



现代地质 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (03): 776-786.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2021.060
收稿日期:2020-11-19
修回日期:2021-04-23
出版日期:2021-06-23
发布日期:2021-06-24
通讯作者:
倪金龙
作者简介:倪金龙,男,副教授,博士后,1974年出生,构造地质学专业,主要从事构造地质相关教学与研究工作。Email: nijlqd@sdust.edu.cn。基金资助:
LI Sheng1,2( ), NI Jinlong1,2(
), NI Jinlong1,2( ), ZHANG Shangkun3, SHEN Ying3
), ZHANG Shangkun3, SHEN Ying3
Received:2020-11-19
Revised:2021-04-23
Online:2021-06-23
Published:2021-06-24
Contact:
NI Jinlong
摘要:
沂沭断裂带内部的岩浆侵入与断裂活动关系密切,开展沂沭断裂带内部岩浆年代学研究,对于沂沭断裂带构造背景研究具有积极的参考意义。选取沂沭断裂带内部的莒县浮来山正长岩体、边部的莒南官坊石英正长岩体及侵入该岩体的闪长玢岩脉,开展岩石学及年代学研究。首次发现晚中生代沂沭断裂带左旋韧性剪切,获得浮来山岩体的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为(125.1±1.7) Ma,官坊岩体年龄为(125.6±2.0) Ma, 发生韧性变形的闪长玢岩脉年龄为(122.8±2.1) Ma。获得的125 Ma岩浆活动年龄与沂沭断裂带东侧的五莲变质核杂岩快速剥露(122~128 Ma)、诸城断陷盆地快速沉降的时间相吻合,该时期沂沭断裂带处于岩石圈减薄与破坏强烈的时期;闪长玢岩脉的122.8 Ma结晶年龄,与五莲变质核杂岩后构造岩体(石场、坊子岩体等)结晶年龄一致,该时期沂沭断裂带处于弱伸展状态,同时也说明胶东半岛岩石圈减薄具有时间上的一致性。晚中生代时期,沂沭断裂带两侧岩浆活动具有逆时针迁移的规律,这一规律可能与伊佐奈岐板块向欧亚板块俯冲的方向、角度、速度的变换有关。
中图分类号:
李盛, 倪金龙, 张尚坤, 申颖. 晚中生代沂沭断裂带左旋韧性剪切与岩浆迁移规律[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(03): 776-786.
LI Sheng, NI Jinlong, ZHANG Shangkun, SHEN Ying. Sinistral Ductile Shear and Magmatic Migration Pattern in the Late Mesozoic Yishu Fault Zone[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(03): 776-786.

图1 沂沭断裂带及其周边断裂和岩浆分布简图[11, 16-17, 21, 25, 29-30]
Fig.1 Simplified geologic map of the Yishu fault zone and its surrounding areas, showing the distribution of major faults and magmatic bodies

图2 采样点野外露头特征 (a) (b) 18YS12采样点露头;(c)17JN15-1采样露头;(d)遭受韧性剪切的闪长玢岩脉(样品17JN15-2采样点);(e)(d)图的薄片显微照片,钾长石构成σ状残斑,示左旋剪切
Fig.2 Outcrop photos of the sampling site
| 点号 | Th/U | 比值 | 年龄/Ma | 谐和度% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 207Pb/ | 207Pb/ | 206Pb/ | 207Pb/ | 207Pb/ | 206Pb/ | ||||
| 206Pb±1σ | 235U±1σ | 238U±1σ | 206Pb±1σ | 235U±1σ | 238U±1σ | ||||
| 18YS12-1 | 0.99 | 0.051 4±0.002 3 | 0.141 9±0.006 1 | 0.020 0±0.000 4 | 135±5 | 128±3 | 128±4 | 94 | |
| 18YS12-2 | 1.3 | 0.056 9±0.004 1 | 0.150 7±0.008 6 | 0.019 9±0.000 5 | 143±8 | 127±3 | 132±5 | 88 | |
| 18YS12-3 | 1.48 | 0.050 5±0.001 7 | 0.136 1±0.004 3 | 0.019 5±0.000 3 | 130±4 | 124±2 | 122±3 | 96 | |
| 18YS12-4 | 0.72 | 0.057 7±0.004 7 | 0.154 5±0.011 6 | 0.019 1±0.000 4 | 146±10 | 122±2 | 142±8 | 82 | |
| 18YS12-5 | 0.92 | 0.050 6±0.002 2 | 0.133 3±0.005 4 | 0.019 3±0.000 3 | 127±5 | 123±2 | 126±4 | 97 | |
| 18YS12-6 | 0.88 | 0.052 4±0.002 9 | 0.136 6±0.006 7 | 0.019 2±0.000 3 | 130±6 | 122±2 | 141±4 | 93 | |
| 18YS12-7 | 2.14 | 0.046 7±0.002 3 | 0.123 9±0.006 3 | 0.019 4±0.000 4 | 119±6 | 124±2 | 127±4 | 95 | |
| 18YS12-8 | 1.63 | 0.053 4±0.005 5 | 0.132 5±0.011 2 | 0.019 2±0.000 6 | 126±10 | 123±4 | 130±6 | 97 | |
| 18YS12-9 | 1.25 | 0.051 4±0.003 7 | 0.140 6±0.010 7 | 0.019 6±0.000 5 | 134±10 | 125±3 | 132±6 | 93 | |
