华北克拉通与扬子克拉通汇聚形成.对于秦岭大别造山带及其周缘地区的研究,可以为这一大陆碰撞造山带的形成与演化过程提供重要信息.本文整合研究区域的接收函数与背景噪声数据,采用H-κ叠加分析、接收函数与背景噪声联合反演、克希霍夫偏移成像等方法,得到了沿秦岭东西方向具有高分辨率的地壳及上地幔结构.研究结果显示:(1)莫霍面深度由西向东逐步抬升,由剖面西侧最深约55 km上升至剖面东侧最浅约30 km;莫霍面于东西秦岭之间起伏明显;桐柏以及东大别下方莫霍面局部加深.(2)西秦岭中下地壳观测到的高速异常阻隔了青藏高原东北缘地壳低速异常的向东扩张,反映了青藏高原东北缘的中下地壳流没有通过西秦岭继续向东流动.(3)西秦岭岩石圈地幔顶部高速异常延伸至100 km深度(剖面底部),桐柏—西大别岩石圈地幔顶部高速延伸至70 km深度,东大别、东秦岭岩石圈地幔顶部未见较大深度范围的高速异常.
Abstract:The Qinling-Tongbai-Dabie orogenic belt (QD)is the important element of the China Central Orogenic Systems, which was formed by the convergence of the North China Craton and the Yangtze Craton. Due to its key position in the Central Orogenic Systems, the QD is an ideal place to study the orogenic processes between collided continents. To reveal the fine crustal and uppermost mantle structure with high resolution beneath the QD and surrounding areas, this work integrates seismic data available around the QD, which consist of raw seismic data, ambient noise data, and receiver function data. We adopted the Kirchhoff migration method to obtain a preliminary image of the Moho, used the H-κ analysis to calculate the crustal thickness and VP/VS, and utilized a joint inversion of ambient noise and receiver functions to construct a high resolution VS velocity model beneath the QD. Finally, we obtained a profile crossing the QD from west to east with detailed structures in the crust and uppermost mantle. The results reveal that: (1) Moho depth gradually becomes shallower from west to east, from the deepest about 55 km in the west to the shallowest about 30 km in the east of the profile.(2) The high velocity anomaly in the middle and lower crust of the West Qinling blocks the eastward expansion of the low velocity anomaly in the crust of the Northeast Tibetan Plateau, which provides unambiguous evidence that the crustal ductile flow within the Northeast Tibetan Plateau does not continue to flow eastward through the West Qinling.(3) In the uppermost mantle, the West Qinling is underlain by high velocity down to at least 100 km depth, the Tongbai and East Dabie are underlain by high velocity down to 70 km depth, however, the high velocity is not shown beneath East Qinling or East Dabie.
-

-
-
Afonso J C, Fernàndez M, Ranalli G, et al. 2008. Integrated geophysical-petrological modeling of the lithosphere and sublithospheric upper mantle: Methodology and applications. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 9(5): Q05008, doi:10.1029/2007GC001834.
Bao X W, Sun X X, Xu M J, et al. 2015. Two crustal low-velocity channels beneath SE Tibet revealed by joint inversion of Rayleigh wave dispersion and receiver functions. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 415: 16-24. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2015.01.020
Barmin M P, Ritzwoller M H, Levshin A L. 2001. A fast and reliable method for surface wave tomography. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 158(8): 1351-1375. doi: 10.1007/PL00001225
Bensen G D, Ritzwoller M H, Barmin M P, et al. 2007. Processing seismic ambient noise data to obtain reliable broad-band surface wave dispersion measurements. Geophysical Journal International, 169(3): 1239-1260. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2007.03374.x
Brocher T M. 2005. Empirical relations between elastic wavespeeds and density in the earth's crust. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 95(6): 2081-2092. doi: 10.1785/0120050077
Clark M K, Royden L H. 2000. Topographic ooze: Building the eastern margin of Tibet by lower crustal flow. Geology, 28(8): 703-706. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28<703:TOBTEM>2.0.CO;2
Dellinger J A, Gray S H, Murphy G E, et al. 2000. Efficient 2.5-D true-amplitude migration. Geophysics, 65(3): 943-950. doi: 10.1190/1.1444790
Dong Y P, Zhang G W, Neubauer F, et al. 2011. Tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogen, China: Review and synthesis. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 41(3): 213-237. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.03.002
Dong Y P, Santosh M. 2016. Tectonic architecture and multiple orogeny of the Qinling Orogenic Belt, Central China. Gondwana Research, 29(1): 1-40. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.06.009
Enkelmann E, Ratschbacher L, Jonckheere R, et al. 2006. Cenozoic exhumation and deformation of northeastern Tibet and the Qinling: is Tibetan lower crustal flow diverging around the Sichuan Basin? GSA Bulletin, 118(5-6): 651-671. doi: 10.1130/B25805.1
Feng M, An M J, Dong S W. 2017. Tectonic history of the Ordos Block and Qinling Orogen inferred from crustal thickness. Geophysical Journal International, 210(1): 303-320. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggx163
Guo Z, Tang Y C, Chen Y S, et al. 2012. A study on crustal and upper mantle structures in east part of North China Craton using receiver functions. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 55(11): 3591-3600. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/285793498_A_study_on_crustal_and_upper_mantle_structures_in_east_part_of_North_China_Craton_using_receiver_functions
Guo Z, Chen Y J, Ning J Y, et al. 2015. High resolution 3-D crustal structure beneath NE China from joint inversion of ambient noise and receiver functions using NECESSArray data. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 416: 1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2015.01.044
Guo Z, Chen Y J. 2017. Mountain building at northeastern boundary of Tibetan Plateau and craton reworking at Ordos block from joint inversion of ambient noise tomography and receiver functions. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 463: 232-242. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2017.01.026
