



现代地质 ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (03): 466-482.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.023
收稿日期:2019-03-23
修回日期:2020-01-13
出版日期:2020-07-04
发布日期:2020-07-05
通讯作者:
苏尚国
作者简介:苏尚国,男,教授,博士生导师,1965年出生,矿物学、岩石学、矿床学专业,主要从事岩浆作用与岩浆矿床方面的研究。Email: susg@cugb.edu.cn。基金资助:
WANG Di1,2( ), ZHAO Guochun1, SU Shangguo1(
), ZHAO Guochun1, SU Shangguo1( ), LI Hongxing3
), LI Hongxing3
Received:2019-03-23
Revised:2020-01-13
Online:2020-07-04
Published:2020-07-05
Contact:
SU Shangguo
摘要:
通过岩相学、地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学对位于大兴安岭主脊上的马勒根坝岩体、朝阳沟岩体和大兴安岭东坡区域的野猪沟岩体、布敦化岩体的4个不同花岗岩岩体的岩石类型、主量和微量元素特征、年代学及构造背景进行对比分析,讨论了研究区在晚侏罗世—早白垩世的岩浆活动及地质背景。LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄显示:主脊朝阳沟岩体和东坡布敦化岩体年龄分别为(154±1) Ma和(154.1±1.6) Ma,属于晚侏罗世岩体,主脊马勒根坝岩体和东坡野猪沟岩体年龄分别为(144.62±0.74) Ma和(140.2±2.7) Ma,属于早白垩世岩体。岩相学和地球化学特征显示:主脊岩体为高钾钙碱性-准铝质-过铝质花岗岩岩体,东坡岩体为钙碱性-高钾钙碱性-准铝质-弱过铝质TTG型岩体;主脊比东坡岩体更加亏损Ba、Nb、Sr、P、Ti、Eu元素,为高分异I型花岗岩,东坡岩体为正常的I型花岗岩。结合区域地质资料分析,认为在晚侏罗世—早白垩世伊泽奈崎板块NNW向俯冲和蒙古—鄂霍次克洋闭合共同作用于大兴安岭南段地区,在大兴安岭主脊形成断裂带,导致幔源岩浆上涌底侵下地壳而形成沿断裂带分布的花岗岩体;主脊处于碰撞向伸展环境过渡的时期,东坡区域此时应处于俯冲时期。
中图分类号:
王迪, 赵国春, 苏尚国, 李宏星. 大兴安岭南段晚中生代侵入岩时空分布及主脊与东坡岩体特征对比[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(03): 466-482.
WANG Di, ZHAO Guochun, SU Shangguo, LI Hongxing. Spatial-temporal Distribution of Late Mesozoic Intrusive Rocks in South Daxing’anling Mountains and the Characteristic Contrast of Rocks in the Mid Ridge and the East Slope[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(03): 466-482.
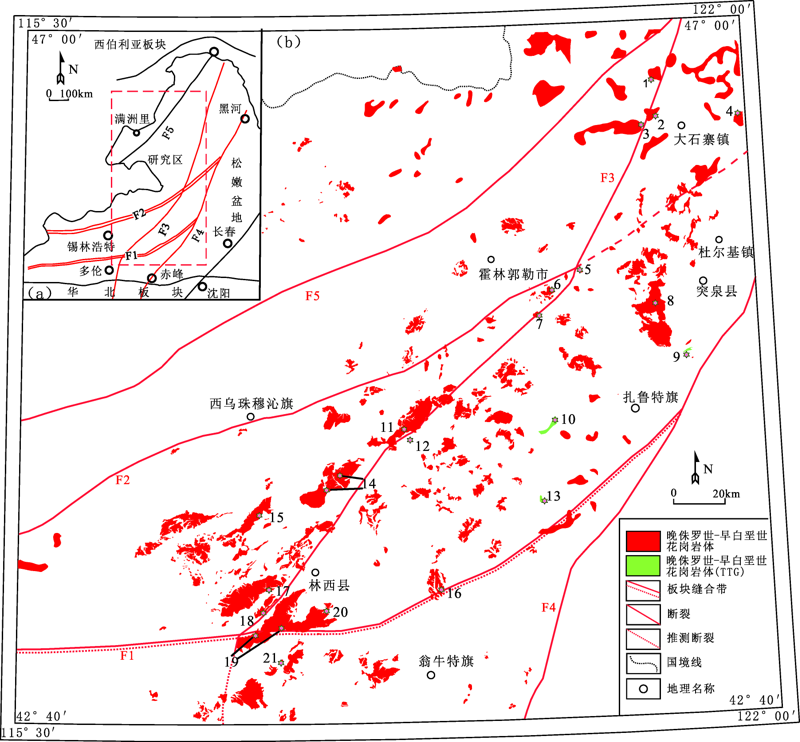
图1 研究区构造位置图(a)及大兴安岭南段地区晚侏罗世—早白垩世侵入岩体时空分布图(b)(据文献[18,19]修改) F1.索伦—西拉木伦河缝合带;F2.二连—贺根山断裂带;F3.大兴安岭主脊断裂带;F4.嫩江—八里罕断裂带;F5.德布尔干断裂;1.索伦岩体;2.乌兰毛多岩体;3.沙布台岩体;4.青山岩体;5.巴尔哲岩体;6.哈马尔乌拉岩体;7.毛伊勒吐岩体;8.杜尔基岩体;9.布敦化岩体;10.敖仑花岩体;11.马勒根坝岩体;12.白音诺尔岩体;13.半砬山钼矿;14.朝阳沟岩体;15.北大山岩体;16.野猪沟岩体;17.黄岗梁岩体;18.大营子岩体;19.经棚岩体;20.林西县小城子岩体;21.小东沟岩体
Fig.1 Tectonic location of the study area (a) and temporal-spatial distribution map of Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous intrusive rocks of south Daxing’anling mountains(b) (modified after references [18-19])
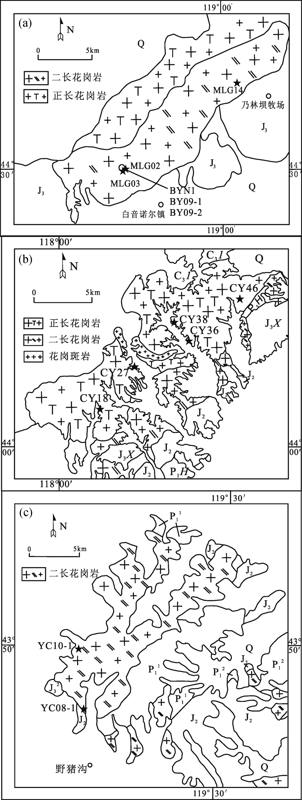
图2 马勒根坝岩体(a)、朝阳沟岩体(b)和野猪沟岩体(c)地质略图(据文献[19]修改) J3.中、酸性火山岩及碎屑岩;Q.第四系; C3l.石炭系林西组;J3x.侏罗系下兴安岭组凝灰岩、流纹岩;J2.侏罗系灰色泥岩、砂岩;P1h.二叠系黄岗梁组粉砂岩、砂岩、凝灰岩;J32.上侏罗统中部凝灰砂岩、凝灰砾岩;J31.上侏罗统下部酸性熔岩、安山岩及中酸性凝灰岩、角砾岩;P12.下二叠统上部凝灰砂岩、粉砂岩;P11.下二叠统下部安山岩、粉砂岩
Fig.2 Sketch geological maps of Malegenba intrusive body(a), Chaoyanggou intrusive body(b) and Yezhugou intrusive body(c)
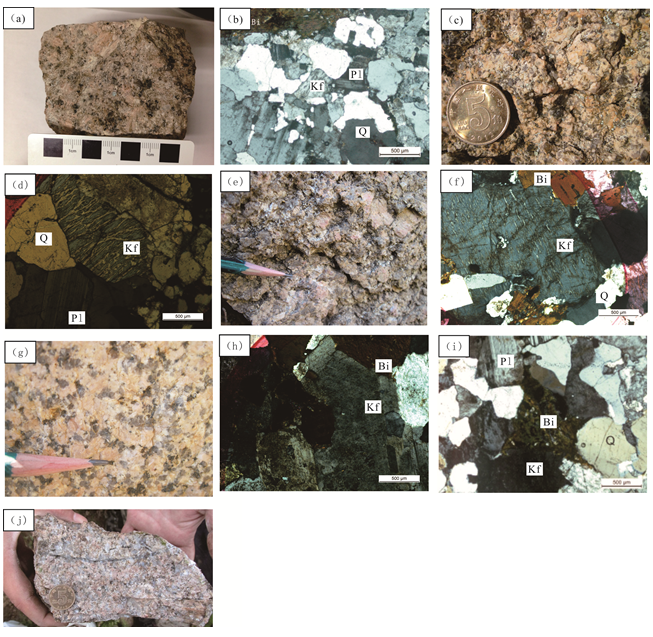

图3 马勒根坝岩体、朝阳沟岩体及野猪沟岩体镜下照片和野外照片 (a)、 (b)斑状黑云母二长花岗岩野外照片、镜下照片;(C)、 (d)正长花岗岩野外照片、镜下照片;(e)、 (f)二长花岗岩野外照片、镜下照片;(g)、(h)含 品洞正长花岗岩野外照片、镜下照片;(i)、(j)二长花岗岩镜下照片、野外照片;Q.石英; Kf.钾长石;Pl.斜长石;Bi.黑云母.2.2 主脊朝阳沟岩体朝阳沟岩体位于林西五十家子以西的朝阳沟一带,为复式岩体,整体呈北北东向展布,出露面积125 km2(图2(b))。主要岩性包括黑云母正长花岗岩、黑云母二长花岗岩和含晶洞正长花岗岩。正长花岗岩风化面灰白色,新鲜面为肉红色,中粗粒结构,块状构造。主要矿物为钾长石,含量40%~50%,自形程度好,大小3~8 mm;斜长石含量约10%,大小2~4 mm,可见斜长石被钾长石包裹的嵌晶结构;石英含量25%,它形粒状,大小1~5 mm;暗色矿物主要为黑云母,含量约为3%,大小0.1~4.0 mm(图3(c)、(d))。二长花岗岩风化面灰白色,新鲜面浅肉红色,似斑状结构,块状构造。斑晶为钾长石,含量约2%,大的斑晶可达1 cm×3 cm;基质为中粗粒花岗结构,主要成分为钾长石、斜长石和石英,钾长石含量约40%,斜长石含量约30%,石英含量约25%;暗色矿物主要为黑云母,含量3%~5%(图3(e)、(f))。岩石中发育细粒闪长质包体。含晶洞正长花岗岩为浅肉红色,中粗粒结构,块状构造。主要矿物为钾长石,含量约45%,自形-半自形,大小2~7 mm;斜长石含量约20%,自形-半自形,大小1~6 mm;石英含量约为30%,它形粒状和自形晶均发育,大小0.5~6.0 mm;暗色矿物主要为黑云母,含量约5%(图3(g)、(h))。岩石中发育晶洞,可见自形晶结构的石英晶体,呈六方椎柱状,大者长度可达6 mm。
Fig.3 Field photographs and micrographs of intrusive rocks from Malegenba, Chaoy anggou and Y ezhugou
| 岩体 名称 | 岩性 | 样品号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 马勒根 坝岩体 | 斑状黑云母 二长花岗岩 | MLG02-2 | 75.75 | 0.13 | 12.63 | 0.52 | 1.03 | 0.070 | 0.21 | 0.61 | 4.04 | 4.53 | 0.03 | 0.34 | 99.89 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG03-1 | 75.58 | 0.12 | 12.54 | 0.42 | 1.26 | 0.070 | 0.22 | 0.76 | 4.18 | 4.26 | 0.03 | 0.41 | 99.85 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG14-2 | 73.13 | 0.19 | 13.61 | 0.28 | 1.61 | 0.070 | 0.35 | 1.09 | 4.28 | 4.34 | 0.05 | 0.78 | 99.78 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BYN1* | 75.66 | 0.13 | 11.72 | 0.77 | 0.75 | 0.036 | 0.15 | 0.71 | 3.82 | 4.73 | 0.03 | 1.15 | 99.66 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-1* | 77.44 | 0.11 | 10.69 | 0.94 | 0.55 | 0.037 | 0.11 | 0.79 | 3.85 | 4.34 | 0.02 | 0.75 | 99.63 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-2* | 77.20 | 0.08 | 11.34 | 0.60 | 0.35 | 0.025 | 0.10 | 0.59 | 3.63 | 4.58 | 0.02 | 1.16 | 99.67 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 朝阳沟 岩体 | 含晶洞花岗岩 | CY18-2 | 76.22 | 0.08 | 12.54 | 0.70 | 0.85 | 0.060 | 0.14 | 0.43 | 4.45 | 4.14 | 0.02 | 0.31 | 99.94 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 二长花岗岩 | CY27-2 | 71.53 | 0.34 | 14.01 | 0.49 | 2.08 | 0.100 | 0.68 | 1.63 | 4.49 | 4.04 | 0.10 | 0.28 | 99.77 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 正长花岗岩 | CY36-2 | 74.30 | 0.13 | 13.18 | 0.16 | 1.60 | 0.060 | 0.18 | 0.82 | 4.31 | 4.72 | 0.03 | 0.31 | 99.80 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY38-2 | 71.35 | 0.25 | 14.29 | 0.10 | 2.45 | 0.070 | 0.37 | 1.37 | 4.47 | 4.54 | 0.07 | 0.40 | 99.73 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY46-2 | 74.28 | 0.12 | 13.63 | 0.20 | 1.12 | 0.070 | 0.20 | 0.89 | 4.44 | 4.56 | 0.03 | 0.26 | 99.80 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 野猪沟 岩体 | 二长花岗岩 | YC10-1 | 75.85 | 0.22 | 12.69 | 0.73 | 0.60 | 0.079 | 0.28 | 1.00 | 4.45 | 3.52 | 0.07 | 0.37 | 99.86 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| YC08-1 | 76.58 | 0.19 | 12.34 | 0.88 | 0.36 | 0.103 | 0.27 | 0.31 | 4.55 | 3.36 | 0.05 | 0.61 | 99.58 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 岩体 名称 | 岩性 | 样品号 | A/CNK | DI | AR | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 马勒根 坝岩体 | 斑状黑云母 二长花岗岩 | MLG02-2 | 0.998 | 94.13 | 4.67 | 24.80 | 66.80 | 5.84 | 20.20 | 3.78 | 0.25 | 3.68 | 0.56 | 3.22 | 0.64 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG03-1 | 0.974 | 93.45 | 4.47 | 24.60 | 62.60 | 5.87 | 19.60 | 3.57 | 0.20 | 3.52 | 0.52 | 2.98 | 0.59 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG14-2 | 0.992 | 90.52 | 3.84 | 19.20 | 38.70 | 5.33 | 19.30 | 3.74 | 0.37 | 3.33 | 0.54 | 3.41 | 0.70 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BYN1* | 0.923 | 95.59 | 5.41 | 36.70 | 69.10 | 7.99 | 28.10 | 5.20 | 0.36 | 4.44 | 0.81 | 5.31 | 1.04 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-1* | 0.857 | 94.87 | 5.98 | 37.00 | 72.80 | 8.28 | 29.30 | 5.44 | 0.25 | 4.22 | 0.78 | 5.08 | 1.