| 18YS12-10 | 1.15 | 0.050 9±0.005 5 | 0.134 9±0.012 7 | 0.019 6±0.000 8 | 128±11 | 125±5 | 126±5 | 97 | |
| 18YS12-11 | 1.46 | 0.051 7±0.002 2 | 0.136 3±0.005 7 | 0.019 5±0.000 4 | 130±5 | 124±3 | 126±5 | 95 | |
| 18YS12-12 | 1.22 | 0.049 0±0.002 8 | 0.132 6±0.007 3 | 0.019 9±0.000 4 | 126±7 | 127±2 | 134±3 | 99 | |
| 18YS12-13 | 1.13 | 0.050 7±0.002 6 | 0.136 6±0.006 6 | 0.019 8±0.000 3 | 130±6 | 126±2 | 123±4 | 96 | |
| 18YS12-14 | 1.29 | 0.052 3±0.002 9 | 0.137 6±0.005 8 | 0.019 0±0.000 3 | 131±5 | 122±2 | 122±3 | 92 | |
| 18YS12-15 | 1.31 | 0.047 3±0.008 9 | 0.121 3±0.020 3 | 0.019 1±0.001 1 | 116±18 | 122±7 | 111±12 | 95 | |
| 18YS12-16 | 1.07 | 0.049 5±0.011 9 | 0.123 3±0.026 1 | 0.019 2±0.001 4 | 118±24 | 122±9 | 123±17 | 96 | |
| 18YS12-17 | 1 | 0.049 6±0.002 7 | 0.134 7±0.007 0 | 0.019 7±0.000 4 | 128±6 | 126±2 | 138±5 | 98 | |
| 18YS12-18 | 0.96 | 0.051 7±0.003 3 | 0.139 6±0.008 1 | 0.019 6±0.000 5 | 133±7 | 125±3 | 124±5 | 94 | |
| 18YS12-19 | 1.43 | 0.049 3±0.002 0 | 0.134 0±0.005 3 | 0.019 6±0.000 3 | 128±5 | 125±2 | 127±3 | 98 | |
| 17JN15-1-1 | 1.88 | 0.050 8±0.003 7 | 0.139 2±0.010 2 | 0.019 9±0.000 4 | 232±167 | 132±9 | 127±3 | 96 | |
| 17JN15-1-2 | 2.04 | 0.051 0±0.004 9 | 0.136 4±0.012 7 | 0.019 7±0.000 6 | 243±28 | 130±11 | 126±4 | 96 | |
| 17JN15-1-3 | 1.57 | 0.049 9±0.004 7 | 0.135 1±0.012 0 | 0.019 4±0.000 6 | 191±204 | 129±11 | 124±4 | 96 | |
| 17JN15-1-4 | 2.51 | 0.055 6±0.005 3 | 0.144 2±0.012 4 | 0.019 4±0.000 6 | 439±211 | 137±11 | 124±4 | 89 | |
| 17JN15-1-5 | 1.55 | 0.046 2±0.003 8 | 0.121 0±0.008 4 | 0.019 8±0.000 5 | 9±189 | 116±8 | 127±3 | 91 | |
| 17JN15-1-6 | 1.47 | 0.051 0±0.004 6 | 0.133 4±0.010 2 | 0.019 7±0.000 6 | 243±207 | 127±9 | 126±4 | 98 | |
| 17JN15-1-7 | 1.21 | 0.054 2±0.003 3 | 0.138 7±0.007 7 | 0.019 2±0.000 4 | 389±135 | 132±7 | 122±3 | 92 | |
| 17JN15-1-8 | 1.28 | 0.048 7±0.006 7 | 0.126 2±0.015 9 | 0.019 5±0.000 7 | 132±296 | 121±14 | 124±5 | 96 | |
| 17JN15-1-9 | 1.65 | 0.050 0±0.006 0 | 0.122 1±0.011 8 | 0.019 4±0.000 7 | 195±259 | 117±11 | 124±4 | 94 | |
| 17JN15-1-10 | 2.11 | 0.057 7±0.004 9 | 0.153 8±0.012 8 | 0.019 5±0.000 6 | 520±189 | 145±11 | 124±4 | 84 | |
| 17JN15-1-11 | 1.4 | 0.049 7±0.003 2 | 0.134 0±0.008 4 | 0.019 7±0.000 4 | 189±145 | 128±8 | 126±2 | 98 | |
| 17JN15-1-12 | 2.23 | 0.052 6±0.007 3 | 0.142 8±0.018 0 | 0.019 4±0.000 9 | 309±289 | 136±16 | 124±6 | 91 | |
| 17JN15-1-13 | 1.34 | 0.053 0±0.004 1 | 0.145 4±0.011 7 | 0.019 8±0.000 7 | 328±178 | 138±10 | 127±5 | 91 | |
| 17JN15-1-14 | 1.52 | 0.053 3±0.005 2 | 0.139 3±0.011 8 | 0.019 7±0.000 6 | 343±224 | 132±11 | 126±4 | 95 | |
| 17JN15-1-15 | 1.86 | 0.049 1±0.003 1 | 0.132 3±0.007 5 | 0.019 8±0.000 5 | 150±150 | 126±7 | 126±3 | 99 | |
| 17JN15-1-16 | 1.71 | 0.072 3±0.011 1 | 0.152 4±0.017 0 | 0.019 5±0.001 0 | 994±312 | 144±15 | 125±6 | 85 | |
| 17JN15-1-17 | 1.46 | 0.054 6±0.004 8 | 0.145 2±0.010 3 | 0.019 8±0.000 5 | 394±200 | 138±9 | 126±3 | 91 | |
| 17JN15-1-18 | 1.32 | 0.048 9±0.003 3 | 0.126 7±0.007 9 | 0.019 3±0.000 4 | 143±157 | 121±7 | 123±2 | 98 | |
| 17JN15-1-19 | 1.57 | 0.046 3±0.004 7 | 0.119 2±0.010 8 | 0.019 3±0.000 6 | 13±230 | 114±10 | 124±4 | 92 | |
| 17JN15-1-20 | 1.5 | 0.048 9±0.004 6 | 0.123 6±0.009 2 | 0.019 6±0.000 6 | 143±207 | 118±8 | 125±3 | 94 | |
| 17JN15-2-1 | 3.67 | 0.046 6±0.003 4 | 0.120 6±0.007 6 | 0.019 3±0.000 5 | 33±161 | 116±7 | 123±3 | 96 | |
| 17JN15-2-2 | 1.34 | 0.050 5±0.004 0 | 0.133 2±0.010 0 | 0.019 7±0.000 6 | 217±179 | 127±9 | 125±4 | 96 | |
| 17JN15-2-3 | 1.59 | 0.052 0±0.007 0 | 0.141 5±0.019 2 | 0.019 6±0.001 1 | 287±281 | 134±17 | 125±7 | 96 | |
| 17JN15-2-4 | 1.57 | 0.059 4±0.005 3 | 0.154 7±0.013 4 | 0.019 6±0.000 6 | 583±194 | 146±12 | 125±4 | 89 | |
| 17JN15-2-5 | 1.44 | 0.048 6±0.006 1 | 0.113 3±0.014 5 | 0.018 8±0.000 7 | 132±335 | 109±13 | 120±5 | 91 | |
| 点号 | Th/U | 比值 | 年龄/Ma | 谐和度% | |||||
| 207Pb/ | 207Pb/ | 206Pb/ | 207Pb/ | 207Pb/ | 206Pb/ | ||||
| 206Pb±1σ | 235U±1σ | 238U±1σ | 206Pb±1σ | 235U±1σ | 238U±1σ | ||||
| 17JN15-2-6 | 2.05 | 0.057 8±0.008 7 | 0.136 1±0.018 8 | 0.019 2±0.000 7 | 520±333 | 130±17 | 122±4 | 98 | |
| 17JN15-2-7 | 1.75 | 0.052 2±0.007 6 | 0.135 7±0.017 5 | 0.019 0±0.000 9 | 295±304 | 129±16 | 122±6 | 92 | |
| 17JN15-2-8 | 1.33 | 0.050 1±0.006 0 | 0.129 3±0.012 6 | 0.019 4±0.000 7 | 198±259 | 123±11 | 124±4 | 96 | |
| 17JN15-2-9 | 1.46 | 0.057 5±0.006 8 | 0.139 9±0.013 6 | 0.019 0±0.000 6 | 522±263 | 133±12 | 121±4 | 94 | |
| 17JN15-2-10 | 1.95 | 0.062 7±0.012 8 | 0.157 5±0.024 2 | 0.019 6±0.001 0 | 698±446 | 149±21 | 125±6 | 84 | |
| 17JN15-2-11 | 1.81 | 0.053 0±0.006 5 | 0.146 0±0.021 9 | 0.019 2±0.001 0 | 328±283 | 138±19 | 123±6 | 98 | |
| 17JN15-2-12 | 1.58 | 0.062 7±0.013 5 | 0.144 5±0.024 4 | 0.019 2±0.001 3 | 698±466 | 137±22 | 123±8 | 91 | |
| 17JN15-2-13 | 1.36 | 0.047 2±0.005 9 | 0.113 8±0.013 0 | 0.019 4±0.000 7 | 58±287 | 109±12 | 124±4 | 91 | |
| 17JN15-2-14 | 1.37 | 0.055 4±0.004 3 | 0.148 7±0.010 0 | 0.019 6±0.000 5 | 432±169 | 141±9 | 125±3 | 95 | |
| 17JN15-2-15 | 1.38 | 0.050 5±0.003 5 | 0.126 8±0.007 7 | 0.018 8±0.000 4 | 220±157 | 121±7 | 120±2 | 99 | |
| 17JN15-2-16 | 1.49 | 0.060 7±0.009 9 | 0.139 0±0.017 9 | 0.019 0±0.001 0 | 628±356 | 132±16 | 121±7 | 85 | |
| 17JN15-2-17 | 1.93 | 0.054 7±0.008 6 | 0.133 2±0.017 5 | 0.019 5±0.001 0 | 467±356 | 127±16 | 124±6 | 91 | |
| 17JN15-2-18 | 1.39 | 0.054 7±0.006 6 | 0.134 4±0.015 5 | 0.018 8±0.000 8 | 467±272 | 128±14 | 120±5 | 98 | |
| 17JN15-2-19 | 1.7 | 0.057 5±0.005 4 | 0.147 7±0.010 6 | 0.019 6±0.000 6 | 522±203 | 140±9 | 125±4 | 92 | |
表1 沂沭断裂带浮来山岩体(18YS12)以及官坊岩体(17JN15-1和17JN15-2)LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age of the Fulaishan pluton (sample 18YS12) and Guanfang pluton (samples 17JN15-1 and 17JN15-2) in the Yishu fault zone
| 点号 | Th/U | 比值 | 年龄/Ma | 谐和度% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 207Pb/ | 207Pb/ | 206Pb/ | 207Pb/ | 207Pb/ | 206Pb/ | ||||
| 206Pb±1σ | 235U±1σ | 238U±1σ | 206Pb±1σ | 235U±1σ | 238U±1σ | ||||
| 18YS12-1 | 0.99 | 0.051 4±0.002 3 | 0.141 9±0.006 1 | 0.020 0±0.000 4 | 135±5 | 128±3 | 128±4 | 94 | |
| 18YS12-2 | 1.3 | 0.056 9±0.004 1 | 0.150 7±0.008 6 | 0.019 9±0.000 5 | 143±8 | 127±3 | 132±5 | 88 | |
| 18YS12-3 | 1.48 | 0.050 5±0.001 7 | 0.136 1±0.004 3 | 0.019 5±0.000 3 | 130±4 | 124±2 | 122±3 | 96 | |
| 18YS12-4 | 0.72 | 0.057 7±0.004 7 | 0.154 5±0.011 6 | 0.019 1±0.000 4 | 146±10 | 122±2 | 142±8 | 82 | |
| 18YS12-5 | 0.92 | 0.050 6±0.002 2 | 0.133 3±0.005 4 | 0.019 3±0.000 3 | 127±5 | 123±2 | 126±4 | 97 | |
| 18YS12-6 | 0.88 | 0.052 4±0.002 9 | 0.136 6±0.006 7 | 0.019 2±0.000 3 | 130±6 | 122±2 | 141±4 | 93 | |
| 18YS12-7 | 2.14 | 0.046 7±0.002 3 | 0.123 9±0.006 3 | 0.019 4±0.000 4 | 119±6 | 124±2 | 127±4 | 95 | |
| 18YS12-8 | 1.63 | 0.053 4±0.005 5 | 0.132 5±0.011 2 | 0.019 2±0.000 6 | 126±10 | 123±4 | 130±6 | 97 | |
| 18YS12-9 | 1.25 | 0.051 4±0.003 7 | 0.140 6±0.010 7 | 0.019 6±0.000 5 | 134±10 | 125±3 | 132±6 | 93 | |
| 18YS12-10 | 1.15 | 0.050 9±0.005 5 | 0.134 9±0.012 7 | 0.019 6±0.000 8 | 128±11 | 125±5 | 126±5 | 97 | |
| 18YS12-11 | 1.46 | 0.051 7±0.002 2 | 0.136 3±0.005 7 | 0.019 5±0.000 4 | 130±5 | 124±3 | 126±5 | 95 | |
| 18YS12-12 | 1.22 | 0.049 0±0.002 8 | 0.132 6±0.007 3 | 0.019 9±0.000 4 | 126±7 | 127±2 | 134±3 | 99 | |
| 18YS12-13 | 1.13 | 0.050 7±0.002 6 | 0.136 6±0.006 6 | 0.019 8±0.000 3 | 130±6 | 126±2 | 123±4 | 96 | |
| 18YS12-14 | 1.29 | 0.052 3±0.002 9 | 0.137 6±0.005 8 | 0.019 0±0.000 3 | 131±5 | 122±2 | 122±3 | 92 | |
| 18YS12-15 | 1.31 | 0.047 3±0.008 9 | 0.121 3±0.020 3 | 0.019 1±0.001 1 | 116±18 | 122±7 | 111±12 | 95 | |
| 18YS12-16 | 1.07 | 0.049 5±0.011 9 | 0.123 3±0.026 1 | 0.019 2±0.001 4 | 118±24 | 122±9 | 123±17 | 96 | |
| 18YS12-17 | 1 | 0.049 6±0.002 7 | 0.134 7±0.007 0 | 0.019 7±0.000 4 | 128±6 | 126±2 | 138±5 | 98 | |
| 18YS12-18 | 0.96 | 0.051 7±0.003 3 | 0.139 6±0.008 1 | 0.019 6±0.000 5 | 133±7 | 125±3 | 124±5 | 94 | |
| 18YS12-19 | 1.43 | 0.049 3±0.002 0 | 0.134 0±0.005 3 | 0.019 6±0.000 3 | 128±5 | 125±2 | 127±3 | 98 | |
| 17JN15-1-1 | 1.88 | 0.050 8±0.003 7 | 0.139 2±0.010 2 | 0.019 9±0.000 4 | 232±167 | 132±9 | 127±3 | 96 | |
| 17JN15-1-2 | 2.04 | 0.051 0±0.004 9 | 0.136 4±0.012 7 | 0.019 7±0.000 6 | 243±28 | 130±11 | 126±4 | 96 | |
| 17JN15-1-3 | 1.57 | 0.049 9±0.004 7 | 0.135 1±0.012 0 | 0.019 4±0.000 6 | 191±204 | 129±11 | 124±4 | 96 | |
| 17JN15-1-4 | 2.51 | 0.055 6±0.005 3 | 0.144 2±0.012 4 | 0.019 4±0.000 6 | 439±211 | 137±11 | 124±4 | 89 | |
| 17JN15-1-5 | 1.55 | 0.046 2±0.003 8 | 0.121 0±0.008 4 | 0.019 8±0.000 5 | 9±189 | 116±8 | 127±3 | 91 | |
| 17JN15-1-6 | 1.47 | 0.051 0±0.004 6 | 0.133 4±0.010 2 | 0.019 7±0.000 6 | 243±207 | 127±9 | 126±4 | 98 | |
| 17JN15-1-7 | 1.21 | 0.054 2±0.003 3 | 0.138 7±0.007 7 | 0.019 2±0.000 4 | 389±135 | 132±7 | 122±3 | 92 | |
| 17JN15-1-8 | 1.28 | 0.048 7±0.006 7 | 0.126 2±0.015 9 | 0.019 5±0.000 7 | 132±296 | 121±14 | 124±5 | 96 | |
| 17JN15-1-9 | 1.65 | 0.050 0±0.006 0 | 0.122 1±0.011 8 | 0.019 4±0.000 7 | 195±259 | 117±11 | 124±4 | 94 | |
| 17JN15-1-10 | 2.11 | 0.057 7±0.004 9 | 0.153 8±0.012 8 | 0.019 5±0.000 6 | 520±189 | 145±11 | 124±4 | 84 | |
| 17JN15-1-11 | 1.4 | 0.049 7±0.003 2 | 0.134 0±0.008 4 | 0.019 7±0.000 4 | 189±145 | 128±8 | 126±2 | 98 | |
| 17JN15-1-12 | 2.23 | 0.052 6±0.007 3 | 0.142 8±0.018 0 | 0.019 4±0.000 9 | 309±289 | 136±16 | 124±6 | 91 | |
| 17JN15-1-13 | 1.34 | 0.053 0±0.004 1 | 0.145 4±0.011 7 | 0.019 8±0.000 7 | 328±178 | 138±10 | 127±5 | 91 | |
| 17JN15-1-14 | 1.52 | 0.053 3±0.005 2 | 0.139 3±0.011 8 | 0.019 7±0.000 6 | 343±224 | 132±11 | 126±4 | 95 | |
| 17JN15-1-15 | 1.86 | 0.049 1±0.003 1 | 0.132 3±0.007 5 | 0.019 8±0.000 5 | 150±150 | 126±7 | 126±3 | 99 | |
| 17JN15-1-16 | 1.71 | 0.072 3±0.011 1 | 0.152 4±0.017 0 | 0.019 5±0.001 0 | 994±312 | 144±15 | 125±6 | 85 | |
| 17JN15-1-17 | 1.46 | 0.054 6±0.004 8 | 0.145 2±0.010 3 | 0.019 8±0.000 5 | 394±200 | 138±9 | 126±3 | 91 | |
| 17JN15-1-18 | 1.32 | 0.048 9±0.003 3 | 0.126 7±0.007 9 | 0.019 3±0.000 4 | 143±157 | 121±7 | 123±2 | 98 | |
| 17JN15-1-19 | 1.57 | 0.046 3±0.004 7 | 0.119 2±0.010 8 | 0.019 3±0.000 6 | 13±230 | 114±10 | 124±4 | 92 | |
| 17JN15-1-20 | 1.5 | 0.048 9±0.004 6 | 0.123 6±0.009 2 | 0.019 6±0.000 6 | 143±207 | 118±8 | 125±3 | 94 | |
| 17JN15-2-1 | 3.67 | 0.046 6±0.003 4 | 0.120 6±0.007 6 | 0.019 3±0.000 5 | 33±161 | 116±7 | 123±3 | 96 | |
| 17JN15-2-2 | 1.34 | 0.050 5±0.004 0 | 0.133 2±0.010 0 | 0.019 7±0.000 6 | 217±179 | 127±9 | 125±4 | 96 | |
| 17JN15-2-3 | 1.59 | 0.052 0±0.007 0 | 0.141 5±0.019 2 | 0.019 6±0.001 1 | 287±281 | 134±17 | 125±7 | 96 | |
| 17JN15-2-4 | 1.57 | 0.059 4±0.005 3 | 0.154 7±0.013 4 | 0.019 6±0.000 6 | 583±194 | 146±12 | 125±4 | 89 | |
| 17JN15-2-5 | 1.44 | 0.048 6±0.006 1 | 0.113 3±0.014 5 | 0.018 8±0.000 7 | 132±335 | 109±13 | 120±5 | 91 | |
| 点号 | Th/U | 比值 | 年龄/Ma | 谐和度% | |||||
| 207Pb/ | 207Pb/ | 206Pb/ | 207Pb/ | 207Pb/ | 206Pb/ | ||||
| 206Pb±1σ | 235U±1σ | 238U±1σ | 206Pb±1σ | 235U±1σ | 238U±1σ | ||||
| 17JN15-2-6 | 2.05 | 0.057 8±0.008 7 | 0.136 1±0.018 8 | 0.019 2±0.000 7 | 520±333 | 130±17 | 122±4 | 98 | |
| 17JN15-2-7 | 1.75 | 0.052 2±0.007 6 | 0.135 7±0.017 5 | 0.019 0±0.000 9 | 295±304 | 129±16 | 122±6 | 92 | |
| 17JN15-2-8 | 1.33 | 0.050 1±0.006 0 | 0.129 3±0.012 6 | 0.019 4±0.000 7 | 198±259 | 123±11 | 124±4 | 96 | |
| 17JN15-2-9 | 1.46 | 0.057 5±0.006 8 | 0.139 9±0.013 6 | 0.019 0±0.000 6 | 522±263 | 133±12 | 121±4 | 94 | |
| 17JN15-2-10 | 1.95 | 0.062 7±0.012 8 | 0.157 5±0.024 2 | 0.019 6±0.001 0 | 698±446 | 149±21 | 125±6 | 84 | |
| 17JN15-2-11 | 1.81 | 0.053 0±0.006 5 | 0.146 0±0.021 9 | 0.019 2±0.001 0 | 328±283 | 138±19 | 123±6 | 98 | |
| 17JN15-2-12 | 1.58 | 0.062 7±0.013 5 | 0.144 5±0.024 4 | 0.019 2±0.001 3 | 698±466 | 137±22 | 123±8 | 91 | |
| 17JN15-2-13 | 1.36 | 0.047 2±0.005 9 | 0.113 8±0.013 0 | 0.019 4±0.000 7 | 58±287 | 109±12 | 124±4 | 91 | |
| 17JN15-2-14 | 1.37 | 0.055 4±0.004 3 | 0.148 7±0.010 0 | 0.019 6±0.000 5 | 432±169 | 141±9 | 125±3 | 95 | |
| 17JN15-2-15 | 1.38 | 0.050 5±0.003 5 | 0.126 8±0.007 7 | 0.018 8±0.000 4 | 220±157 | 121±7 | 120±2 | 99 | |
| 17JN15-2-16 | 1.49 | 0.060 7±0.009 9 | 0.139 0±0.017 9 | 0.019 0±0.001 0 | 628±356 | 132±16 | 121±7 | 85 | |
| 17JN15-2-17 | 1.93 | 0.054 7±0.008 6 | 0.133 2±0.017 5 | 0.019 5±0.001 0 | 467±356 | 127±16 | 124±6 | 91 | |
| 17JN15-2-18 | 1.39 | 0.054 7±0.006 6 | 0.134 4±0.015 5 | 0.018 8±0.000 8 | 467±272 | 128±14 | 120±5 | 98 | |
| 17JN15-2-19 | 1.7 | 0.057 5±0.005 4 | 0.147 7±0.010 6 | 0.019 6±0.000 6 | 522±203 | 140±9 | 125±4 | 92 | |
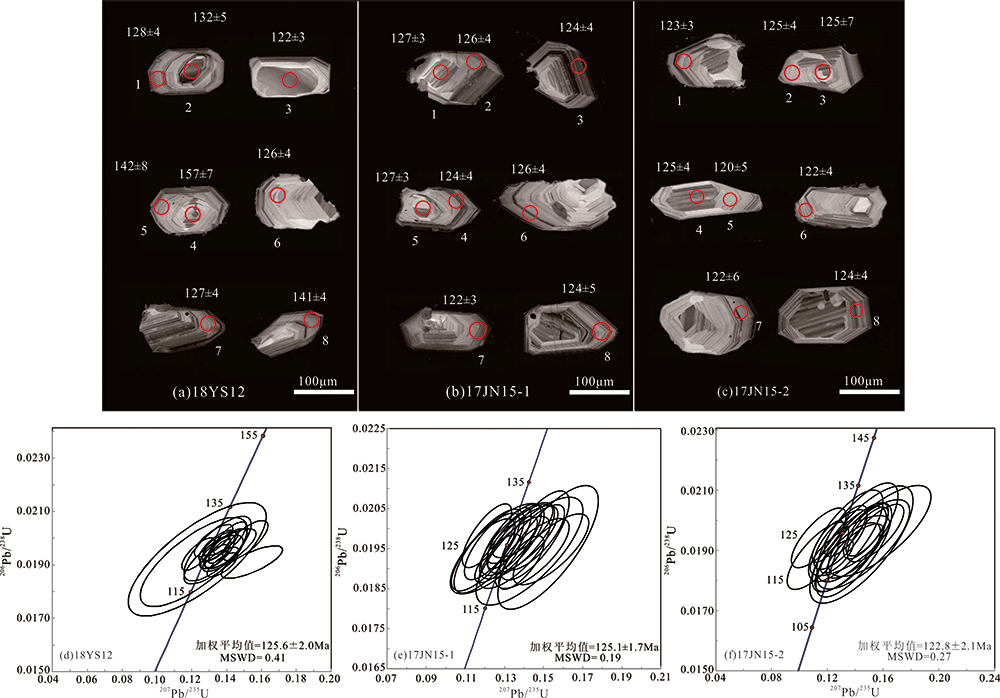
图4 沂沭断裂带浮来山岩体((a)和(d),样品18YS12)以及官坊岩体((b)(e),样品17JN15-1;(c)(f)17JN15-2)锆石阴极发光(CL)图像和锆石U-Pb年龄谐和图
Fig.4 Representative zircon CL images and concordia U-Pb diagrams for the Fulaishan pluton ((a) and (d), sample 18YS12) and Guanfang pluton ((b) and (e), sample 17JN15-1; (c) and (f), sample 17JN15-2) in the Yishu fault zone
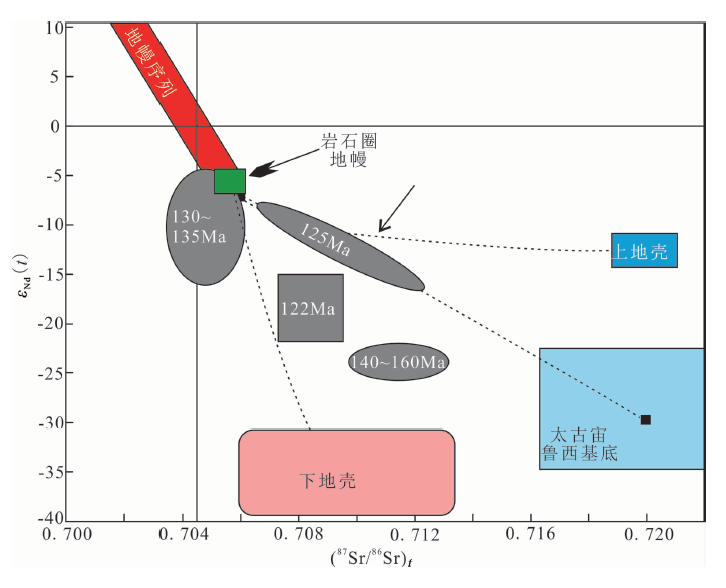
图6 沂沭断裂带及其两侧晚中生代岩浆岩Sr、Nd同位素比值对比(数据据文献[24, 39, 50])
Fig.6 Diagram of ε Nd(t) vs.(87Sr/86Sr)t for the Late Mesozoic magmatic rocks in/around the Yishu fault zone (data after refs.[24, 39, 50])

图7 沂沭断裂带及周边地区岩浆活动迁移规律图(a)以及沂沭断裂带晚中生代演化动力学模式简图(b)
Fig.7 Diagram of magma activity migration pattern in/around the Yishu fault zone (a) and schematic diagram of late Mesozoic dynamic evolution model of the Yishu fault zone (b)
| [1] |
LIU J G, CAI R H, PEARSON D G, et al. Thinning and destruction of the lithospheric mantle root beneath the North China Craton: A review[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2019, 196:102873.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
ZHU G, CHEN Y, JIANG D Z, et al. Rapid change from compression to extension in the North China Craton during the Early Cretaceous: Evidence from the Yunmengshan metamorphic core complex[J]. Tectonophysics, 2015, 656:91-110.
DOI URL |
| [3] | DAVIS GREGORY A, 郑亚东, 王琮, 等. 中生代燕山褶皱冲断带的构造演化——以河北省和辽宁省为重点的研究[J]. 北京地质, 2002, 14(4): 1-40. |
| [4] | 张进江. 小秦岭变质核杂岩的构造特征、形成机制及构造演化[D]. 北京: 北京大学, 1997. |
| [5] | 张岳桥, 董树文. 郯庐断裂带中生代构造演化史: 进展与新认识[J]. 地质通报, 2008, 27(9): 1371-1390. |
| [6] |
REN J, TAMAKI K, LI S, et al. Late Mesozoic and Cenozoic rifting and its dynamic setting in Eastern China and adjacent areas[J]. Tectonophysics, 2002, 344:175-205.
DOI URL |
| [7] | 李刚, 薛吉祥, 刘正宏, 等. 华北东部晚中生代区域伸展背景下同构造花岗岩体的起源与就位[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(8): 2413-2430. |
| [8] | 朱光, 刘程, 顾承串, 等. 郯庐断裂带晚中生代演化对西太平洋俯冲历史的指示[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2018, 48(4): 415-435. |
| [9] | 李洪奎, 陈国栋, 梁太涛, 等. 沂沭断裂带构造活动与胶东金矿形成关系之探讨[J]. 山东国土资源, 2017, 33(11): 6-14. |
| [10] | 朱光, 王薇, 顾承串, 等. 郯庐断裂带晚中生代演化历史及其对华北克拉通破坏过程的指示[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(4): 935-949. |
| [11] | 石文杰. 山东沂沭断裂带及邻区晚中生代构造-岩浆活动与金成矿作用[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2014. |
| [12] | 王勇生, 朱光, 胡召齐, 等. 郯庐断裂带沂沭段伸展活动断层泥K-Ar同位素定年[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2009, 39(5): 580-593. |
| [13] | 王先美, 钟大赉, 张进江, 等. 沂沭断裂带晚白垩世—早古新世左行走滑的低温年代学约束[J]. 地质学报, 2007, 81(4): 454-465. |
| [14] | 牛漫兰, 朱光, 宋传中, 等. 郯庐断裂带中南段新生代玄武岩源区地幔特征及其演化[J]. 现代地质, 2001, 15(4): 383-390. |
| [15] | 朱光, 王道轩, 刘国生, 等. 郯庐断裂带的伸展活动及其动力学背景[J]. 地质科学, 2001, 36(3): 269-278. |
| [16] | 匡永生, 庞崇进, 罗震宇, 等. 胶东青山群基性火山岩的Ar-Ar年代学和地球化学特征:对华北克拉通破坏过程的启示[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(4): 1073-1091. |
| [17] | 匡永生, 庞崇进, 洪路兵, 等. 胶莱盆地晚白垩世玄武岩的年代学和地球化学特征及其对华北岩石圈减薄-增生的制约[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2012, 36(4): 559-571. |
| [18] | 邱检生, 王德滋, 罗清华, 等. 鲁东胶莱盆地青山组火山岩的40Ar-39Ar定年——以五莲分岭山火山机构为例[J]. 高校地质学报, 2001, 7(3): 351-355. |
| [19] | 邱检生, 王德滋, 周金城, 等. 山东中生代橄榄安粗岩系火山岩的地质、地球化学特征及岩石成因[J]. 地球科学, 1996, 21(5): 92-98. |
| [20] | 杨承海. 鲁西中生代高镁闪长岩的年代学与地球化学:对华北克拉通岩石圈演化的制约[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2007. |
| [21] | 徐义刚, 巫祥阳, 罗震宇, 等. 山东中侏罗世—早白垩世侵入岩的锆石Hf同位素组成及其意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(2): 307-316. |
| [22] | 杨承海, 许文良, 杨德彬, 等. 鲁西中生代高Mg闪长岩的成因:年代学与岩石地球化学证据[J]. 地球科学, 2006, 31(1): 81-92. |
| [23] | 赛盛勋, 赵天明, 王中亮, 等. 玲珑黑云母花岗岩成因:矿物学特征约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(8): 2477-2493. |
| [24] |
CAO G Y, XUE H M, LIU Z, et al. U-Pb zircon, geochemical, and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic data for late Mesozoic volcanic rocks along the Tan-Lu fault zone of Shandong Province, eastern China: constraints on magma genesis and lithospheric thinning[J]. International Geology Review, 2019, 61(8): 972-996.
DOI URL |
| [25] | 曹光跃, 薛怀民, 刘哲, 等. 鲁西临朐地区早白垩世青山群火山岩的年代学、地球化学及岩石成因[J]. 地质学报, 2018, 92(3): 503-519. |
| [26] | 王浩. 山东邹平火山岩盆地早白垩世岩浆作用与铜成矿关系研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2015. |
| [27] | 牛漫兰, 傅朋远, 吴齐, 等. 蒙阴盆地早白垩世火山岩地球化学特征及其岩石成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(12): 4125-4138. |
| [28] | 张鹏, 王良书, 石火生, 等. 郯庐断裂带山东段的中新生代构造演化特征[J]. 地质学报, 2010, 84(9): 1316-1323. |
| [29] | 吴齐, 牛漫兰, 朱光, 等. 郯庐断裂带莒县地区早白垩世中酸性火山岩成因及其地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2013, 87(7): 979-993. |
| [30] | 唐嘉锋, 刘玉琳, 王启飞. 山东中生代火山岩年代学研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(6): 1333-1338. |
| [31] |
XIE Y X, WENK H R, MATTHIES S. Plagioclase preferred orientation by TOF neutron diffraction and SEM-EBSD[J]. Tectonophysics, 2003, 370(1/2/3/4): 269-286.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
JACKSON S E, PEARSON N J, GRIFFIN W L, et al. The application of laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry to in situ U-Pb zircon geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 211(1/2): 47-69.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
ANDERSEN T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 192(1): 59-79.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
BELOUSOVA E, GRIFFIN W, O'REILLY S Y, et al. Igneous zircon: trace element composition as an indicator of source rock type[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2002, 143(5): 602-622.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
DAI F, ZHAO Z, ZHENG Y, et al. The geochemical nature of mantle sources for two types of Cretaceous basaltic rocks from Luxi and Jiaodong in east-central China[J]. Lithos, 2019, 344/345:409-424.
DOI URL |
| [36] | XU L X, LI S L, GUO L G, et al. Impaction of the Tan-Lu Fault Zone on uplift of the Luxi Rise: Constraints from apatite fission track thermochronology[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2016, 32(4): 1153-1170. |
| [37] |
NI J L, LIU J L, TANG X L. et al, Early Cretaceous exhumation of the Sulu orogenic belt as a consequence of the eastern Eurasian tectonic extension: insights from the newly discovered Wulian metamorphic core complex, eastern China[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2016, 173(3): 531-549.
DOI URL |
| [38] | 刘俊来, 关会梅, 纪沫, 等. 华北晚中生代变质核杂岩构造及其对岩石圈减薄机制的约束[J]. 自然科学进展, 2006, 16(1): 21-26. |
| [39] |
YANG J H, WU F Y, CHUNG S L, et al. Petrogenesis of Early Cretaceous intrusions in the Sulu ultrahigh-pressure orogenic belt, east China and their relationship to lithospheric thinning[J]. Chemical Geology, 2005, 222:200-231.
DOI URL |
| [40] | 张岳桥, 李金良, 张田, 等, 胶莱盆地及其邻区白垩纪—古新世沉积构造演化历史及其区域动力学意义[J]. 地质学报, 2008, 82(9): 1229-1257. |
| [41] | 凌文黎, 谢先军, 柳小明, 等. 鲁东中生代标准剖面青山群火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其构造意义[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2006, 36(5): 401-411. |
| [42] |
ISOZAKI Y. Permo-Triassic boundary superanoxia and stratified superocean: records from lost deep sea[J]. Science, 1997, 276:235-238.
DOI URL |
| [43] | YANG D B, XU W L, PEI F P, et al. Spatial extent of the influence of the deeply subducted South China Block on the southeastern North China Block: Constraints from Sr-Nd-Pb isotopes in Mesozoic mafic igneous rocks [J]. Lithos, 2012, 136/137/138/139:246-260. |
| [44] | 李三忠, 王金铎, 刘建忠, 等. 鲁西地块中生代构造格局及其形成背景[J]. 地质学报, 2005, 79(4): 487-497. |
| [45] |
MARUYAMA S, ISOZAKI Y, KIMURA G, et al. Paleogeographic maps of the Japanese Islands: Plate tectonic synjournal from 750 Ma to the present[J]. Island Arc, 1997, 6(1): 121-142.
DOI URL |
| [46] | ENGEBRETSON D C, COX A, GORDON R G. Relative Motions Between Oceanic and Continental Plates in the Pacific Basin[M]//GSA. Geological Society of America Special Paper. Washington D C: The Geological Society of America, 1985: 1-60. |
| [47] | 张田, 张岳桥. 胶东半岛中生代侵入岩浆活动序列及其构造制约[J]. 高校地质学报, 2007, 13(2): 323-336. |
| [48] | ZHAI M, ZHU X, ZHOU Y, et al. Continental crustal evolution and synchronous metallogeny through time in the North China Craton[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2020, 194, 104169. |
| [49] |
LI S R, SANTOSH M. Metallogeny and craton destruction: Records from the North China Craton[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2014, 56:376-414.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
YANG J H, WU F Y, CHUNG S L, et al. Multiple sources for the origin of granites: Geochemical and Nd/Sr isotopic evidence from the Gudaoling granite and its mafic enclaves, northeast China[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2004, 68:4469-4483.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 陈耀新, 刘文恒, 王凯兴, 刘晓东, 孙立强, 尹冬华. 甘肃青山堡中牌细粒花岗岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 169-182. |
| [2] | 杨俊峰, 张娟, 刘新星, 邱佳炜, 王猛, 成嘉伟, 卢克轩, 王瑛雪. 赣南金竹坪钨矿床多期成矿作用特征及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1449-1466. |
| [3] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [4] | 胡子奇, 张德贤, 刘磊. 束斑直径和能量密度对锆石U-Pb定年准确度的影响研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 722-732. |
| [5] | 王昭阳, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 裴磊, 李佐臣, 刘成军, 赵少伟, 王盟, 陈有炘, 周海, 赵杰, 许丽丽. 勉略构造带新元古代中期构造演化特征:来自略阳关天门变质沉积岩碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 770-795. |
| [6] | 杨延伟, 卢欣祥, 王丽伟, 杨一, 杨崇科, 黄凡. 青海南山当家寺花岗岩体与晚三叠世脉岩及其对早中生代构造环境的约束[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 796-811. |
| [7] | 周桐, 孙珍军, 于赫楠, 王承洋, 刘广虎. 内蒙古浩布高铅锌矿床小罕山岩体年代学、Hf同位素及地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 282-294. |
| [8] | 吕钊, 王建平, 王继春, 许展, 袁硕浦. 内蒙古白乃庙铜金矿床侵入岩年代学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 307-320. |
| [9] | 欧伟程, 李承东, 张永清, 赵利刚, 许腾, 许雅雯, 孙烜烨. 北秦岭二郎坪群抱树坪组碎屑锆石LA-MC-ICP-MS U-Pb定年及物源特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 347-361. |
| [10] | 葛战林, 郝迪, 张晓星, 郑艳荣, 李晓东, 武海文, 张龙. 东秦岭大蛇沟钨矿区赋矿围岩成因:锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学证据[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1633-1650. |
| [11] | 吴龙, 柳长峰, 刘文灿, 张宏远. 青藏高原东北缘祁连山三叠系砂岩碎屑锆石U-Pb定年及其物源分析[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1178-1193. |
| [12] | 程天赦, 杨文静, 张学斌, 吴荣泽, 周长红. 内蒙古乌兰乌台花岗闪长岩U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1231-1239. |
| [13] | 寇冠玉, 周晔, 郑远川, 于佳兴. 伊朗马斯杰德达吉(Masjed Daghi)始新世斑岩成因:来自光谱学与U-Pb年代学和地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(02): 535-551. |
| [14] | 陈欢, 康志强, 吴佳昌, 李岱鲜, 曹延, 韦天伟, 韦乃韶, 刘迪, 周桐, 刘冬梅, 蓝海洋. 广西大瑶山朴全岩体形成时代、成因及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(06): 1277-1290. |
| [15] | 欧阳鑫, 顾雪祥, 章永梅, 刘丽, 刘涛, 王文东. 内蒙古撰山子金矿床成岩成矿年代学与地球化学[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(04): 635-652. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||