He R Z, Shang X F, Yu C Q, et al. 2014. A unified map of Moho depth andVp/Vs ratio of continental China by receiver function analysis. Geophysical Journal International, 199(3): 1910-1918. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggu365
Hu F Y, Liu S W, Ducea M N, et al. 2017. The geochemical evolution of the granitoid rocks in the South Qinling Belt: insights from the Dongjiangkou and Zhashui intrusions, central China. Lithos, 278-281: 195-214. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2017.01.021
Jiang M M, Ai Y S, Chen L, et al. 2013. Local modification of the lithosphere beneath the central and western North China craton: 3-D constraints from Rayleigh wave tomography. Gondwana Research, 24(3-4): 849-864. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.06.018
Julià J, Ammon C J, Herrmann R B, et al. 2000. Joint inversion of receiver function and surface wave dispersion observations. Geophysics Journal International, 143(1): 99-112. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-246x.2000.00217.x
Lei J S, Zhao D P. 2016. Teleseismic P-wave tomography and mantle dynamics beneath Eastern Tibet. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 17(5): 1861-1884. doi: 10.1002/2016GC006262
Li S L, Guo Z, Chen Y J, et al. 2018. Lithospheric structure of the northern Ordos from ambient noise and teleseismic surface wave tomography. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 123(8): 6940-6957. https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1029/2017JB015256
Ligorría J P, Ammon C J. 1999. Iterative deconvolution and receiver-function estimation. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 89(5): 1395-1400. doi: 10.1785/BSSA0890051395
Liu Q Y, Kind R, Chen J H, et al. 2005. The break-slip structure and low-speed body in crust at the boundary of crust-mantle in Dabie orogen. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences (in Chinese), 35(4): 304-313. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-ed200507003
Luo Y H, Xu Y X, Yang Y J. 2012. Crustal structure beneath the Dabie orogenic belt from ambient noise tomography. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 313-314: 12-22. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2011.11.004
Luo Y H, Zhao K F, Tang C C, et al. 2018. Seismic evidence for multiple-stage exhumation of high/ultrahigh pressure metamorphic rocks in the eastern Dabie orogenic belt. Geophysical Journal International, 2018, 214(2): 1379-1390. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/327539991_Seismic_evidence_for_multiple-stage_exhumation_of_highultrahigh_pressure_metamorphic_rocks_in_the_eastern_Dabie_orogenic_belt
Meng Q R, Zhang G W. 1999. Timing of collision of the North and South China blocks: Controversy and reconciliation. Geology, 27(2): 123-126. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1999)027<0123:TOCOTN>2.3.CO;2
Meng Q R, Zhang G W. 2000. Geologic framework and tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogen, central China. Tectonophysics, 323(3-4): 183-196. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(00)00106-2
Meng Q R. 2017. Origin of the Qinling mountains. Scientia Sinica Terrae (in Chinese), 47(4): 412-420. doi: 10.1360/N072016-00422
Shen W S, Ritzwoller M H, Kang D, et al. 2016. A seismic reference model for the crust and uppermost mantle beneath China from surface wave dispersion. Geophysical Journal International, 2016, 206(2): 954-79. http://smartsearch.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=d93a777f91c486d08716a41ff6618b28
Song P H, Teng J W, Zhang X M, et al. 2018. Flyover crustal structures beneath the Qinling orogenic belt and its tectonic implications. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 123(8): 6703-6718. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2017JB015401
Wang C Y, Ding Z F, Song J L, et al. 1997a. Shear wave velocity structure in Dabieshan orogenic belt. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (Acta Geophysica Sinica) (in Chinese), 40(3): 337-346. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX199703005.htm
Wang C Y, Zhang X K, Ding Z F, et al. 1997b. Finite-difference tomography of upper crustal structure in Dabieshan orogenic belt. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (Acta Geophysica Sinica) (in Chinese), 40(4): 495-502. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX199704006.htm
Wang C Y, Sandvol E, Zhu L, et al. 2014. Lateral variation of crustal structure in the Ordos block and surrounding regions, North China, and its tectonic implications. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 387: 198-211. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2013.11.033
Wang X X, Wang T, Zhang C L. 2013. Neoproterozoic, Paleozoic, and Mesozoic granitoid magmatism in the Qinling Orogen, China: Constraints on orogenic process. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 72: 129-151. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.11.037
Watanabe T. 1993. Effects of water and melt on seismic velocities and their application to characterization of seismic reflectors. Geophysical Research Letters, 20(24): 2933-2936. doi: 10.1029/93GL03170
Wilson D, Aster R. 2005. Seismic imaging of the crust and upper mantle using regularized joint receiver functions, frequency-wave number filtering, and multimode Kirchhoff migration. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 110(B5): B05305, doi:10.1029/2004JB003430.