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-2* | 0.945 | 96.58 | 5.41 | 31.70 | 62.60 | 6.89 | 24.20 | 4.02 | 0.23 | 3.55 | 0.62 | 3.97 | 0.75 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 朝阳沟 岩体 | 含晶洞花岗岩 | CY18-2 | 0.997 | 95.45 | 4.92 | 22.60 | 82.00 | 6.58 | 22.80 | 4.04 | 0.05 | 3.74 | 0.46 | 2.26 | 0.41 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 二长花岗岩 | CY27-2 | 0.952 | 86.94 | 3.40 | 24.70 | 44.80 | 5.81 | 19.80 | 3.88 | 0.49 | 3.36 | 0.53 | 3.20 | 0.63 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 正长花岗岩 | CY36-2 | 0.963 | 93.10 | 4.63 | 28.10 | 85.20 | 7.46 | 27.70 | 5.42 | 0.28 | 4.76 | 0.72 | 3.88 | 0.70 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY38-2 | 0.968 | 88.22 | 3.71 | 40.30 | 68.40 | 9.81 | 34.20 | 5.92 | 0.65 | 5.31 | 0.77 | 4.27 | 0.78 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY46-2 | 0.984 | 93.08 | 4.26 | 30.20 | 66.80 | 8.82 | 33.00 | 7.76 | 0.29 | 6.30 | 1.10 | 6.73 | 1.28 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 野猪沟 岩体 | 二长花岗岩 | YC10-1 | 0.979 | 92.84 | 3.79 | 20.32 | 44.11 | 5.09 | 18.45 | 3.73 | 0.57 | 3.09 | 0.50 | 2.90 | 0.60 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| YC08-1 | 1.057 | 95.42 | 4.34 | 20.50 | 43.51 | 4.97 | 18.02 | 3.43 | 0.55 | 3.04 | 0.53 | 3.10 | 0.67 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 岩体 名称 | 岩性 | 样品号 | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Rb | Ba | Th | U | Nb | Ta | Pb | Sr | Zr | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 马勒根 坝岩体 | 斑状黑云母 二长花岗岩 | MLG02-2 | 1.88 | 0.31 | 2.11 | 0.32 | 230.00 | 157.00 | 29.80 | 3.32 | 12.80 | 2.46 | 23.90 | 55.50 | 97.60 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG03-1 | 1.64 | 0.29 | 1.95 | 0.27 | 210.00 | 102.00 | 31.50 | 13.40 | 10.50 | 1.86 | 22.40 | 60.50 | 89.60 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG14-2 | 2.12 | 0.38 | 2.72 | 0.42 | 278.00 | 217.00 | 31.00 | 9.02 | 11.90 | 3.04 | 20.10 | 111.00 | 125.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BYN1* | 3.62 | 0.66 | 4.38 | 0.70 | 266.00 | 162.00 | 43.60 | 5.87 | 15.60 | 1.59 | 30.30 | 69.20 | 250.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-1* | 3.36 | 0.58 | 3.98 | 0.60 | 216.00 | 79.10 | 45.50 | 5.61 | 9.67 | 0.98 | 30.80 | 53.10 | 246.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-2* | 2.41 | 0.49 | 3.04 | 0.54 | 216.00 | 97.50 | 44.70 | 4.71 | 12.50 | 1.41 | 74.80 | 36.50 | 281.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 朝阳沟 岩体 | 含晶洞花岗岩 | CY18-2 | 1.16 | 0.16 | 1.12 | 0.15 | 243.00 | 34.70 | 27.20 | 4.90 | 14.50 | 1.61 | 22.40 | 21.00 | 115.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 二长花岗岩 | CY27-2 | 1.83 | 0.30 | 2.09 | 0.30 | 182.00 | 300.00 | 14.00 | 3.68 | 10.30 | 1.69 | 14.00 | 177.00 | 112.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 正长花岗岩 | CY36-2 | 1.94 | 0.30 | 1.92 | 0.27 | 213.00 | 239.00 | 22.90 | 5.50 | 10.60 | 1.53 | 21.60 | 48.20 | 170.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY38-2 | 2.26 | 0.36 | 2.33 | 0.35 | 213.00 | 452.00 | 19.30 | 5.37 | 9.03 | 1.22 | 13.70 | 132.00 | 192.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY46-2 | 3.55 | 0.61 | 4.12 | 0.60 | 312.00 | 172.00 | 36.80 | 10.80 | 22.00 | 5.30 | 39.80 | 57.10 | 130.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 野猪沟 岩体 | 二长花岗岩 | YC10-1 | 1.76 | 0.31 | 2.03 | 0.30 | 81.70 | 648.20 | 6.32 | 0.60 | 14.29 | 0.52 | 18.80 | 163.10 | 71.10 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| YC08-1 | 1.95 | 0.36 | 2.29 | 0.36 | 64.80 | 501.50 | 5.92 | 0.76 | 11.81 | 0.51 | 17.80 | 70.30 | 83.50 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 岩体名称 | 岩性 | 样品号 | Hf | Y | tzr | ∑REE | δEu | FeOT | FeOT/(FeOT+MgO) | Mg# | (LREE/HREE)N | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 马勒根 坝岩体 | 斑状黑云母 二长花岗岩 | MLG02-2 | 5.24 | 15.80 | 744.00 | 134.39 | 0.20 | 1.50 | 0.877 | 0.42 | 5.54 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG03-1 | 4.02 | 14.60 | 735.00 | 128.20 | 0.17 | 1.64 | 0.882 | 0.37 | 5.74 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG14-2 | 5.34 | 18.70 | 761.00 | 100.26 | 0.31 | 1.86 | 0.841 | 0.45 | 3.69 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BYN1* | 11.30 | 33.80 | 818.00 | 168.40 | 0.22 | 1.44 | 0.906 | 0.42 | 4.08 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-1* | 9.10 | 31.70 | 810.00 | 172.67 | 0.15 | 1.40 | 0.927 | 0.42 | 4.53 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-2* | 10.70 | 22.80 | 834.00 | 145.01 | 0.18 | 0.89 | 0.899 | 0.56 | 4.89 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 朝阳沟 岩体 | 含晶洞花岗岩 | CY18-2 | 5.62 | 7.68 | 758.00 | 147.53 | 0.04 | 1.48 | 0.914 | 0.35 | 8.46 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 二长花岗岩 | CY27-2 | 4.37 | 16.70 | 744.00 | 111.72 | 0.41 | 2.52 | 0.788 | 0.62 | 4.71 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 正长花岗岩 | CY36-2 | 7.00 | 16.00 | 785.00 | 168.65 | 0.16 | 1.74 | 0.906 | 0.25 | 6.17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY38-2 | 6.47 | 20.50 | 791.00 | 175.71 | 0.35 | 2.54 | 0.873 | 0.33 | 5.62 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY46-2 | 6.52 | 33.10 | 764.00 | 171.16 | 0.12 | 1.30 | 0.867 | 0.38 | 3.50 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 野猪沟 岩体 | 二长花岗岩 | YC10-1 | 4.65 | 16.91 | 718.00 | 103.76 | 0.50 | 1.26 | 0.816 | 0.80 | 4.65 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YC08-1 | 4.49 | 18.53 | 739.00 | 103.29 | 0.51 | 1.14 | 0.812 | 1.07 | 4.28 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
表1 大兴安岭南段主脊和东坡岩体主量、稀土及微量元素分析结果
Table 1 Major, REE and trace elements content of granite samples from the mid ridge and east slope of south Daxing’anling Mountains
| 岩体 名称 | 岩性 | 样品号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 马勒根 坝岩体 | 斑状黑云母 二长花岗岩 | MLG02-2 | 75.75 | 0.13 | 12.63 | 0.52 | 1.03 | 0.070 | 0.21 | 0.61 | 4.04 | 4.53 | 0.03 | 0.34 | 99.89 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG03-1 | 75.58 | 0.12 | 12.54 | 0.42 | 1.26 | 0.070 | 0.22 | 0.76 | 4.18 | 4.26 | 0.03 | 0.41 | 99.85 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG14-2 | 73.13 | 0.19 | 13.61 | 0.28 | 1.61 | 0.070 | 0.35 | 1.09 | 4.28 | 4.34 | 0.05 | 0.78 | 99.78 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BYN1* | 75.66 | 0.13 | 11.72 | 0.77 | 0.75 | 0.036 | 0.15 | 0.71 | 3.82 | 4.73 | 0.03 | 1.15 | 99.66 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-1* | 77.44 | 0.11 | 10.69 | 0.94 | 0.55 | 0.037 | 0.11 | 0.79 | 3.85 | 4.34 | 0.02 | 0.75 | 99.63 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-2* | 77.20 | 0.08 | 11.34 | 0.60 | 0.35 | 0.025 | 0.10 | 0.59 | 3.63 | 4.58 | 0.02 | 1.16 | 99.67 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 朝阳沟 岩体 | 含晶洞花岗岩 | CY18-2 | 76.22 | 0.08 | 12.54 | 0.70 | 0.85 | 0.060 | 0.14 | 0.43 | 4.45 | 4.14 | 0.02 | 0.31 | 99.94 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 二长花岗岩 | CY27-2 | 71.53 | 0.34 | 14.01 | 0.49 | 2.08 | 0.100 | 0.68 | 1.63 | 4.49 | 4.04 | 0.10 | 0.28 | 99.77 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 正长花岗岩 | CY36-2 | 74.30 | 0.13 | 13.18 | 0.16 | 1.60 | 0.060 | 0.18 | 0.82 | 4.31 | 4.72 | 0.03 | 0.31 | 99.80 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY38-2 | 71.35 | 0.25 | 14.29 | 0.10 | 2.45 | 0.070 | 0.37 | 1.37 | 4.47 | 4.54 | 0.07 | 0.40 | 99.73 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY46-2 | 74.28 | 0.12 | 13.63 | 0.20 | 1.12 | 0.070 | 0.20 | 0.89 | 4.44 | 4.56 | 0.03 | 0.26 | 99.80 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 野猪沟 岩体 | 二长花岗岩 | YC10-1 | 75.85 | 0.22 | 12.69 | 0.73 | 0.60 | 0.079 | 0.28 | 1.00 | 4.45 | 3.52 | 0.07 | 0.37 | 99.86 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| YC08-1 | 76.58 | 0.19 | 12.34 | 0.88 | 0.36 | 0.103 | 0.27 | 0.31 | 4.55 | 3.36 | 0.05 | 0.61 | 99.58 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 岩体 名称 | 岩性 | 样品号 | A/CNK | DI | AR | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 马勒根 坝岩体 | 斑状黑云母 二长花岗岩 | MLG02-2 | 0.998 | 94.13 | 4.67 | 24.80 | 66.80 | 5.84 | 20.20 | 3.78 | 0.25 | 3.68 | 0.56 | 3.22 | 0.64 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG03-1 | 0.974 | 93.45 | 4.47 | 24.60 | 62.60 | 5.87 | 19.60 | 3.57 | 0.20 | 3.52 | 0.52 | 2.98 | 0.59 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG14-2 | 0.992 | 90.52 | 3.84 | 19.20 | 38.70 | 5.33 | 19.30 | 3.74 | 0.37 | 3.33 | 0.54 | 3.41 | 0.70 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BYN1* | 0.923 | 95.59 | 5.41 | 36.70 | 69.10 | 7.99 | 28.10 | 5.20 | 0.36 | 4.44 | 0.81 | 5.31 | 1.04 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-1* | 0.857 | 94.87 | 5.98 | 37.00 | 72.80 | 8.28 | 29.30 | 5.44 | 0.25 | 4.22 | 0.78 | 5.08 | 1.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-2* | 0.945 | 96.58 | 5.41 | 31.70 | 62.60 | 6.89 | 24.20 | 4.02 | 0.23 | 3.55 | 0.62 | 3.97 | 0.75 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 朝阳沟 岩体 | 含晶洞花岗岩 | CY18-2 | 0.997 | 95.45 | 4.92 | 22.60 | 82.00 | 6.58 | 22.80 | 4.04 | 0.05 | 3.74 | 0.46 | 2.26 | 0.41 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 二长花岗岩 | CY27-2 | 0.952 | 86.94 | 3.40 | 24.70 | 44.80 | 5.81 | 19.80 | 3.88 | 0.49 | 3.36 | 0.53 | 3.20 | 0.63 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 正长花岗岩 | CY36-2 | 0.963 | 93.10 | 4.63 | 28.10 | 85.20 | 7.46 | 27.70 | 5.42 | 0.28 | 4.76 | 0.72 | 3.88 | 0.70 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY38-2 | 0.968 | 88.22 | 3.71 | 40.30 | 68.40 | 9.81 | 34.20 | 5.92 | 0.65 | 5.31 | 0.77 | 4.27 | 0.78 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY46-2 | 0.984 | 93.08 | 4.26 | 30.20 | 66.80 | 8.82 | 33.00 | 7.76 | 0.29 | 6.30 | 1.10 | 6.73 | 1.28 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 野猪沟 岩体 | 二长花岗岩 | YC10-1 | 0.979 | 92.84 | 3.79 | 20.32 | 44.11 | 5.09 | 18.45 | 3.73 | 0.57 | 3.09 | 0.50 | 2.90 | 0.60 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| YC08-1 | 1.057 | 95.42 | 4.34 | 20.50 | 43.51 | 4.97 | 18.02 | 3.43 | 0.55 | 3.04 | 0.53 | 3.10 | 0.67 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 岩体 名称 | 岩性 | 样品号 | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Rb | Ba | Th | U | Nb | Ta | Pb | Sr | Zr | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 马勒根 坝岩体 | 斑状黑云母 二长花岗岩 | MLG02-2 | 1.88 | 0.31 | 2.11 | 0.32 | 230.00 | 157.00 | 29.80 | 3.32 | 12.80 | 2.46 | 23.90 | 55.50 | 97.60 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG03-1 | 1.64 | 0.29 | 1.95 | 0.27 | 210.00 | 102.00 | 31.50 | 13.40 | 10.50 | 1.86 | 22.40 | 60.50 | 89.60 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG14-2 | 2.12 | 0.38 | 2.72 | 0.42 | 278.00 | 217.00 | 31.00 | 9.02 | 11.90 | 3.04 | 20.10 | 111.00 | 125.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BYN1* | 3.62 | 0.66 | 4.38 | 0.70 | 266.00 | 162.00 | 43.60 | 5.87 | 15.60 | 1.59 | 30.30 | 69.20 | 250.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-1* | 3.36 | 0.58 | 3.98 | 0.60 | 216.00 | 79.10 | 45.50 | 5.61 | 9.67 | 0.98 | 30.80 | 53.10 | 246.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-2* | 2.41 | 0.49 | 3.04 | 0.54 | 216.00 | 97.50 | 44.70 | 4.71 | 12.50 | 1.41 | 74.80 | 36.50 | 281.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 朝阳沟 岩体 | 含晶洞花岗岩 | CY18-2 | 1.16 | 0.16 | 1.12 | 0.15 | 243.00 | 34.70 | 27.20 | 4.90 | 14.50 | 1.61 | 22.40 | 21.00 | 115.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 二长花岗岩 | CY27-2 | 1.83 | 0.30 | 2.09 | 0.30 | 182.00 | 300.00 | 14.00 | 3.68 | 10.30 | 1.69 | 14.00 | 177.00 | 112.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 正长花岗岩 | CY36-2 | 1.94 | 0.30 | 1.92 | 0.27 | 213.00 | 239.00 | 22.90 | 5.50 | 10.60 | 1.53 | 21.60 | 48.20 | 170.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY38-2 | 2.26 | 0.36 | 2.33 | 0.35 | 213.00 | 452.00 | 19.30 | 5.37 | 9.03 | 1.22 | 13.70 | 132.00 | 192.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY46-2 | 3.55 | 0.61 | 4.12 | 0.60 | 312.00 | 172.00 | 36.80 | 10.80 | 22.00 | 5.30 | 39.80 | 57.10 | 130.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 野猪沟 岩体 | 二长花岗岩 | YC10-1 | 1.76 | 0.31 | 2.03 | 0.30 | 81.70 | 648.20 | 6.32 | 0.60 | 14.29 | 0.52 | 18.80 | 163.10 | 71.10 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| YC08-1 | 1.95 | 0.36 | 2.29 | 0.36 | 64.80 | 501.50 | 5.92 | 0.76 | 11.81 | 0.51 | 17.80 | 70.30 | 83.50 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 岩体名称 | 岩性 | 样品号 | Hf | Y | tzr | ∑REE | δEu | FeOT | FeOT/(FeOT+MgO) | Mg# | (LREE/HREE)N | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 马勒根 坝岩体 | 斑状黑云母 二长花岗岩 | MLG02-2 | 5.24 | 15.80 | 744.00 | 134.39 | 0.20 | 1.50 | 0.877 | 0.42 | 5.54 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG03-1 | 4.02 | 14.60 | 735.00 | 128.20 | 0.17 | 1.64 | 0.882 | 0.37 | 5.74 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG14-2 | 5.34 | 18.70 | 761.00 | 100.26 | 0.31 | 1.86 | 0.841 | 0.45 | 3.69 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BYN1* | 11.30 | 33.80 | 818.00 | 168.40 | 0.22 | 1.44 | 0.906 | 0.42 | 4.08 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-1* | 9.10 | 31.70 | 810.00 | 172.67 | 0.15 | 1.40 | 0.927 | 0.42 | 4.53 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-2* | 10.70 | 22.80 | 834.00 | 145.01 | 0.18 | 0.89 | 0.899 | 0.56 | 4.89 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 朝阳沟 岩体 | 含晶洞花岗岩 | CY18-2 | 5.62 | 7.68 | 758.00 | 147.53 | 0.04 | 1.48 | 0.914 | 0.35 | 8.46 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 二长花岗岩 | CY27-2 | 4.37 | 16.70 | 744.00 | 111.72 | 0.41 | 2.52 | 0.788 | 0.62 | 4.71 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 正长花岗岩 | CY36-2 | 7.00 | 16.00 | 785.00 | 168.65 | 0.16 | 1.74 | 0.906 | 0.25 | 6.17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY38-2 | 6.47 | 20.50 | 791.00 | 175.71 | 0.35 | 2.54 | 0.873 | 0.33 | 5.62 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY46-2 | 6.52 | 33.10 | 764.00 | 171.16 | 0.12 | 1.30 | 0.867 | 0.38 | 3.50 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 野猪沟 岩体 | 二长花岗岩 | YC10-1 | 4.65 | 16.91 | 718.00 | 103.76 | 0.50 | 1.26 | 0.816 | 0.80 | 4.65 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YC08-1 | 4.49 | 18.53 | 739.00 | 103.29 | 0.51 | 1.14 | 0.812 | 1.07 | 4.28 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

图4 花岗岩岩体A/CNK-A/NK铝饱和指数图解((a),底图据文献[27])和SiO2-K2O图解((b),底图据文献[28]) (野猪沟岩体数据据文献[21],主脊岩体数据据文献[26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35],东坡岩体数据据文献[36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45])
Fig.4 Diagrams showing A/CNK vs.A/NK ((a), after reference[27]) and SiO2 vs. K2O ((b), after reference[28]) for granites
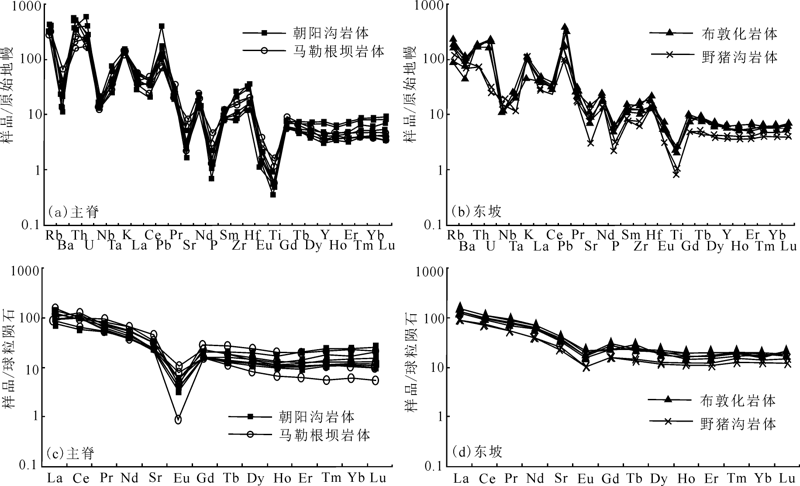
图5 主脊和东坡岩体花岗岩样品原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图与球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图
Fig.5 Primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagram and chondrite-normalized REE patterns of granite samples from the main ridge and the east slope of Daxing’anling Mountains
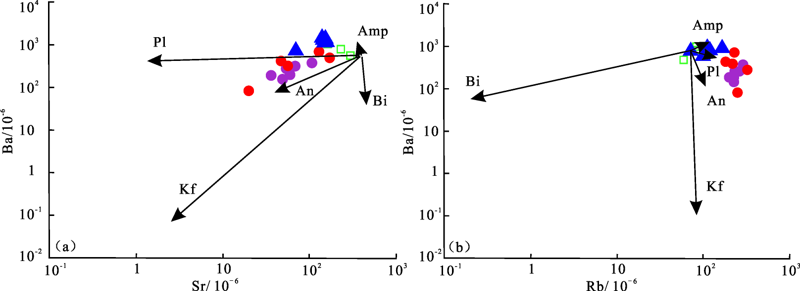
图6 花岗岩岩体Sr-Ba(a)和Rb-Ba图解(b) Bi.黑云母;Amp.角闪石;Kf.钾长石;An.钙长石;Pl.斜长石;角闪石、斜长石、钾长石以及黑云母分配系数据据文献[29];钙长石分配系数据文献[30]
Fig.6 Diagrams of Sr vs. Ba (a) and Rb vs. Ba (b) for granite samples

图7 花岗岩岩体An-Ab-Or(a)和Q-Ab-Or(b)图解(底图据文献[48];图例同图4) An.钙长石;Q.石英;Ab.钠长石;Or.钾长石;Tdj.奥长花岗岩演化趋势;CA.钙碱性演化趋势
Fig.7 An-Ab-Or (a) and Q-Ab-Or (b) diagrams for granites

图8 花岗岩岩体SiO2-MgO((a),曲线引自文献[31])和AR-SiO2((b),底图据文献[32])图解(图例同图4) A.正常安山质岩石系列;MA.镁安山质岩石系列
Fig.8 SiO2-MgO((a), after reference [31]) and AR-SiO2((b), after reference [32]) diagrams for granites
| 测点号 | 岩 体 | 含量/10-6 | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | U | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | |||||||||
| MLG03-1/3 | 马勒根坝 | 16 | 687 | 0.000 1 | 0.001 0 | 0.153 0 | 0.003 3 | 0.022 6 | 0.000 2 | 153 | 48 | 145 | 3 | 144 | 1 | |||||||
| MLG03-1/4 | 48 | 2 138 | 0.049 5 | 0.000 4 | 0.156 5 | 0.001 4 | 0.022 9 | 0.000 2 | 172 | 19 | 148 | 1 | 146 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/5 | 24 | 1 100 | 0.048 9 | 0.000 5 | 0.153 6 | 0.001 8 | 0.022 8 | 0.000 2 | 142 | 25 | 145 | 2 | 145 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/8 | 16 | 684 | 0.049 1 | 0.000 8 | 0.157 1 | 0.002 9 | 0.023 2 | 0.000 2 | 151 | 41 | 148 | 3 | 148 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/10 | 29 | 1 307 | 0.050 0 | 0.000 5 | 0.153 9 | 0.001 7 | 0.022 3 | 0.000 2 | 195 | 24 | 145 | 2 | 142 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/11 | 38 | 1 777 | 0.048 3 | 0.000 4 | 0.149 1 | 0.001 5 | 0.022 4 | 0.000 2 | 112 | 21 | 141 | 1 | 143 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/12 | 43 | 1 955 | 0.049 3 | 0.000 5 | 0.155 6 | 0.002 1 | 0.022 9 | 0.000 2 | 164 | 26 | 147 | 2 | 146 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/13 | 14 | 640 | 0.049 1 | 0.000 9 | 0.152 2 | 0.002 9 | 0.022 5 | 0.000 2 | 154 | 43 | 144 | 3 | 143 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/15 | 4 | 3 760 | 0.049 0 | 0.000 3 | 0.156 6 | 0.001 3 | 0.023 2 | 0.000 2 | 149 | 16 | 148 | 1 | 148 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/16 | 21 | 946 | 0.049 6 | 0.000 6 | 0.152 2 | 0.002 1 | 0.022 2 | 0.000 2 | 177 | 30 | 144 | 2 | 142 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/17 | 16 | 722 | 0.049 4 | 0.000 8 | 0.153 9 | 0.002 7 | 0.022 6 | 0.000 2 | 165 | 38 | 145 | 3 | 144 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/19 | 22 | 1 085 | 0.049 6 | 0.000 7 | 0.152 9 | 0.002 1 | 0.022 4 | 0.000 2 | 175 | 31 | 144 | 2 | 143 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/2 | 朝阳沟 | 6 | 237 | 0.049 3 | 0.003 1 | 0.169 3 | 0.010 6 | 0.024 9 | 0.000 2 | 164 | 145 | 159 | 10 | 158 | 1 | |||||||
| CY19-1/3 | 19 | 750 | 0.049 6 | 0.000 8 | 0.170 4 | 0.002 7 | 0.024 9 | 0.000 2 | 176 | 36 | 160 | 3 | 159 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/4 | 329 | 0.050 1 | 0.002 0 | 0.168 6 | 0.006 7 | 0.024 4 | 0.000 2 | 199 | 92 | 158 | 6 | 155 | 1 | |||||||||
| CY19-1/5 | 49 | 2 067 | 0.049 3 | 0.000 4 | 0.165 5 | 0.001 6 | 0.024 4 | 0.000 2 | 162 | 18 | 156 | 1 | 155 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/7 | 36 | 1 502 | 0.048 7 | 0.000 5 | 0.164 0 | 0.001 7 | 0.024 4 | 0.000 2 | 135 | 22 | 154 | 2 | 155 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/10 | 40 | 1 770 | 0.048 3 | 0.000 5 | 0.158 3 | 0.001 9 | 0.023 8 | 0.000 2 | 115 | 26 | 149 | 2 | 151 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/11 | 9 | 376 | 0.049 2 | 0.001 8 | 0.165 5 | 0.006 2 | 0.024 4 | 0.000 2 | 155 | 87 | 156 | 6 | 156 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/12 | 49 | 2 167 | 0.049 4 | 0.000 4 | 0.159 5 | 0.001 5 | 0.023 4 | 0.000 2 | 167 | 19 | 150 | 1 | 149 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/13 | 29 | 1 239 | 0.049 6 | 0.000 6 | 0.162 5 | 0.002 0 | 0.023 8 | 0.000 2 | 174 | 27 | 153 | 2 | 151 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/14 | 4 | 158 | 0.050 3 | 0.004 6 | 0.166 1 | 0.015 2 | 0.024 0 | 0.000 2 | 208 | 214 | 156 | 14 | 153 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/16 | 15 | 612 | 0.049 2 | 0.001 0 | 0.162 5 | 0.003 6 | 0.023 9 | 0.000 2 | 158 | 50 | 153 | 3 | 153 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/17 | 9 | 357 | 0.049 7 | 0.003 1 | 0.168 1 | 0.011 8 | 0.024 5 | 0.000 3 | 181 | 144 | 158 | 11 | 156 | 2 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/1 | 野猪沟 | 36 | 1 529 | 0.048 84 | 0.033 92 | 0.145 97 | 0.101 23 | 0.021 67 | 0.000 90 | 140 | 1 029 | 138 | 90 | 138 | 6 | |||||||
| YC10-1/2 | 6 | 237 | 0.049 19 | 0.044 43 | 0.152 67 | 0.137 66 | 0.022 50 | 0.001 22 | 157 | 1 147 | 144 | 121 | 143 | 8 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/3 | 19 | 750 | 0.048 61 | 0.004 23 | 0.139 87 | 0.012 07 | 0.020 86 | 0.000 42 | 129 | 155 | 133 | 11 | 133 | 3 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/5 | 49 | 2 067 | 0.049 06 | 0.002 34 | 0.154 95 | 0.007 37 | 0.022 90 | 0.000 38 | 151 | 80 | 146 | 6 | 146 | 2 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/6 | 44 | 1 904 | 0.048 70 | 0.003 43 | 0.145 72 | 0.010 14 | 0.021 69 | 0.000 42 | 133 | 120 | 138 | 9 | 138 | 3 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/8 | 12 | 496 | 0.048 61 | 0.023 62 | 0.127 96 | 0.061 88 | 0.019 09 | 0.000 97 | 129 | 754 | 122 | 56 | 122 | 6 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/11 | 9 | 376 | 0.051 63 | 0.001 86 | 0.161 37 | 0.005 85 | 0.022 66 | 0.000 35 | 269 | 55 | 152 | 5 | 144 | 2 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/13 | 29 | 1 239 | 0.048 88 | 0.004 97 | 0.142 63 | 0.014 46 | 0.021 16 | 0.000 39 | 142 | 192 | 135 | 13 | 135 | 2 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/14 | 4 | 158 | 0.048 94 | 0.003 60 | 0.141 00 | 0.010 31 | 0.020 89 | 0.000 38 | 145 | 130 | 134 | 9 | 133 | 2 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/17 | 9 | 357 | 0.048 60 | 0.007 98 | 0.149 71 | 0.024 43 | 0.022 33 | 0.000 56 | 129 | 283 | 142 | 22 | 142 | 4 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/18 | 12 | 486 | 0.048 63 | 0.003 04 | 0.141 83 | 0.008 81 | 0.021 15 | 0.000 38 | 130 | 106 | 135 | 8 | 135 | 2 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/19 | 8 | 341 | 0.048 64 | 0.004 12 | 0.142 12 | 0.011 95 | 0.021 19 | 0.000 40 | 131 | 153 | 135 | 11 | 135 | 3 | ||||||||
表2 马勒根坝、朝阳沟和野猪沟岩体锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年数据
Table 2 Results of zircons LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating of granite samples from Malegenba, Chaoyanggou and Yezhugou
| 测点号 | 岩 体 | 含量/10-6 | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | U | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | |||||||||
| MLG03-1/3 | 马勒根坝 | 16 | 687 | 0.000 1 | 0.001 0 | 0.153 0 | 0.003 3 | 0.022 6 | 0.000 2 | 153 | 48 | 145 | 3 | 144 | 1 | |||||||
| MLG03-1/4 | 48 | 2 138 | 0.049 5 | 0.000 4 | 0.156 5 | 0.001 4 | 0.022 9 | 0.000 2 | 172 | 19 | 148 | 1 | 146 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/5 | 24 | 1 100 | 0.048 9 | 0.000 5 | 0.153 6 | 0.001 8 | 0.022 8 | 0.000 2 | 142 | 25 | 145 | 2 | 145 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/8 | 16 | 684 | 0.049 1 | 0.000 8 | 0.157 1 | 0.002 9 | 0.023 2 | 0.000 2 | 151 | 41 | 148 | 3 | 148 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/10 | 29 | 1 307 | 0.050 0 | 0.000 5 | 0.153 9 | 0.001 7 | 0.022 3 | 0.000 2 | 195 | 24 | 145 | 2 | 142 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/11 | 38 | 1 777 | 0.048 3 | 0.000 4 | 0.149 1 | 0.001 5 | 0.022 4 | 0.000 2 | 112 | 21 | 141 | 1 | 143 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/12 | 43 | 1 955 | 0.049 3 | 0.000 5 | 0.155 6 | 0.002 1 | 0.022 9 | 0.000 2 | 164 | 26 | 147 | 2 | 146 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/13 | 14 | 640 | 0.049 1 | 0.000 9 | 0.152 2 | 0.002 9 | 0.022 5 | 0.000 2 | 154 | 43 | 144 | 3 | 143 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/15 | 4 | 3 760 | 0.049 0 | 0.000 3 | 0.156 6 | 0.001 3 | 0.023 2 | 0.000 2 | 149 | 16 | 148 | 1 | 148 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/16 | 21 | 946 | 0.049 6 | 0.000 6 | 0.152 2 | 0.002 1 | 0.022 2 | 0.000 2 | 177 | 30 | 144 | 2 | 142 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/17 | 16 | 722 | 0.049 4 | 0.000 8 | 0.153 9 | 0.002 7 | 0.022 6 | 0.000 2 | 165 | 38 | 145 | 3 | 144 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/19 | 22 | 1 085 | 0.049 6 | 0.000 7 | 0.152 9 | 0.002 1 | 0.022 4 | 0.000 2 | 175 | 31 | 144 | 2 | 143 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/2 | 朝阳沟 | 6 | 237 | 0.049 3 | 0.003 1 | 0.169 3 | 0.010 6 | 0.024 9 | 0.000 2 | 164 | 145 | 159 | 10 | 158 | 1 | |||||||
| CY19-1/3 | 19 | 750 | 0.049 6 | 0.000 8 | 0.170 4 | 0.002 7 | 0.024 9 | 0.000 2 | 176 | 36 | 160 | 3 | 159 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/4 | 329 | 0.050 1 | 0.002 0 | 0.168 6 | 0.006 7 | 0.024 4 | 0.000 2 | 199 | 92 | 158 | 6 | 155 | 1 | |||||||||
| CY19-1/5 | 49 | 2 067 | 0.049 3 | 0.000 4 | 0.165 5 | 0.001 6 | 0.024 4 | 0.000 2 | 162 | 18 | 156 | 1 | 155 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/7 | 36 | 1 502 | 0.048 7 | 0.000 5 | 0.164 0 | 0.001 7 | 0.024 4 | 0.000 2 | 135 | 22 | 154 | 2 | 155 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/10 | 40 | 1 770 | 0.048 3 | 0.000 5 | 0.158 3 | 0.001 9 | 0.023 8 | 0.000 2 | 115 | 26 | 149 | 2 | 151 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/11 | 9 | 376 | 0.049 2 | 0.001 8 | 0.165 5 | 0.006 2 | 0.024 4 | 0.000 2 | 155 | 87 | 156 | 6 | 156 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/12 | 49 | 2 167 | 0.049 4 | 0.000 4 | 0.159 5 | 0.001 5 | 0.023 4 | 0.000 2 | 167 | 19 | 150 | 1 | 149 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/13 | 29 | 1 239 | 0.049 6 | 0.000 6 | 0.162 5 | 0.002 0 | 0.023 8 | 0.000 2 | 174 | 27 | 153 | 2 | 151 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/14 | 4 | 158 | 0.050 3 | 0.004 6 | 0.166 1 | 0.015 2 | 0.024 0 | 0.000 2 | 208 | 214 | 156 | 14 | 153 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/16 | 15 | 612 | 0.049 2 | 0.001 0 | 0.162 5 | 0.003 6 | 0.023 9 | 0.000 2 | 158 | 50 | 153 | 3 | 153 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/17 | 9 | 357 | 0.049 7 | 0.003 1 | 0.168 1 | 0.011 8 | 0.024 5 | 0.000 3 | 181 | 144 | 158 | 11 | 156 | 2 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/1 | 野猪沟 | 36 | 1 529 | 0.048 84 | 0.033 92 | 0.145 97 | 0.101 23 | 0.021 67 | 0.000 90 | 140 | 1 029 | 138 | 90 | 138 | 6 | |||||||
| YC10-1/2 | 6 | 237 | 0.049 19 | 0.044 43 | 0.152 67 | 0.137 66 | 0.022 50 | 0.001 22 | 157 | 1 147 | 144 | 121 | 143 | 8 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/3 | 19 | 750 | 0.048 61 | 0.004 23 | 0.139 87 | 0.012 07 | 0.020 86 | 0.000 42 | 129 | 155 | 133 | 11 | 133 | 3 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/5 | 49 | 2 067 | 0.049 06 | 0.002 34 | 0.154 95 | 0.007 37 | 0.022 90 | 0.000 38 | 151 | 80 | 146 | 6 | 146 | 2 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/6 | 44 | 1 904 | 0.048 70 | 0.003 43 | 0.145 72 | 0.010 14 | 0.021 69 | 0.000 42 | 133 | 120 | 138 | 9 | 138 | 3 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/8 | 12 | 496 | 0.048 61 | 0.023 62 | 0.127 96 | 0.061 88 | 0.019 09 | 0.000 97 | 129 | 754 | 122 | 56 | 122 | 6 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/11 | 9 | 376 | 0.051 63 | 0.001 86 | 0.161 37 | 0.005 85 | 0.022 66 | 0.000 35 | 269 | 55 | 152 | 5 | 144 | 2 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/13 | 29 | 1 239 | 0.048 88 | 0.004 97 | 0.142 63 | 0.014 46 | 0.021 16 | 0.000 39 | 142 | 192 | 135 | 13 | 135 | 2 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/14 | 4 | 158 | 0.048 94 | 0.003 60 | 0.141 00 | 0.010 31 | 0.020 89 | 0.000 38 | 145 | 130 | 134 | 9 | 133 | 2 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/17 | 9 | 357 | 0.048 60 | 0.007 98 | 0.149 71 | 0.024 43 | 0.022 33 | 0.000 56 | 129 | 283 | 142 | 22 | 142 | 4 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/18 | 12 | 486 | 0.048 63 | 0.003 04 | 0.141 83 | 0.008 81 | 0.021 15 | 0.000 38 | 130 | 106 | 135 | 8 | 135 | 2 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/19 | 8 | 341 | 0.048 64 | 0.004 12 | 0.142 12 | 0.011 95 | 0.021 19 | 0.000 40 | 131 | 153 | 135 | 11 | 135 | 3 | ||||||||
| 编 号 | 岩体 位置 | 岩体名称 | 采样点 | 岩性 | 年龄/Ma | 测试方法 | 文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 主脊 | 索伦 | 121°13'11″,46°40'58″ | 黑云母碱长花岗岩 | 125±2 | LA-ICP-MS | 周漪等[ | |
| 2 | 乌兰毛多 | 121°14'23″,46°24'42″ | 正长花岗岩 | 131±1 | LA-ICP-MS | Wu等[ | ||
| 3 | 沙布台 | 121°05'32″,46°21'14″ | 二长花岗岩 | 129±2 | LA-ICP-MS | Wu等[ | ||
| 5 | 巴尔哲 | 碱性花岗岩 | 122 | 锆石U-Pb | 赵振华等[ | |||
| 6 | 哈马尔乌拉 | 花岗斑岩 | 124.9±2.5 | 锆石U-Pb | 徐学纯等[ | |||
| 7 | 毛伊勒吐 | 石英闪长岩 | 147.97±0.95 | SHRIMP | 李雪菲等[ | |||
| 11 | 马勒根坝 | 118°49'53.31″,44°29'12.36″ | 黑云母正长花岗岩 | 145 | LA-ICP-MS | 本文 | ||
| 12 | 白音诺尔 | 118°53'12.7″,44°26'52.3″ | 石英斑岩 | 129.0±1.4 | LA-ICP-MS | 江思宏等[ | ||
| 14 | 朝阳沟岩体 | 118°05'12.59″,44°03'23.23″ | 含晶洞正长花岗岩 | 154 | LA-ICP-MS | 本文 | ||
| 15 | 北大山 | 117°32'24″,43°57'15″ | 正长花岗岩 | 136±2 | LA-ICP-MS | 刘翼飞[ | ||
| 17 | 黄岗梁 | 117°37'27″,43°31'09″ | 正长花岗岩 | 141±1 | LA-ICP-MS | Wu等[ | ||
| 18 | 大营子 | 117°36'34″,43°21'43″ | 二长花岗岩 | 132±1 | LA-ICP-MS | Wu等[ | ||
| 19 | 经棚 | 117°32'30″,43°13'33″;117°44'55″, 43°15'50″;117°32'30″,43°13'33″ | 二长花岗岩 | 140±2; 140±2; 141±1 | LA-ICP-MS | Wu等[ | ||
| 4 | 东坡 | 青山岩体 | 46°29'40.6″,122°07'28.6″ | 黑云母花岗闪长岩 | 134±2 | LA-ICP-MS | 葛文春等[ | |
| 8 | 杜尔基 | 121°08'57.4″,45°13'6.9″ | 正长花岗岩 | 154.5±0.5 | LA-ICP-MS | 江思宏等[ | ||
| 9 | 布敦化 | 121°23'36″,44°55'14.8″ | 斜长花岗斑岩 | 154.1±1.6 | SHRIMP | 冯祥发[ | ||
| 10 | 敖仑花 | *120°13',44°33' | 二长花岗斑岩 | 134±4 | SHRIMP | 马星华等[ | ||
| 13 | 半砬山钼矿 | *120°07',44°03' | 花岗闪长斑岩 | 136.5±1.7 | LA-ICP-MS | 张晓静等[ | ||
| 16 | 野猪沟 | 119°20'14.43″,43°50'8.47 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 140.2±2.7 | LA-ICP-MS | 本文 | ||
| 20 | 林西县小城子 | *118°10'00″,44°22'00″ | 石英斑岩脉 | 146.1±0.9 | LA-ICP-MS | 江思宏等[ | ||
| 21 | 小东沟 | 117°44'30″-117°45', 43°00'-43°02'15″ | 斑状花岗岩 | 142.2±2.0 | SHRIMP | 覃锋等[ | ||
表3 晚侏罗世—早白垩世大兴安岭南段花岗岩岩体年龄
Table 3 Granite ages of Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous in south Daxing’anling Mountains
| 编 号 | 岩体 位置 | 岩体名称 | 采样点 | 岩性 | 年龄/Ma | 测试方法 | 文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 主脊 | 索伦 | 121°13'11″,46°40'58″ | 黑云母碱长花岗岩 | 125±2 | LA-ICP-MS | 周漪等[ | |
| 2 | 乌兰毛多 | 121°14'23″,46°24'42″ | 正长花岗岩 | 131±1 | LA-ICP-MS | Wu等[ | ||
| 3 | 沙布台 | 121°05'32″,46°21'14″ | 二长花岗岩 | 129±2 | LA-ICP-MS | Wu等[ | ||
| 5 | 巴尔哲 | 碱性花岗岩 | 122 | 锆石U-Pb | 赵振华等[ | |||
| 6 | 哈马尔乌拉 | 花岗斑岩 | 124.9±2.5 | 锆石U-Pb | 徐学纯等[ | |||
| 7 | 毛伊勒吐 | 石英闪长岩 | 147.97±0.95 | SHRIMP | 李雪菲等[ | |||
| 11 | 马勒根坝 | 118°49'53.31″,44°29'12.36″ | 黑云母正长花岗岩 | 145 | LA-ICP-MS | 本文 | ||
| 12 | 白音诺尔 | 118°53'12.7″,44°26'52.3″ | 石英斑岩 | 129.0±1.4 | LA-ICP-MS | 江思宏等[ | ||
| 14 | 朝阳沟岩体 | 118°05'12.59″,44°03'23.23″ | 含晶洞正长花岗岩 | 154 | LA-ICP-MS | 本文 | ||
| 15 | 北大山 | 117°32'24″,43°57'15″ | 正长花岗岩 | 136±2 | LA-ICP-MS | 刘翼飞[ | ||
| 17 | 黄岗梁 | 117°37'27″,43°31'09″ | 正长花岗岩 | 141±1 | LA-ICP-MS | Wu等[ | ||
| 18 | 大营子 | 117°36'34″,43°21'43″ | 二长花岗岩 | 132±1 | LA-ICP-MS | Wu等[ | ||
| 19 | 经棚 | 117°32'30″,43°13'33″;117°44'55″, 43°15'50″;117°32'30″,43°13'33″ | 二长花岗岩 | 140±2; 140±2; 141±1 | LA-ICP-MS | Wu等[ | ||
| 4 | 东坡 | 青山岩体 | 46°29'40.6″,122°07'28.6″ | 黑云母花岗闪长岩 | 134±2 | LA-ICP-MS | 葛文春等[ | |
| 8 | 杜尔基 | 121°08'57.4″,45°13'6.9″ | 正长花岗岩 | 154.5±0.5 | LA-ICP-MS | 江思宏等[ | ||
| 9 | 布敦化 | 121°23'36″,44°55'14.8″ | 斜长花岗斑岩 | 154.1±1.6 | SHRIMP | 冯祥发[ | ||
| 10 | 敖仑花 | *120°13',44°33' | 二长花岗斑岩 | 134±4 | SHRIMP | 马星华等[ | ||
| 13 | 半砬山钼矿 | *120°07',44°03' | 花岗闪长斑岩 | 136.5±1.7 | LA-ICP-MS | 张晓静等[ | ||
| 16 | 野猪沟 | 119°20'14.43″,43°50'8.47 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 140.2±2.7 | LA-ICP-MS | 本文 | ||
| 20 | 林西县小城子 | *118°10'00″,44°22'00″ | 石英斑岩脉 | 146.1±0.9 | LA-ICP-MS | 江思宏等[ | ||
| 21 | 小东沟 | 117°44'30″-117°45', 43°00'-43°02'15″ | 斑状花岗岩 | 142.2±2.0 | SHRIMP | 覃锋等[ | ||

图11 构造环境判别图解(底图引自文献[49];图例同图4) ORG.洋脊花岗岩;WPG.板内花岗岩;VAG.岛弧花岗岩;syn-COLG.同碰撞花岗岩
Fig.11 Tectonic discrimination diagrams for granite samples(base map after reference[49])
| [1] | 邵济安, 张履桥, 牟保磊. 大兴安岭中生代伸展造山过程中的岩浆作用[J]. 地学前缘, 1999,6(4):339-346. |
| [2] | 邵济安, 赵国龙, 王忠, 等. 大兴安岭中生代火山活动构造背景[J]. 地质论评, 1999,45(增):422-430. |
| [3] | 邵济安, 刘福田, 陈辉, 等. 大兴安岭—燕山晚中生代岩浆活动与俯冲作用关系[J]. 地质学报, 2001,75(1):56-63. |
| [4] | 邵济安, 韩庆军, 李惠民. 华北克拉通早中生代麻粒岩捕虏体的发现[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2000,30(增):148-153. |
| [5] | 邵济安, 张履桥, 牟保磊, 等. 大兴安岭的隆起与地球动力学背景[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007: 18-28. |
| [6] | METELKIN D V, GORDIENKO I V, KLIMUK V S. Paleomagnetism of Upper Jurassic basalts from Transbaikalia:New data on the time of closure of the Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean and Mesozoic intraplate tectonics of central Asia-Russian[J]. Russian Geology and Geophysics, 2007,48(10):825-834. |
| [7] | KRAVEHISKY V A, COGNE J P, HARBERT W P, et al. Evolution of the Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean as constrained by new palaeo-magnetic data from the Mongol-Okhotsk suturezone, Siberia[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2002,148(1):34-57. |
| [8] | 林强, 葛文春, 吴福元, 等. 大兴安岭中生代花岗岩类的地球化学[J]. 岩石学报, 2004,20(3):403-412. |
| [9] | 葛文春, 隋振民, 吴福元, 等. 大兴安岭东北部早古生代花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素特征及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2007,23(2):423-440. |
| [10] | 赵国龙, 杨桂林, 王忠, 等. 大兴安岭中南部中生代火山岩[M]. 北京: 北京科学技术出版社, 1989: 1-200. |
| [11] | 马家骏, 方大赫. 黑龙江省中生代火山岩初步研究[J]. 黑龙江地质, 1991,2(2):1-16. |
| [12] | 邓晋福, 赵海玲, 莫宣学, 等. 中国大陆根-柱构造——大陆动力学的钥匙[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1996: 1-110. |
| [13] | 朱勤文, 路凤香, 谢意红, 等. 大陆边缘扩张型活动带火山岩组合——松辽盆地周边中生代火山岩研究[J]. 岩石学报, 1997,13(4) : 551-562. |
| [14] | 吴福元, 孙德有, 张广良, 等. 论燕山运动的深部地球动力学本质[J]. 高校地质学报, 2000,6(3):379-388. |
| [15] | WANG P J, LIU W Z, WANG S X, et al. 40Ar/39Ar and K/Ar dating on the volcanic rocks in the Songliao basin, NE China: constraints on stratigraphy and basin dynamics [J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2002,91(2):331-340. |
| [16] | 吴福元, 孙德有, 林强. 东北地区显生宙花岗岩的成因与地壳增生[J]. 岩石学报, 1999,15(2):181-189. |
| [17] | FAN W M, GUO F, WANG Y J, et al. Late Mesozoic calc-alkaline volcanism of post-orogenic extension in the northern Da Hinggan mountains, northeastern China[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2003,121(1):115-135. |
| [18] | 曹生儒. 对内蒙古板块构造轮廓的新认识[J]. 中国区域地质, 1993(3):211-215. |
| [19] | 辽宁省第二区域地质测量队. 协里府幅、巴林左旗幅1∶200000区域地质矿产报告书(地质部分)[R]. 大连:辽宁省第二区域地质测量队, 1971. |
| [20] | 武新丽. 内蒙古布敦化铜矿矿床地质特征与成矿研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京), 2013. |
| [21] | 冯祥发. 内蒙古兴安盟布敦化铜矿地质与地球化学特征研究[D]. 内蒙古煤炭经济 2010(4):41-44. |
| [22] | LIU Y S, HU Z C, GAO S, et al. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008,257(1/2):34-43. |
| [23] | 李怀坤, 耿建珍, 郝爽, 等. 用激光烧蚀多接收器等离子体质谱仪(LA-MC-ICPMS)测定锆石U-Pb同位素年龄的研究[J]. 矿物学报, 2009,29(1):600-601. |
| [24] | 张旗. 花岗岩Sr-Yb分类及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2006,22(9):2249-2269. |
| [25] | 冯艳芳, 邓晋福, 王世进, 等. 鲁西地区早前寒武纪花岗岩类中镁安山质岩石系列(MA)的识别及大陆地壳生长[J]. 中国地质, 2010,37(4):1119-1120. |
| [26] | 沈阳地质矿产研究所. 西乌珠穆沁旗幅1∶25万区域地质调查报告[R]. 沈阳:沈阳地质矿产研究所, 2005. |
| [27] | MILLER C F, MCDOWELL S M, MAPES R W. Hot and cold granites ? Implications of zircon saturation temperatures and preservation of inheritance[J]. Geology, 2003,31(6):529-532. |
| [28] | MANIAR P D, PICCOLI P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989,101(5):635-643. |
| [29] | EWART A, GRIFFIN W L. Application of proton-microprobe data to trace-element partitioning in volcanic rocks[J]. Chemical Geology, 1994,117(1/4):251-284. |
| [30] | SUN S S, HANSON G N. Rare earth element evidence for differentiation of McMundo volcanics,Ross Island, Antarctica[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976,54(2):139-155. |
| [31] | 邓晋福, 罗照华, 苏尚国, 等. 岩石成因、构造环境与成矿作用[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2004: 20-30. |
| [32] | WILSON M. Igneous Petrogenesis[M]. London: Allen and Unwin, 1989: 1-10. |
| [33] | 徐学纯, 李雪菲, 赵庆英, 等. 内蒙古哈马尔乌拉花岗斑岩的锆石U-Pb定年及其岩石地球化学特征[J]. 地质与资源, 2011,20(3):161-166. |
| [34] | 赵振华, 熊小林, 韩小东, 等. 花岗岩稀土元素四分组效应形成机理探讨——以千里山和巴尔哲花岗岩为例[J]. 中国科学( D辑), 1999,29(4):331-338. |
| [35] | 周漪, 葛文春, 王清海. 大兴安岭中部乌兰浩特地区中生代花岗岩的成因——地球化学及Sr-Nd-Hf同位素制约[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2011,30(5):901-923. |
| [36] | 刘翼飞. 内蒙古克什克腾旗拜仁达坝银多金属矿床成因研究[D]. 北京:中国地质科学院, 2009. |
| [37] | WU F Y, SUN D Y, GE W C, et al. Geochronology of the phanerozoic granitoids in northeastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011,41:1-30. |
| [38] | 李雪菲, 赵庆英, 王晓志, 等. 内蒙古扎鲁特地区毛伊勒吐岩体形成时代及构造环境[J]. 地质与资源, 2012,21(2):194-199. |
| [39] | 江思宏, 聂凤军, 刘翼飞, 等. 内蒙古孟恩陶勒盖银多金属矿床及其附近侵入岩的年代学[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2011,41(6):1755-1769. |
| [40] | 张晓静, 张连昌, 靳新娣, 等. 内蒙古半砬山钼矿含矿斑岩U-Pb年龄和地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2010,26(5):1411-1422. |
| [41] | 葛文春, 吴福元, 周长勇, 等. 大兴安岭中部乌兰浩特地区中生代花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2005,21(3):749-762. |
| [42] | 马星华, 陈斌, 赖勇, 等. 内蒙古敖仑花斑岩钼矿床成岩成矿年代学及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2009,25(11):2939-2950. |
| [43] | 江思宏, 梁清玲, 刘翼飞, 等. 内蒙古大井矿区及外围岩浆岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其对成矿时间的约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2012,28(2):495-507. |
| [44] | 覃锋, 刘建明, 曾庆栋, 等. 内蒙古克什克腾旗小东沟斑岩型钼矿床成岩成矿机制探讨[J]. 岩石学报, 2009,25(12):3357-3368. |
| [45] | WU F Y, JAHN B M, WILDER S A, et al. Highly fractionated I-type granites in NE China (I):Geochronology and petrogenesis[J]. Lithos, 2003,66(3/4):241-273. |
| [46] | CHAPPELL B W. Aluminium saturation in I- and S-type granites and the characterization of fractionated haplogranites[J]. Lithos, 1999,46(3):535-551. |
| [47] | 张旗. 花岗岩与地壳厚度关系探讨[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2011,35(2):259-269. |
| [48] | LIEGEOIS J P, NAVEZ J, HERTOGEN J, et al. Contrasting origin of post-collisional high-K calc-alkaline and shoshonitic versus alkaline and peralkaline granitoids the use of sliding normalization[J]. Lithos, 1998,45(1/4):1-28. |
| [49] | PEARCE J A. Source and settings of granitic rocks[J]. Episodes, 1996,19(4):120-125. |
| [50] | ZHOU X M, LI W X. Origin of Late Mesozoic igneous rocks in southeastern China: Implications for lithosphere subduction and underplating of mafic magmas[J]. Tectonophysics, 2000,326(3/4):269-287. |
| [51] | MARUYAMA S, SENO T. Orogeny and relative plate motions:Example of the Japanese Island[J]. Tectonophysics, 1986,127(3/4):305-329. |
| [52] | ENGEBRETSON D C, COX A, GORDON R G. Relative Motions Between Oceanic and Continental Plates in the Pacific Basin[M]. Washington:Geological Society of America Specical Paper, 1985: 1-59. |
| [53] | 包汉勇, 郭战峰, 张罗磊, 等. 太平洋板块形成以来的中国东部构造动力学背景[J]. 地球科学进展, 2013,28(3):337-346. |
| [54] | 张旗. 中国东部中生代岩浆活动与太平洋板块向西俯冲有关吗?[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2013,32(1):113-128. |
| [55] | MARUYAMA S, ISOZAKI Y, KIMURA G, et al. Paleogeographic maps of the Japanese Islands: Plate tectonic sysjournal from 750Ma to the present[J]. Island Arc, 1997,6:121-142. |
| [56] | ISOZAKI Y, KAZUMASA A, NAKAMA T, et al. New insight into a subduction-related orogen: A reappraisal of the geotectonic framework and evolution of the Japanese Islands[J]. Gondwana Research, 2010,18(1):82-105. |
| [1] | 何云龙, 张国宾, 杨言辰, 冯玥, 孔金贵, 陈兴凯. 锡霍特—阿林造山带那丹哈达地体四平山金矿床成因与构造背景:锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石和流体地球化学制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 128-153. |
| [2] | 刘青占, 蒋孝君, 王果, 李天瑜, 李东鹏. 内蒙古南炮台花岗斑岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 154-168. |
| [3] | 周延, 范飞鹏, 康丛轩, 赵希林, 肖凡, 徐敏成, 沈莽庭, 朱意萍. 闽西南地区天池塘花岗闪长岩地质年代学和地球化学特征:对区域成矿作用的指示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1467-1481. |
| [4] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [5] | 罗海怡, 罗先熔, 刘攀峰, 马明亮, 陆显盛, 蒋小明, 鲍官桂, 蒋羽雄. 广西崇左市那渠地区土壤地球化学特征及找矿前景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1553-1566. |
| [6] | 梁鸣, 高文, 罗先熔, 王晓东, 刘秀娟, 陈皓, 刘攀峰, 竹峰, 李伟. 冀北高尖子地区土壤地球化学特征及其找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1567-1579. |
| [7] | 杨元江, 邓昌州, 李成禄, 杨文鹏, 符安宗, 郑博, 袁茂文, 张立东. 小兴安岭翠峦地区早侏罗世A型花岗岩成因与动力学背景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1597-1608. |
| [8] | 杜俊, 刘洪微, 常洪伦. 斜长石中人工合成流体包裹体的实验研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1634-1643. |
| [9] | 陈曦, 肖玲, 王明瑜, 郝晨曦, 王峰, 唐红南. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘长8油层组物源与古沉积环境恢复:来自岩石地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1264-1281. |
| [10] | 李志鹏, 余麒麟, 昝灵, 余文端, 张枝焕. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷阜二段不同岩性烃源岩的地球化学特征及生烃潜力对比[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1345-1357. |
| [11] | 可行, 赵青芳, 吴飘, 杨传胜, 廖晶, 龚建明. 胶莱盆地东北部白垩系烃源岩特征与评价[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1358-1368. |
| [12] | 王瑞廷, 李青锋, 秦西社, 张斌, 王博闻, 冀月飞. 南秦岭太白河地区石英二长闪长岩锆石U-Pb同位素年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 562-572. |
| [13] | 鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 王海波, 王超, 孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 573-585. |
| [14] | 王向伟, 张保涛, 杨浩强, 韩进国. 青海省海晏县团宝山一带变质岩年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 586-598. |
| [15] | 薛仲凯, 范堡程, 黄豪擎, 唐卫东, 葛战林, 李朋伟, 胡建辉, 杨晓奇, 郭永超, 李空. 内蒙古北山地区中基性岩脉年代学和地球化学特征:对塔里木板块北缘构造演化的启示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 627-644. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||