Windley B F, Maruyama S, Xiao W J. 2010. Delamination/thinning of sub-continental lithospheric mantle under Eastern China: the role of water and multiple subduction. American Journal of Science, 310(10): 1250-1293. doi: 10.2475/10.2010.03
Wessel P, Smith W H F. 1998. New, improved version of the Generic Mapping Tools released. EOS Trans, AGU, 79: 579. doi: 10.1029/98EO00426
Wu Q J, Li Y H, Zhang R Q, et al. 2007. A feasibility study of cloud base height remote sensing by simulating ground-based thermal infrared brightness temperature measurements. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 50(2): 539-545. doi: 10.1002/cjg2.1064
Wu Y B, Zheng Y F. 2013. Tectonic evolution of a composite collision orogen: An overview on the Qinling-Tongbai-Hong'an-Dabie-Sulu orogenic belt in central China. Gondwana Research, 23(4): 1402-1428. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.09.007
Xu Y X, Zhang S, Griffin W L, et al. 2016. How did the Dabie Orogen collapse? Insights from 3-D magnetotelluric imaging of profile data. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 121(7): 5169-5185. doi: 10.1002/2015JB012717
Yu Y, Chen Y J. 2016. Seismic anisotropy beneath the southern Ordos block and the Qinling-Dabie orogen, China: Eastward Tibetan asthenospheric flow around the southern Ordos. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 455: 1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2016.08.026
Zhai M G, Fan Q C, Zhang H F, et al. 2007. Lower crustal processes leading to Mesozoic lithospheric thinning beneath eastern North China: Underplating, replacement and delamination. Lithos, 96(1-2): 36-54. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2006.09.016
Zhang A Q, Guo Z, Afonso J C, et al. 2020. The deep thermochemical structure of the Dabie orogenic belt from multiobservable probabilistic inversion. Tectonophysics, 787: 228478. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2020.228478
Zhang F X, Wu Q J, Li Y H, et al. 2018. Seismic tomography of Eastern Tibet: implications for the Tibetan Plateau growth. Tectonics, 37(9): 2833-2847. doi: 10.1029/2018TC004977
Zhao X X, Coe R S, Gilder S A, et al. 1996. Palaeomagnetic constraints on the palaeogeography of China: implications for Gondwanaland. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 43(6): 643-672. doi: 10.1080/08120099608728285
Zheng Y, Yang Y J, Ritzwoller M H, et al. 2010. Crustal structure of the northeastern Tibetan plateau, the Ordos block and the Sichuan basin from ambient noise tomography. Earthquake Science, 23(5): 465-476. doi: 10.1007/s11589-010-0745-3
Zhu L P, Kanamori H. 2000. Moho depth variation in southern California from teleseismic receiver functions. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 105(B2): 2969-2980. doi: 10.1029/1999JB900322
Zhu R X, Yang Z Y, Wu H N, et al. 1998. Paleomagnetic constraints on the tectonic history of the major blocks of China during the Phanerozoic. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 41(S2): 1-19. doi: 10.1007/BF02984508
郭震, 唐有彩, 陈永顺等. 2012. 华北克拉通东部地壳和上地幔结构的接收函数研究. 地球物理学报, 55(11): 3591-3600, doi:10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.11.008. http://www.geophy.cn//CN/abstract/abstract9053.shtml
刘启元, Kind R, 陈九辉等. 2005. 大别造山带壳幔界面的断错结构和壳内低速体. 中国科学D辑: 地球科学, 35(4): 304-313. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200504001.htm
孟庆任. 2017. 秦岭的由来. 中国科学: 地球科学, 47(4): 412-420. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201704005.htm
王椿镛, 丁志峰, 宋建立等. 1997a. 大别造山带地壳S波速度结构. 地球物理学报, 40(3): 337-346. http://www.geophy.cn//CN/abstract/abstract3992.shtml
王椿镛, 张先康, 丁志峰等. 1997b. 大别造山带上部地壳结构的有限差分层析成像. 地球物理学报, 40(4): 495-502. http://www.geophy.cn//CN/abstract/abstract3999.shtml
吴庆举, 李永华, 张瑞青等. 2007. 接收函数的克希霍夫2D偏移方法. 地球物理学报, 50(2): 539-545. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2007.02.027 http://www.geophy.cn//CN/abstract/abstract1410.shtml
朱日祥, 杨振宇, 马醒华等. 1998. 中国主要地块显生宙古地磁视极移曲线与地块运动. 中国科学(D辑), 28(S1): 1-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK1998S1000.htm
-



 下载:
下载: